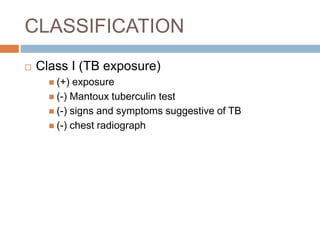
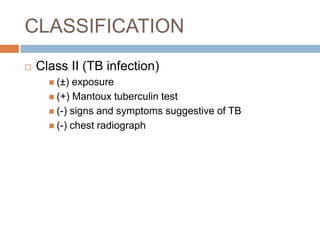
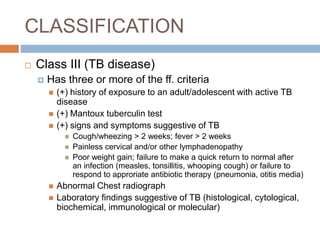
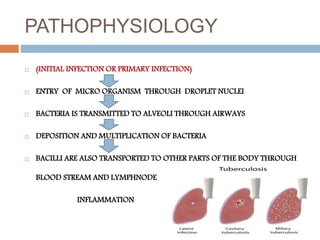
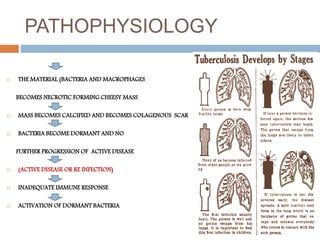
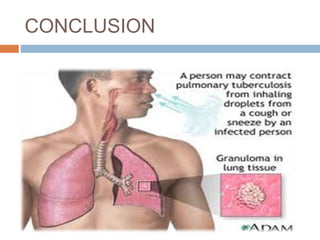
Pulmonary tuberculosis is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis and is spread through inhaling droplets from an infected person when they cough, sneeze, or laugh. It is a chronic infection characterized by weight loss. Diagnosis involves chest x-rays, sputum tests, and the Mantoux tuberculin skin test. Treatment requires taking multiple antibiotics like isoniazid and rifampin daily for 6-12 months to prevent resistance. Complications can include infection of bones, brain, liver or kidneys if left untreated. Prevention involves proper ventilation, covering coughs, mask wearing, vaccination, and completing the full drug regimen.