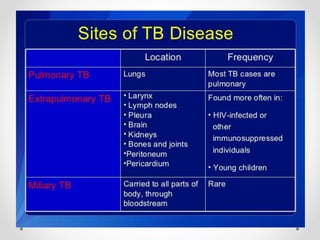
Tuberculosis (TB) is a chronic bacterial infection primarily affecting the lungs, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and is spread through respiratory droplets. The disease has a high global prevalence, affecting half of the world's population, with significant mortality rates, particularly among vulnerable groups. Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and various tests, while treatment typically includes a course of anti-tuberculosis medications lasting 6 to 12 months.