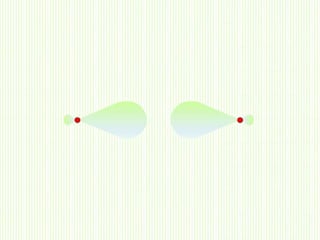
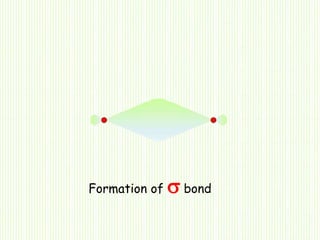
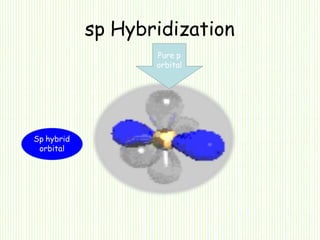
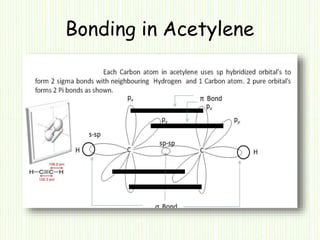
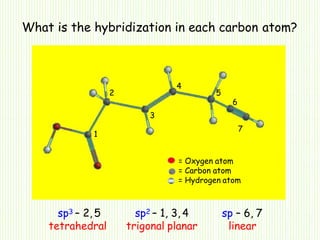
Hybridization involves mixing atomic orbitals of different energies to form new hybrid orbitals suitable for bond formation. There are three main types of hybridization: sp3, sp2, and sp. Sp3 hybridization results in orbitals pointing towards the corners of a tetrahedron and occurs when a carbon is bonded to four groups. Sp2 hybridization produces orbitals at 120 degrees in a triangle and takes place when a carbon has three bonds. Sp hybridization forms linear orbitals 180 degrees apart and occurs for a carbon with two bonds.