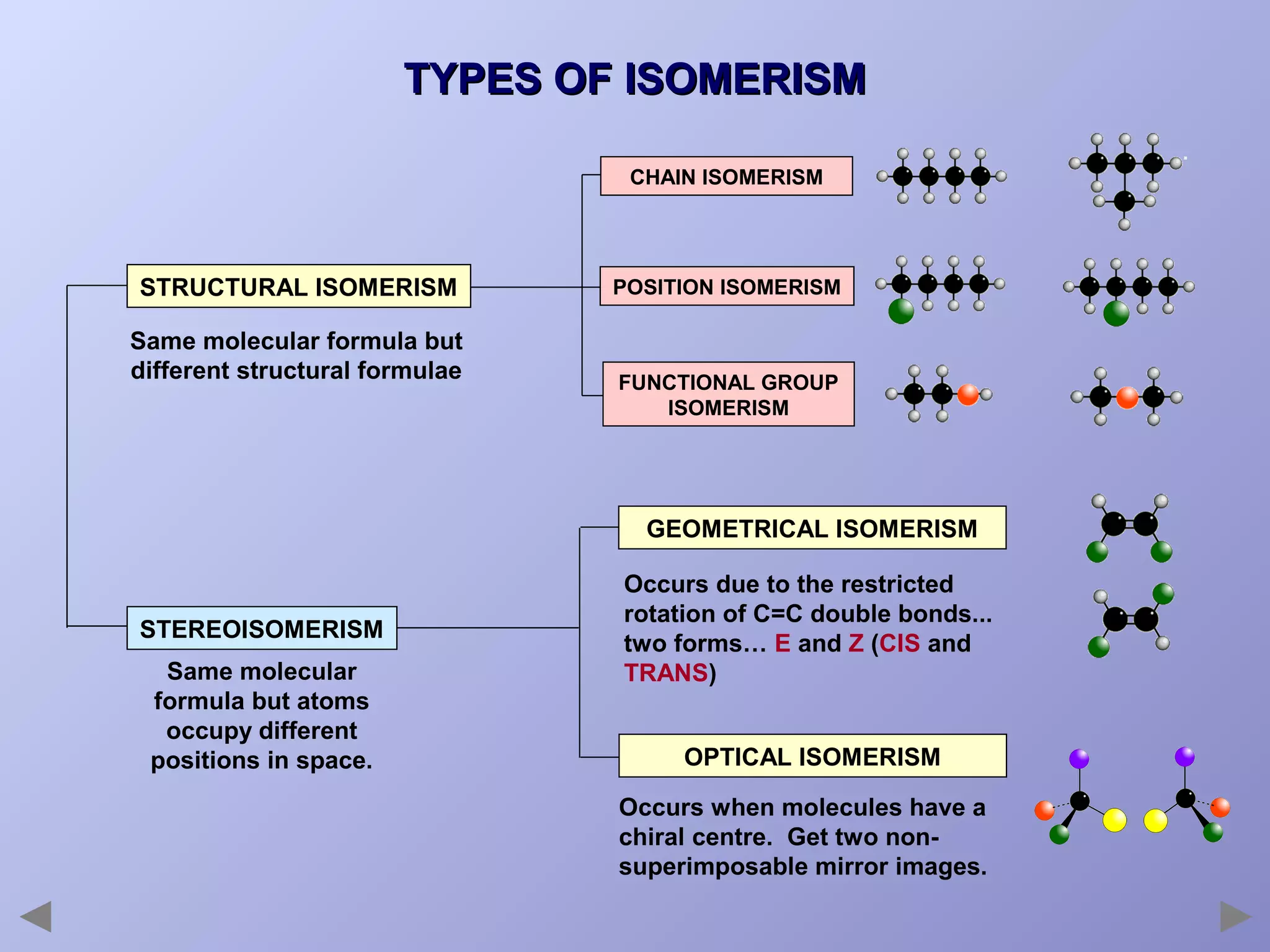
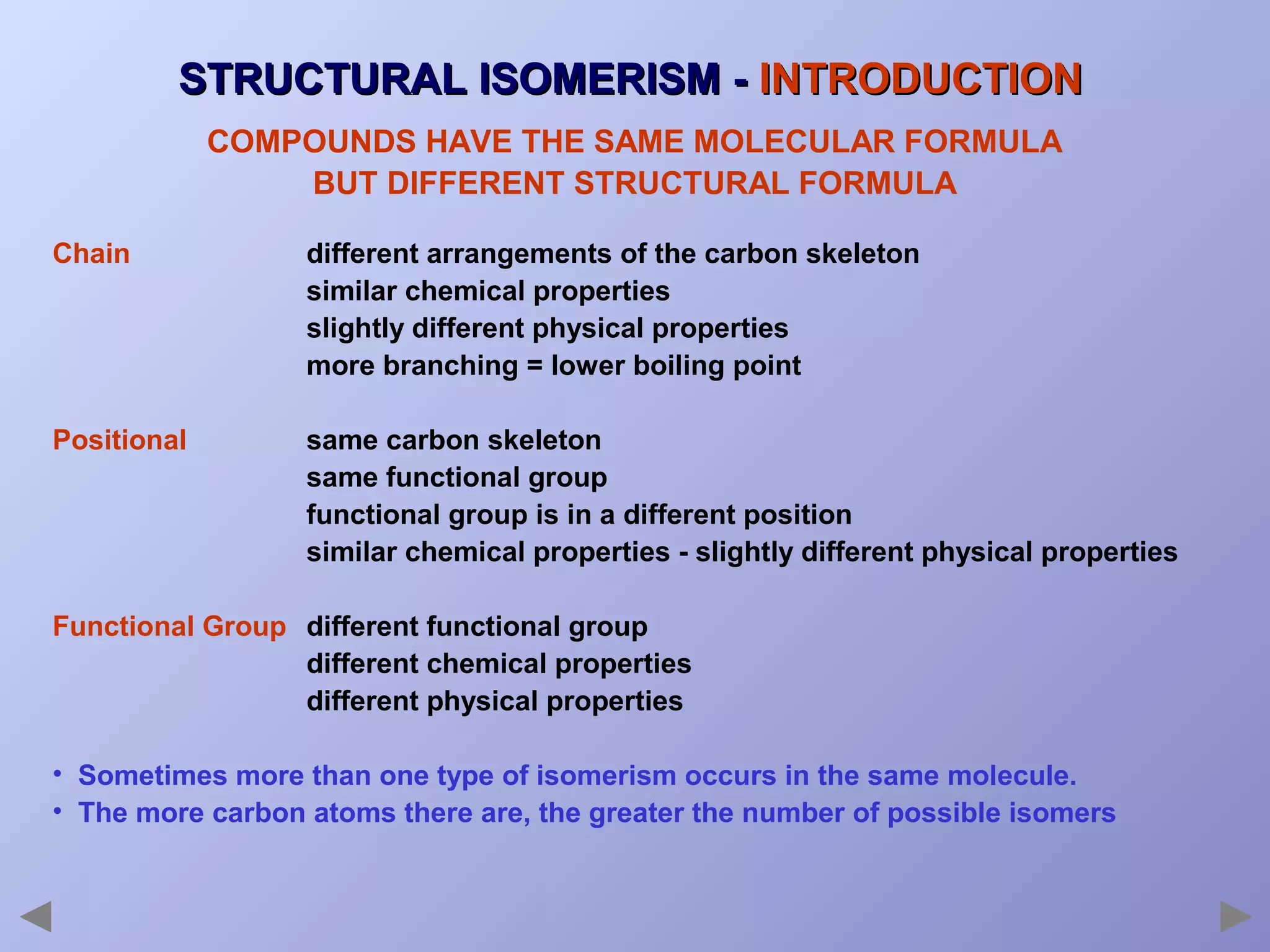
