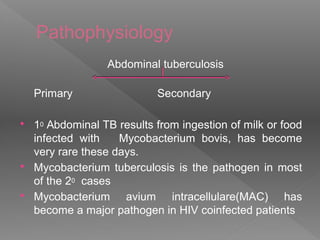
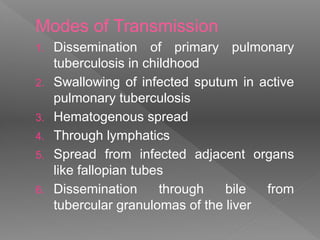
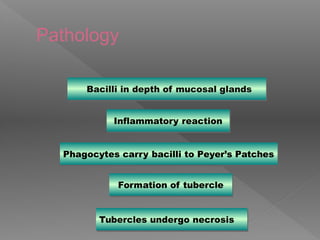
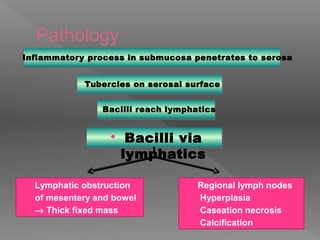
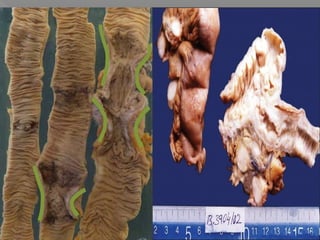
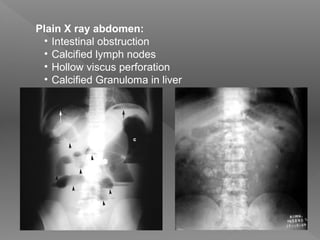
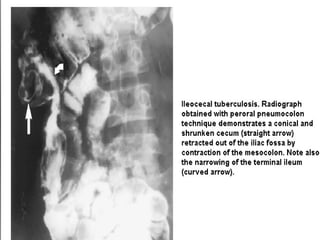
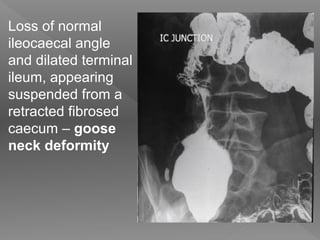
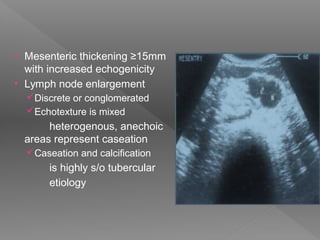
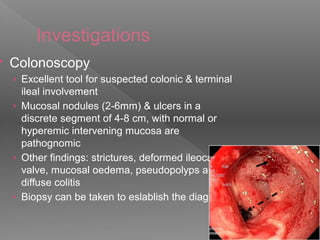
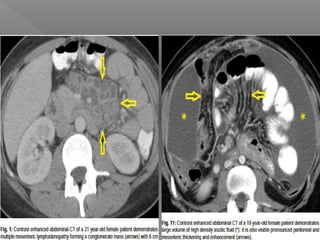
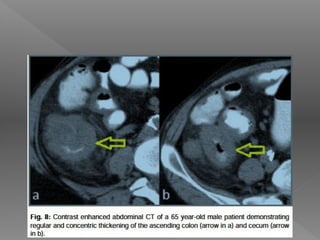
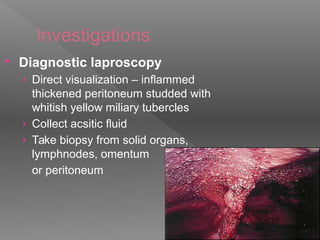
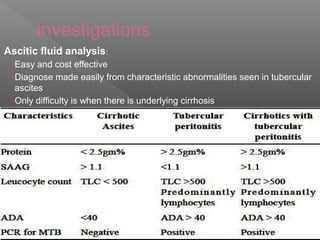
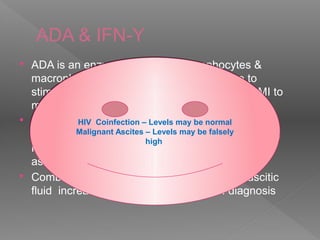
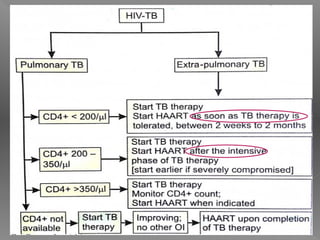
Abdominal tuberculosis is a common form of extrapulmonary tuberculosis, accounting for 3-4% of all tuberculosis cases. It most commonly involves the ileocecal region of the small intestine. Clinical presentations can include constitutional symptoms like fever and weight loss as well as abdominal pain. Diagnosis is challenging and relies on clinical suspicion combined with imaging findings and histopathological evidence from biopsies. Common investigative tools include barium studies, ultrasound, and colonoscopy. Treatment involves a standard antitubercular therapy regimen.