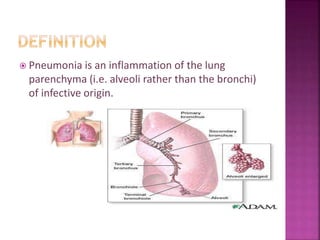
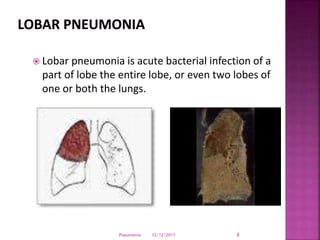
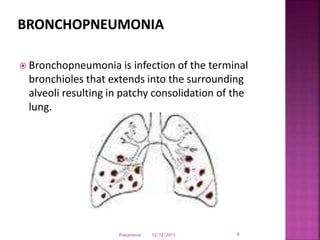
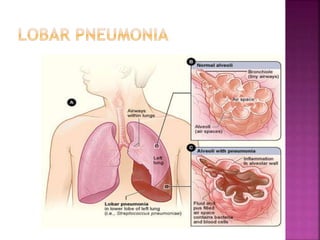
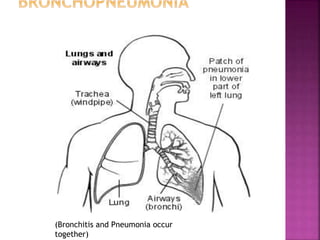
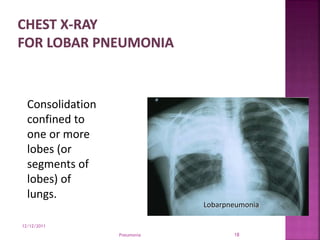
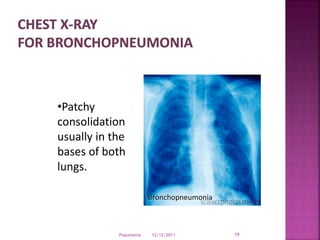
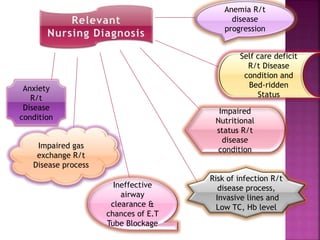
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung parenchyma that is usually caused by an infection. It is characterized by consolidation of the lungs due to inflammatory exudate, bacteria, and white blood cells filling the alveoli. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It occurs in people of all ages but clinical manifestations tend to be more severe in young children, the elderly, and chronically ill patients. Pneumonia is classified based on location in the lungs and place of acquisition. Treatment involves antibiotics and supportive care, while vaccination can help prevent pneumonia.