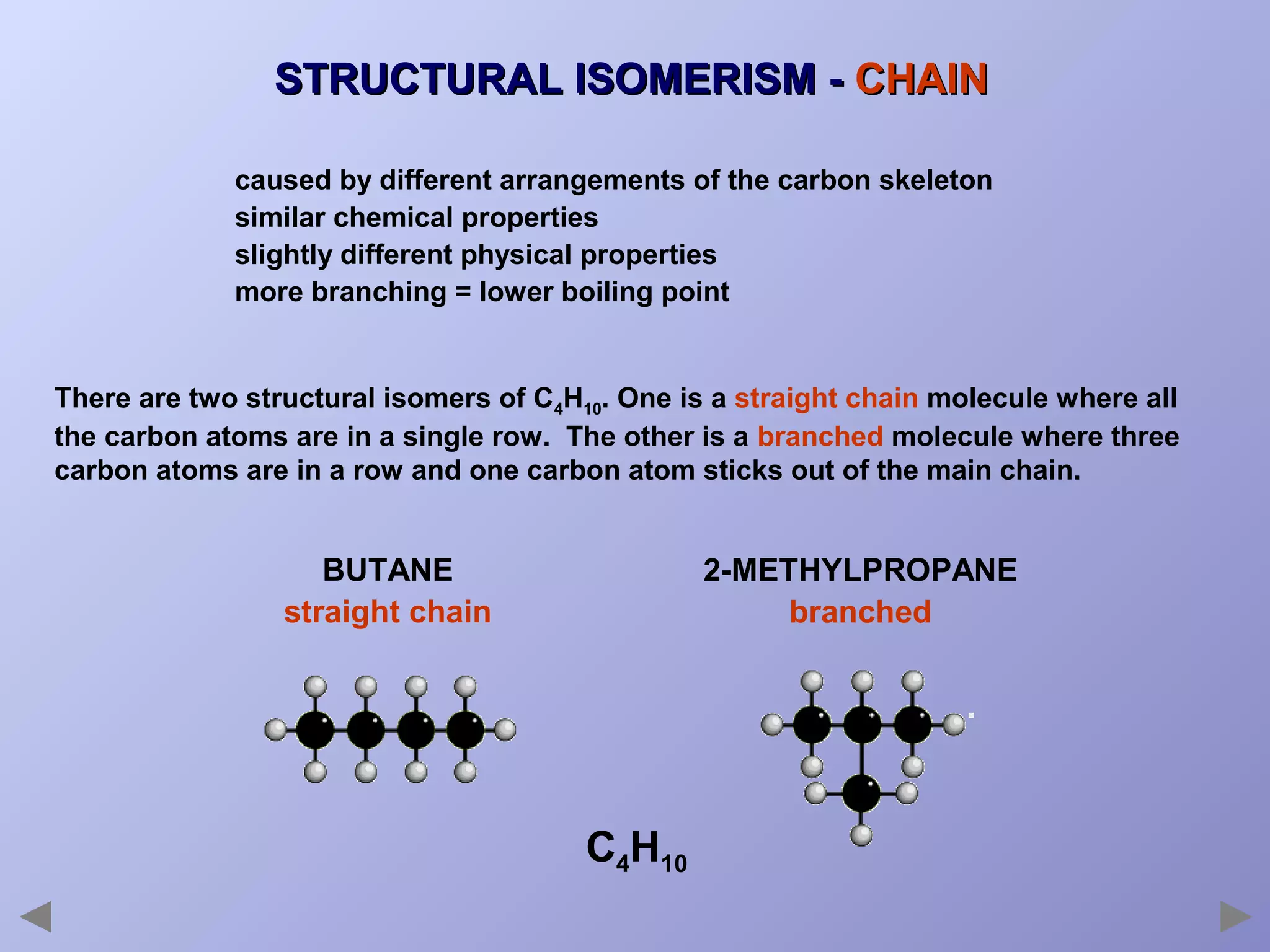
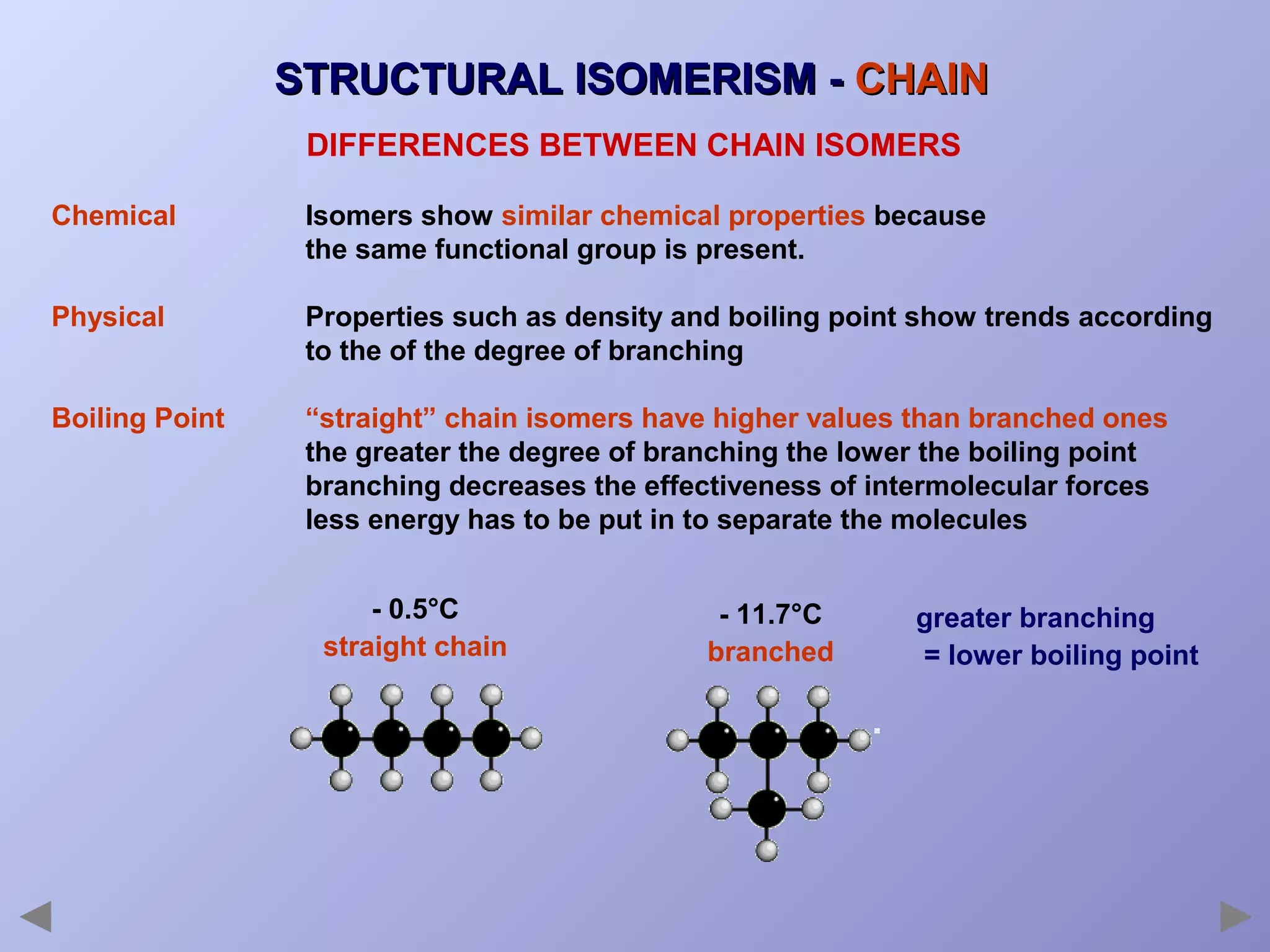
