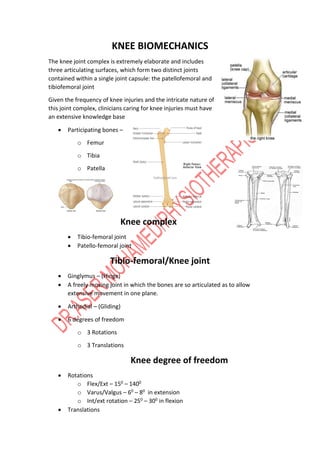
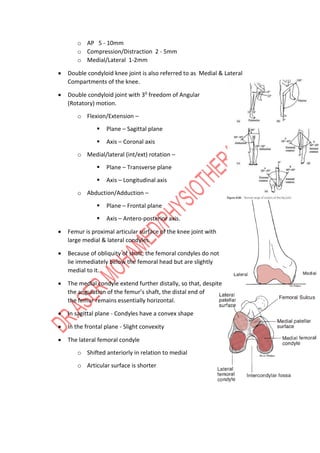
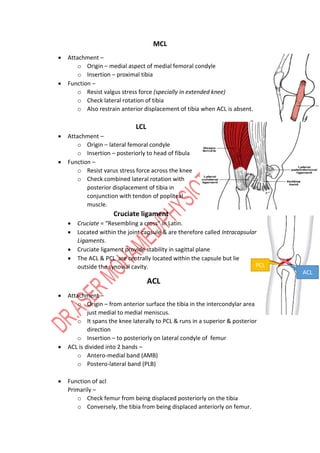
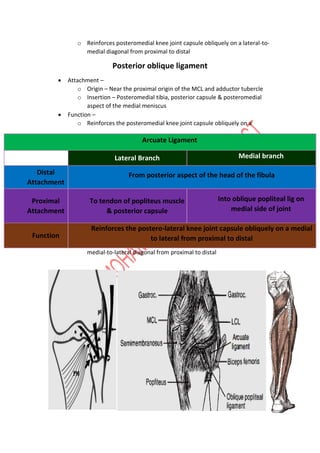
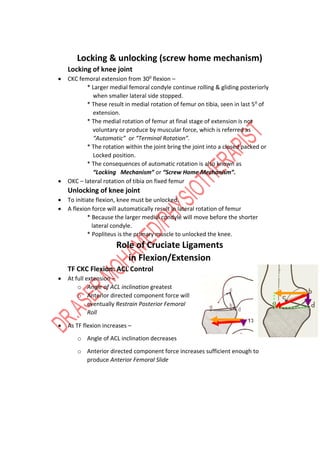
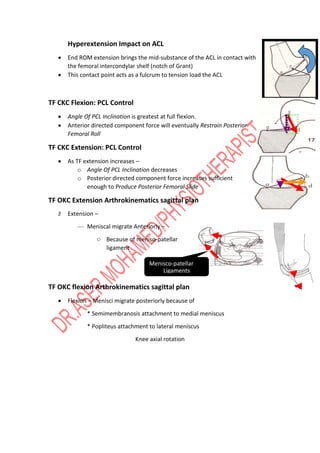
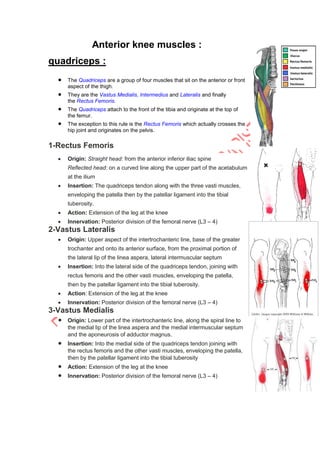
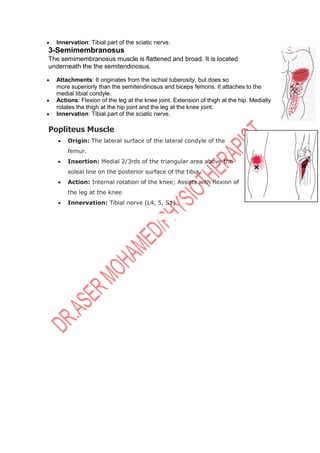
The knee joint is complex with three bones - the femur, tibia, and patella - forming two joints, the patellofemoral and tibiofemoral joints. The knee allows for flexion/extension in the sagittal plane as well as medial/lateral rotation in the transverse plane. Cruciate ligaments like the ACL and PCL provide stability while menisci absorb shock and increase joint congruence. Proper biomechanics and alignment of the femur and tibia distribute weight forces evenly across the knee. Injuries require clinicians to have extensive knowledge of the knee's intricate nature.