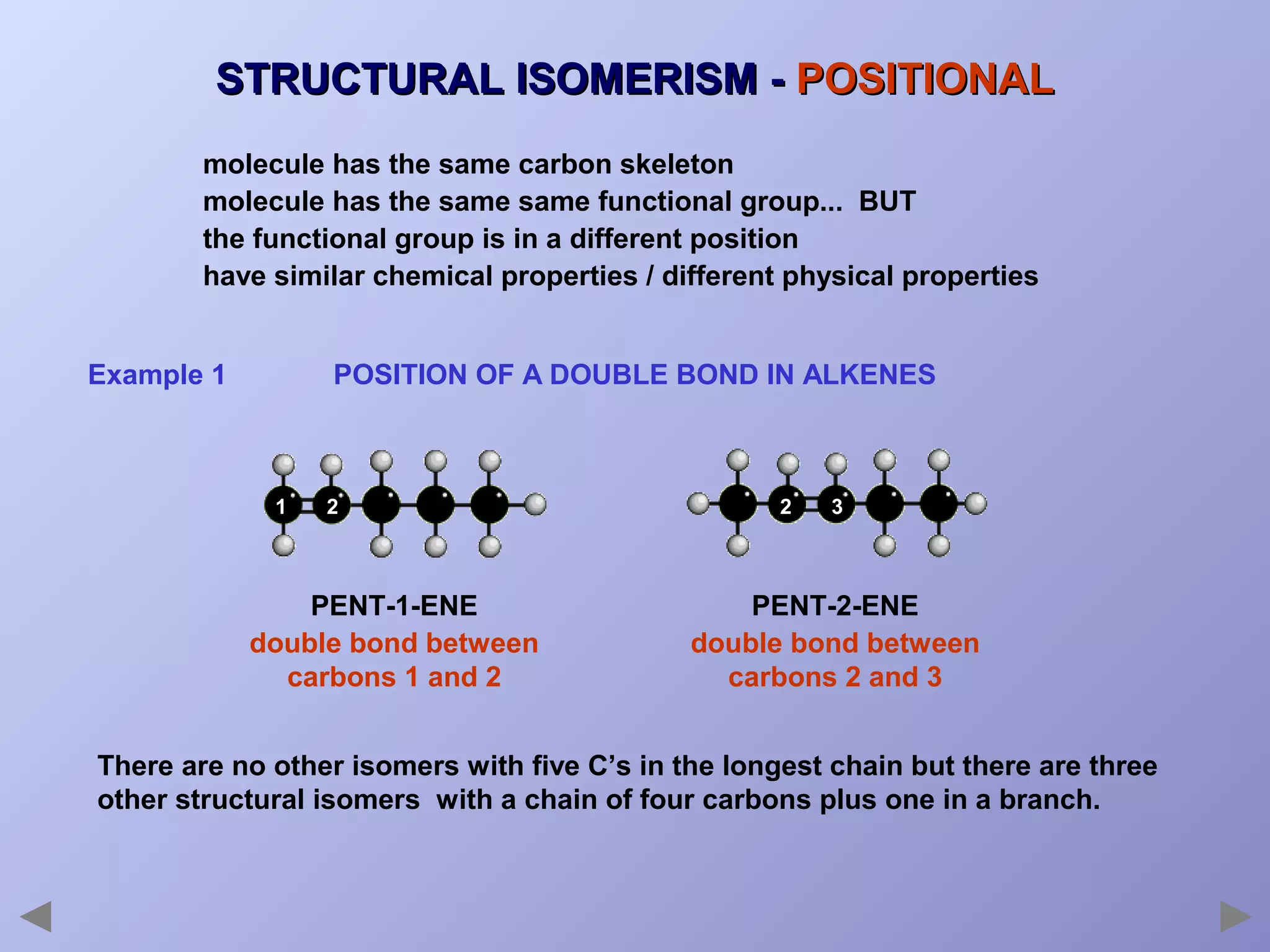
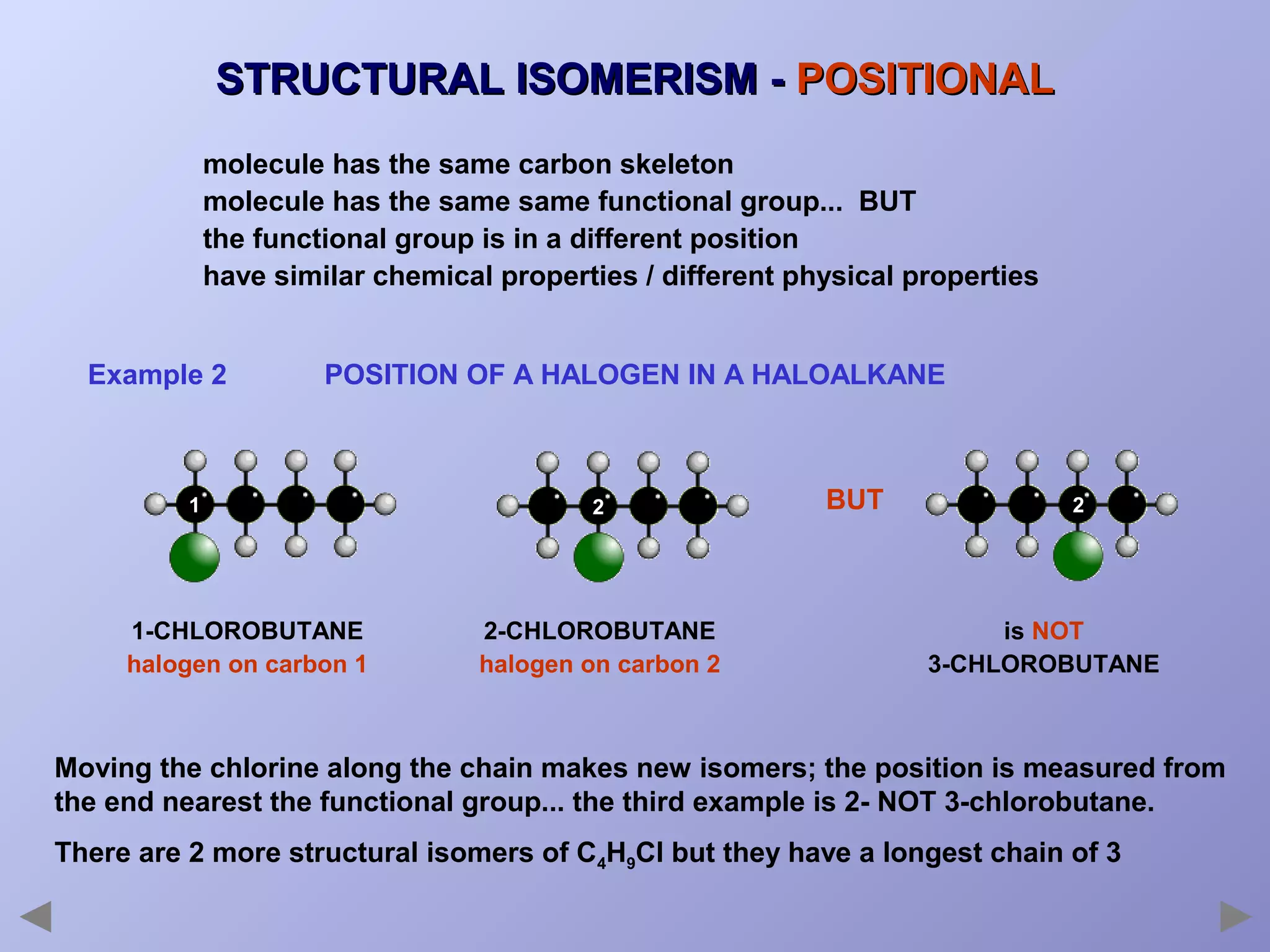
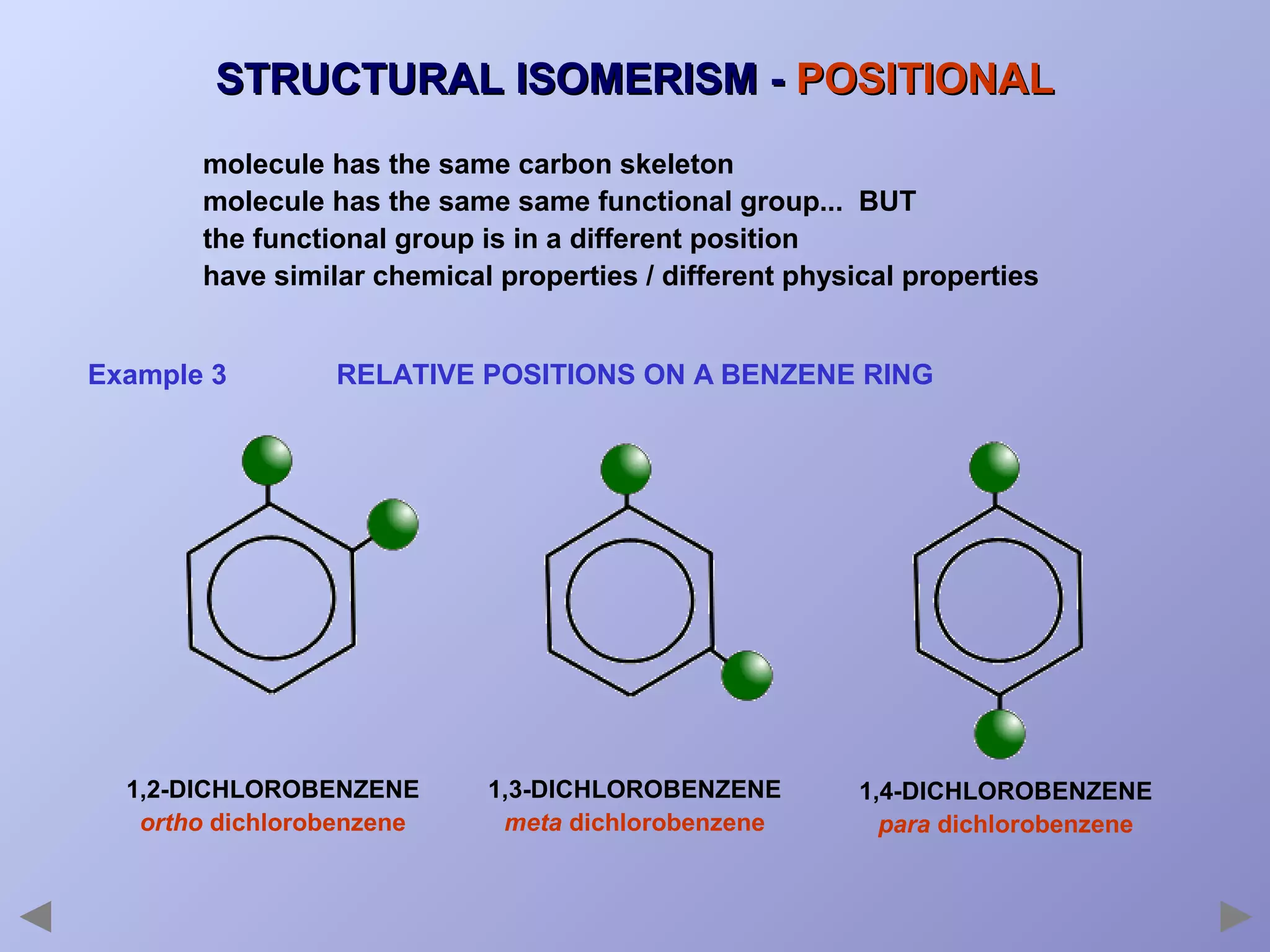
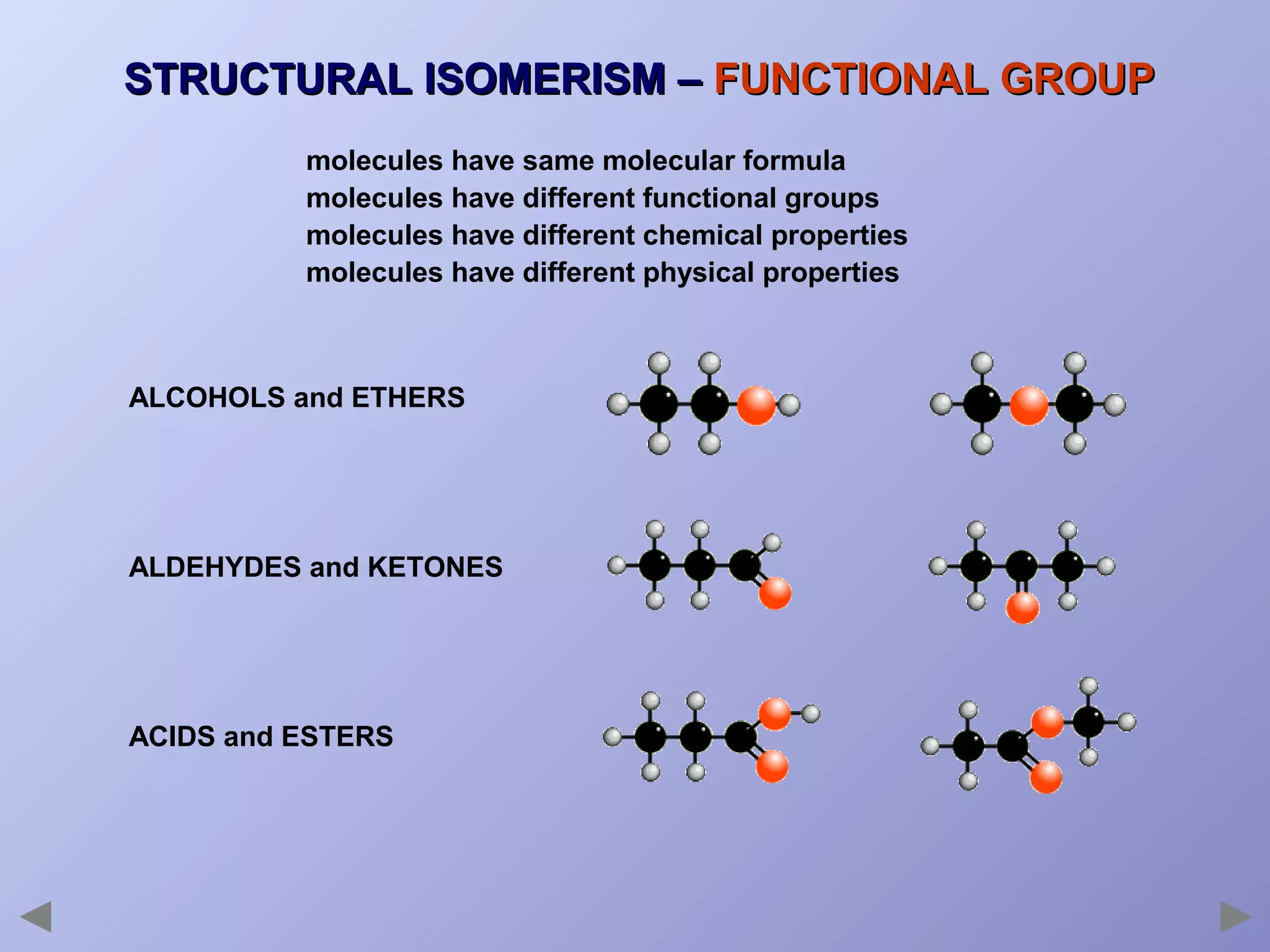
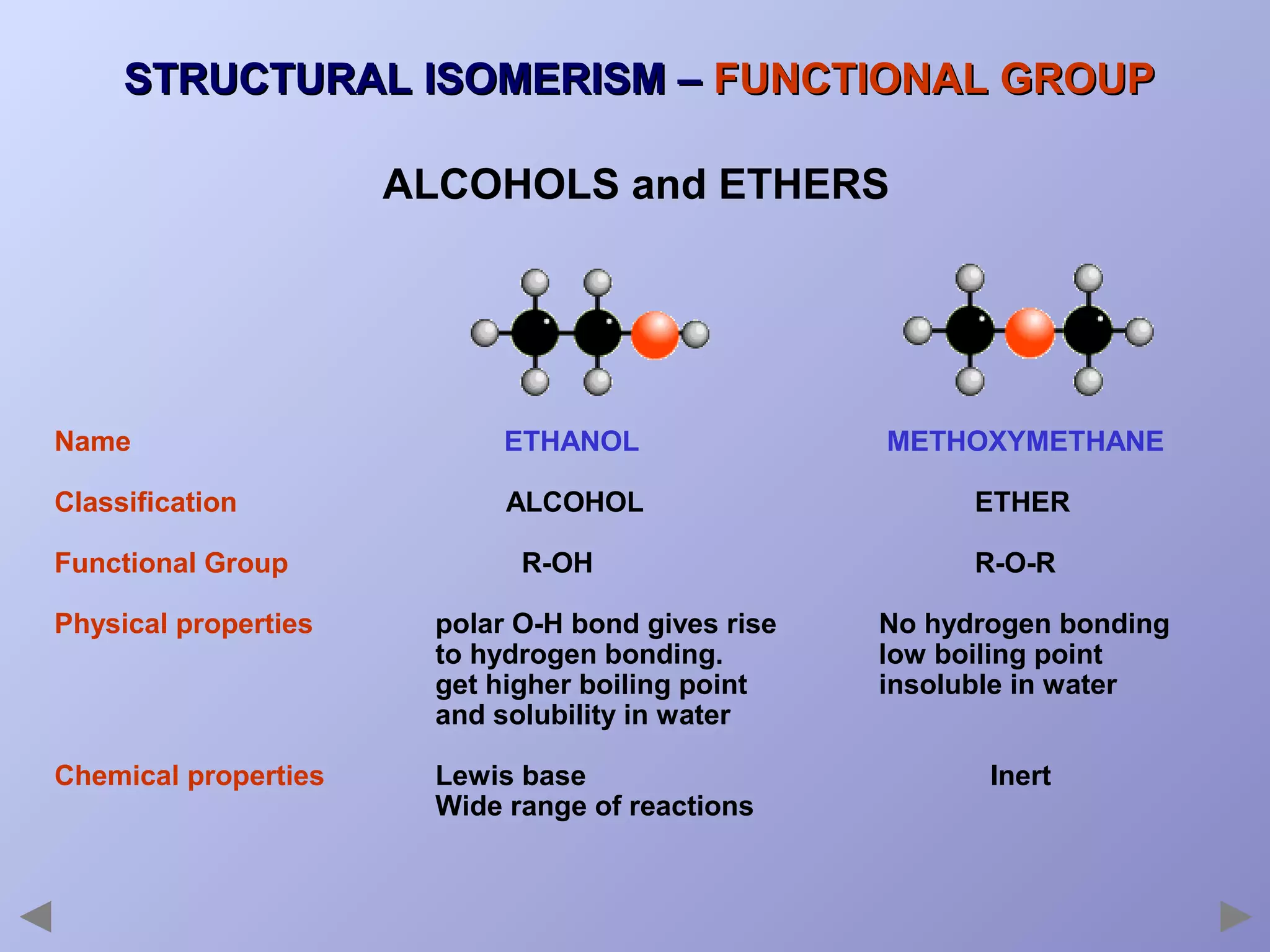
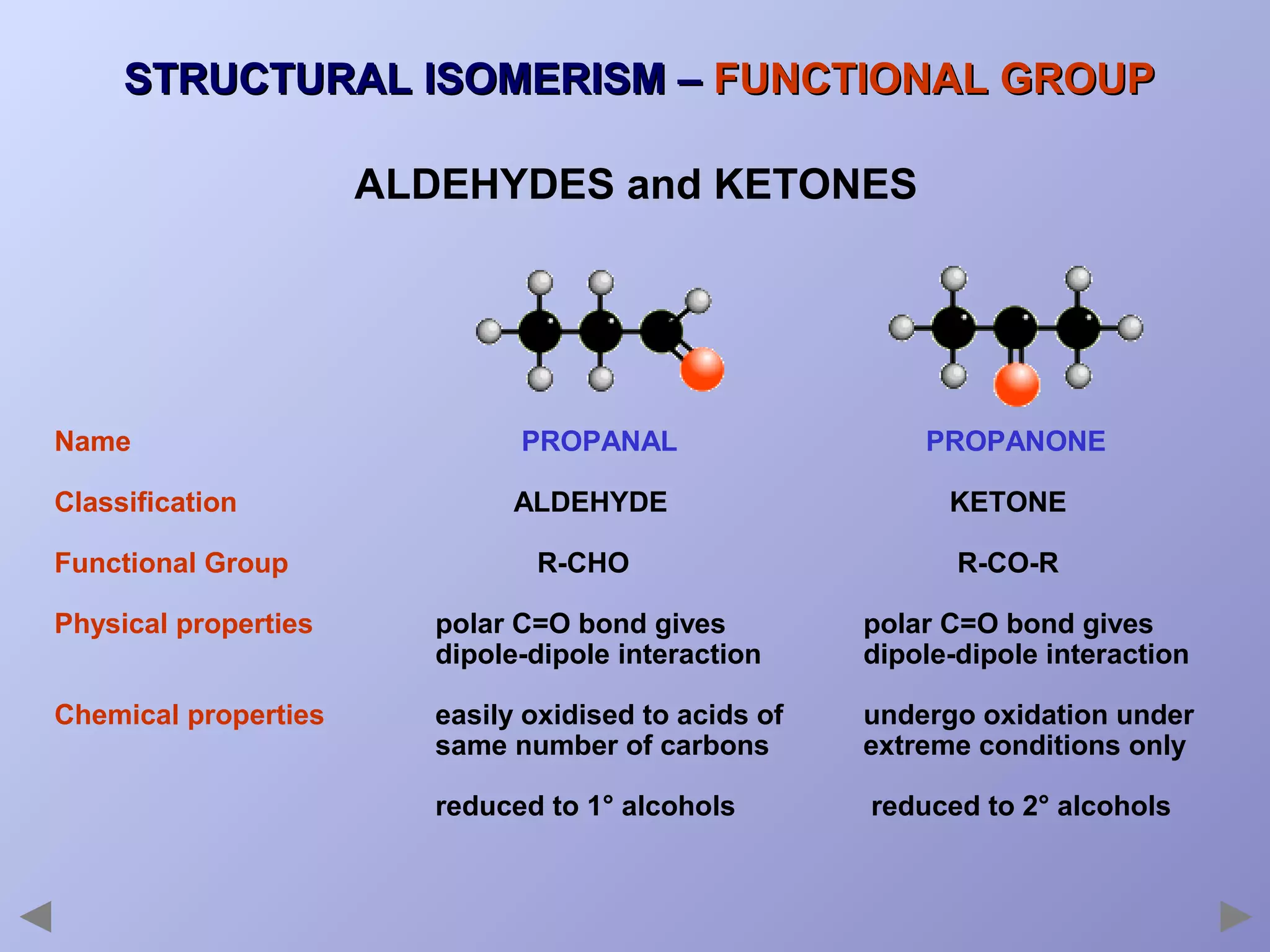
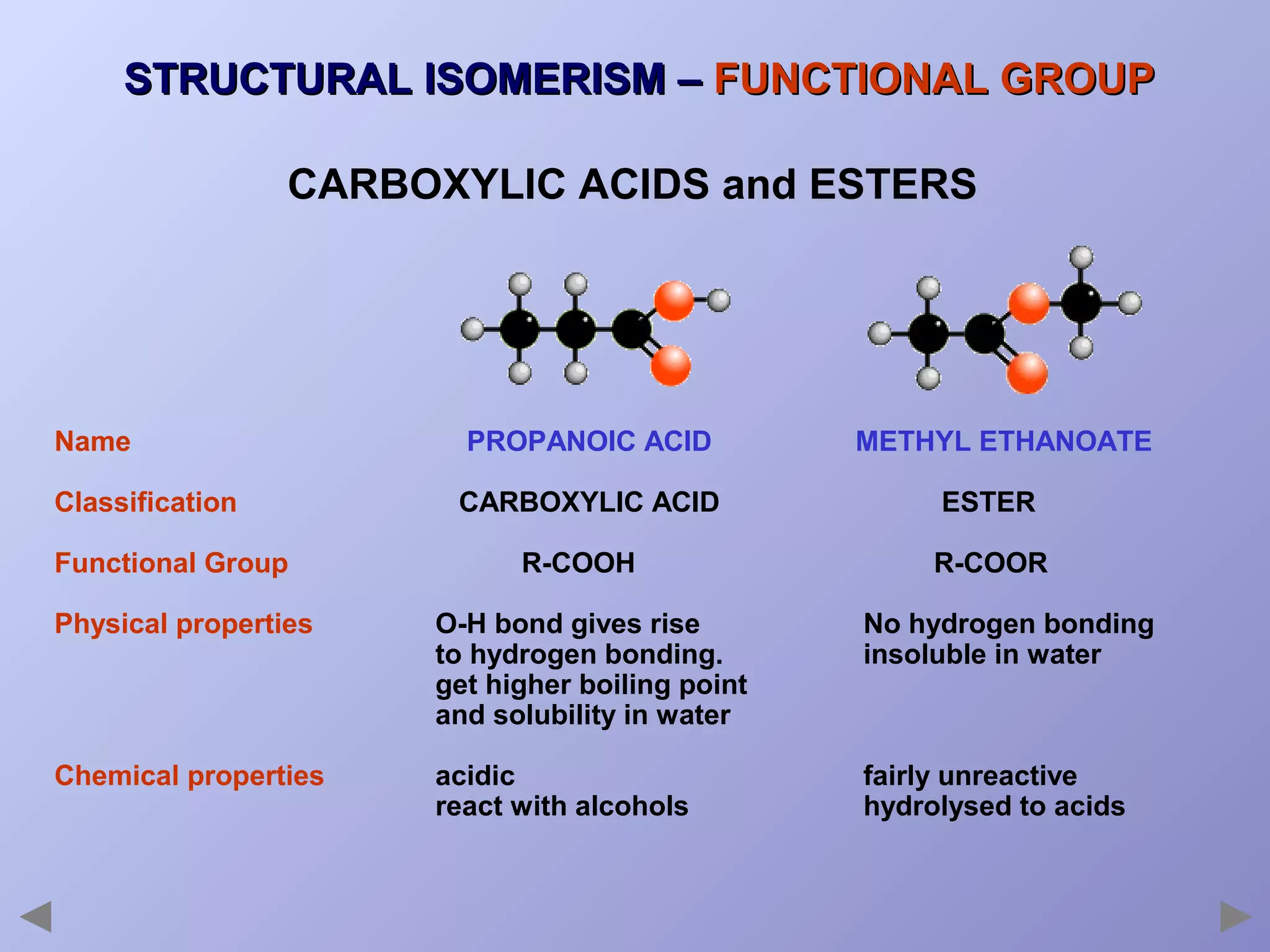
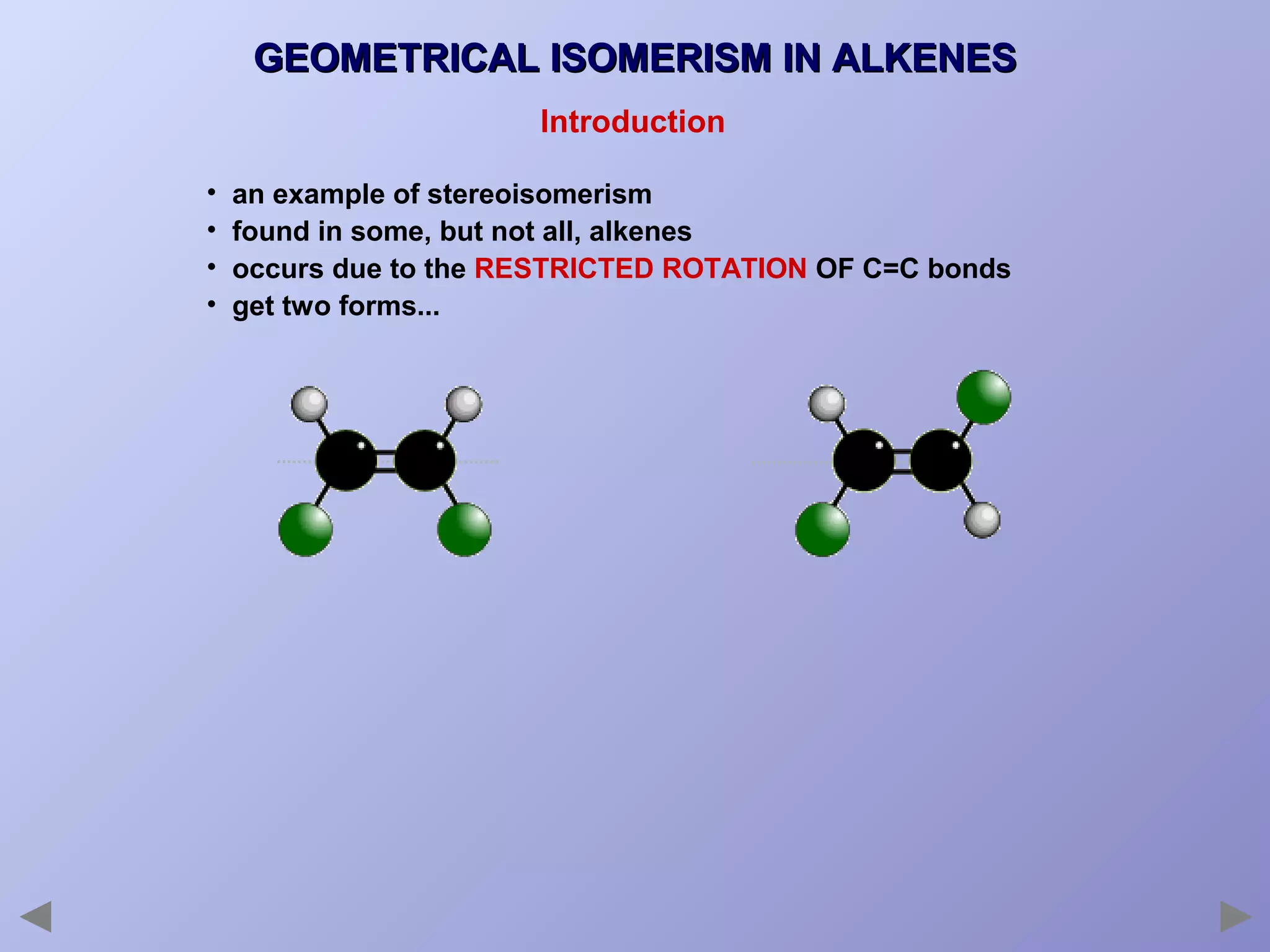
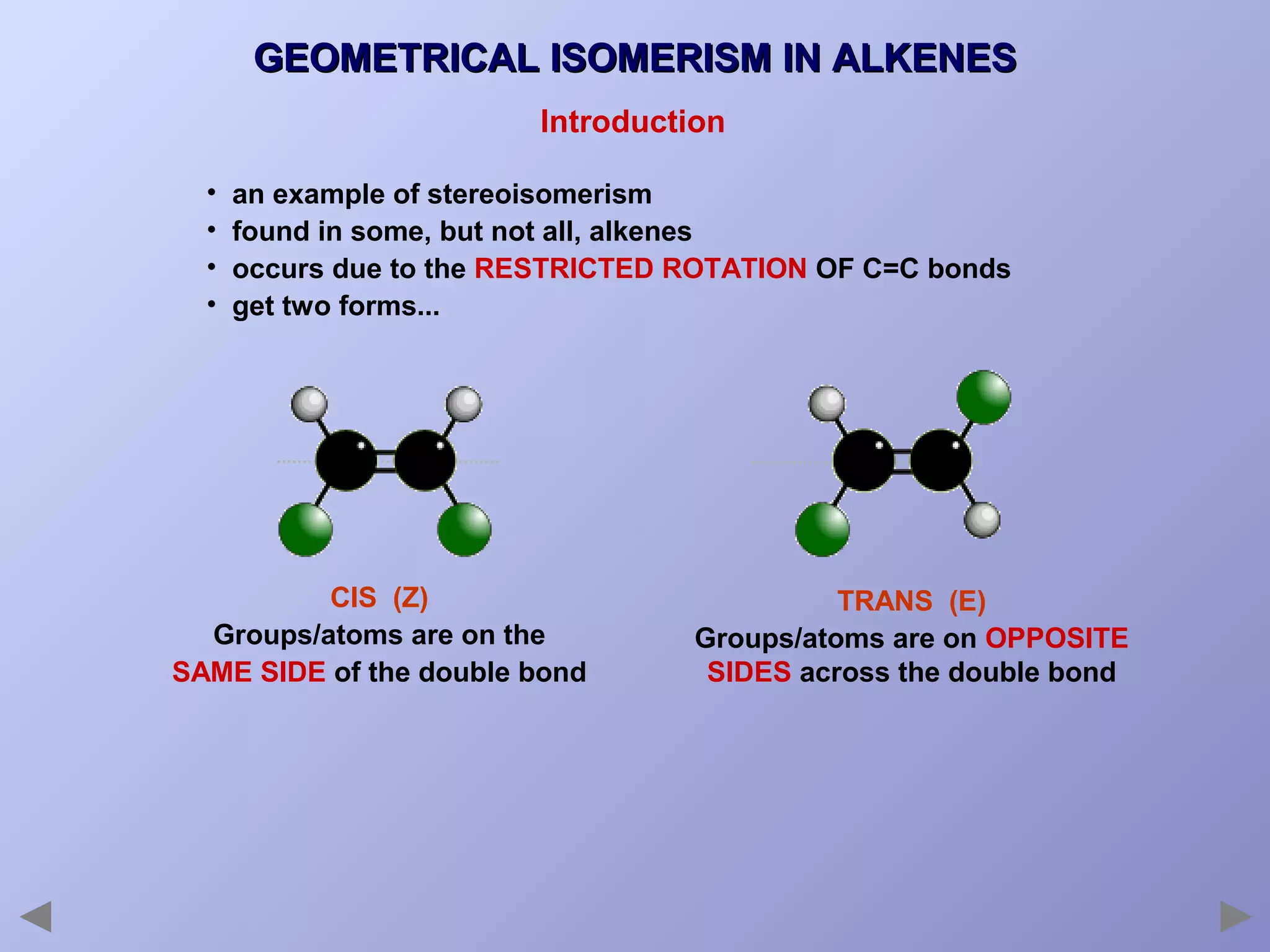
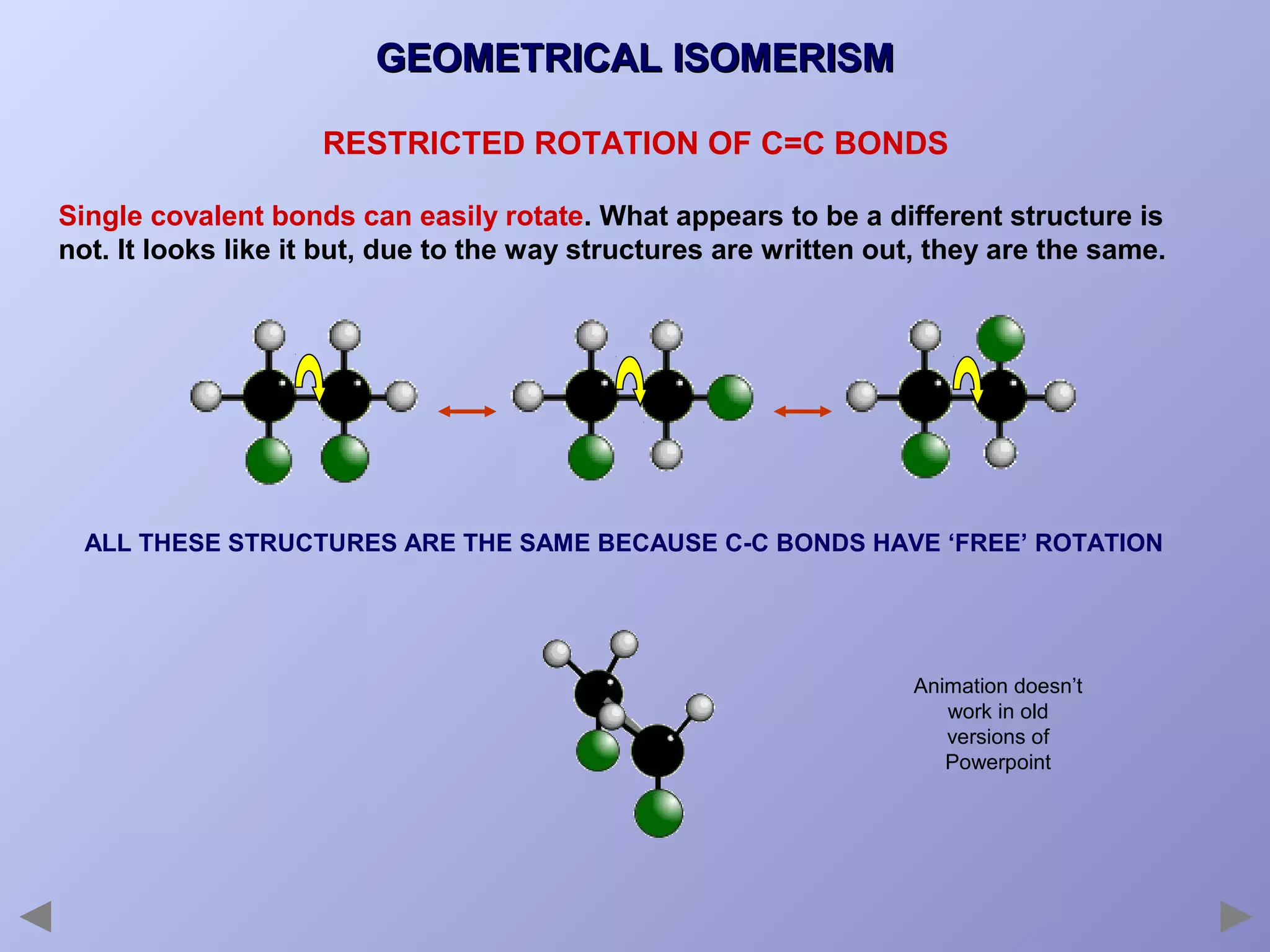
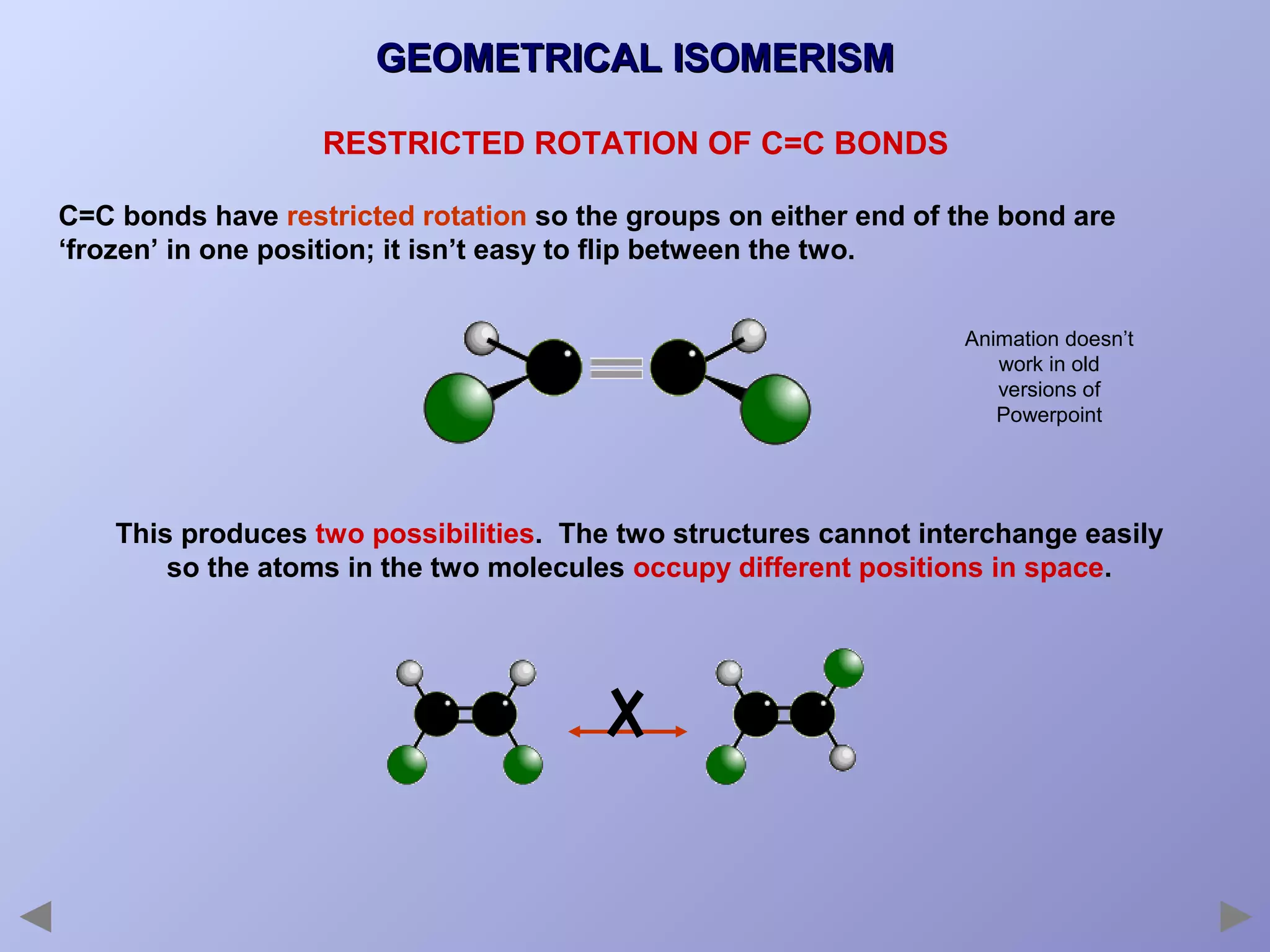
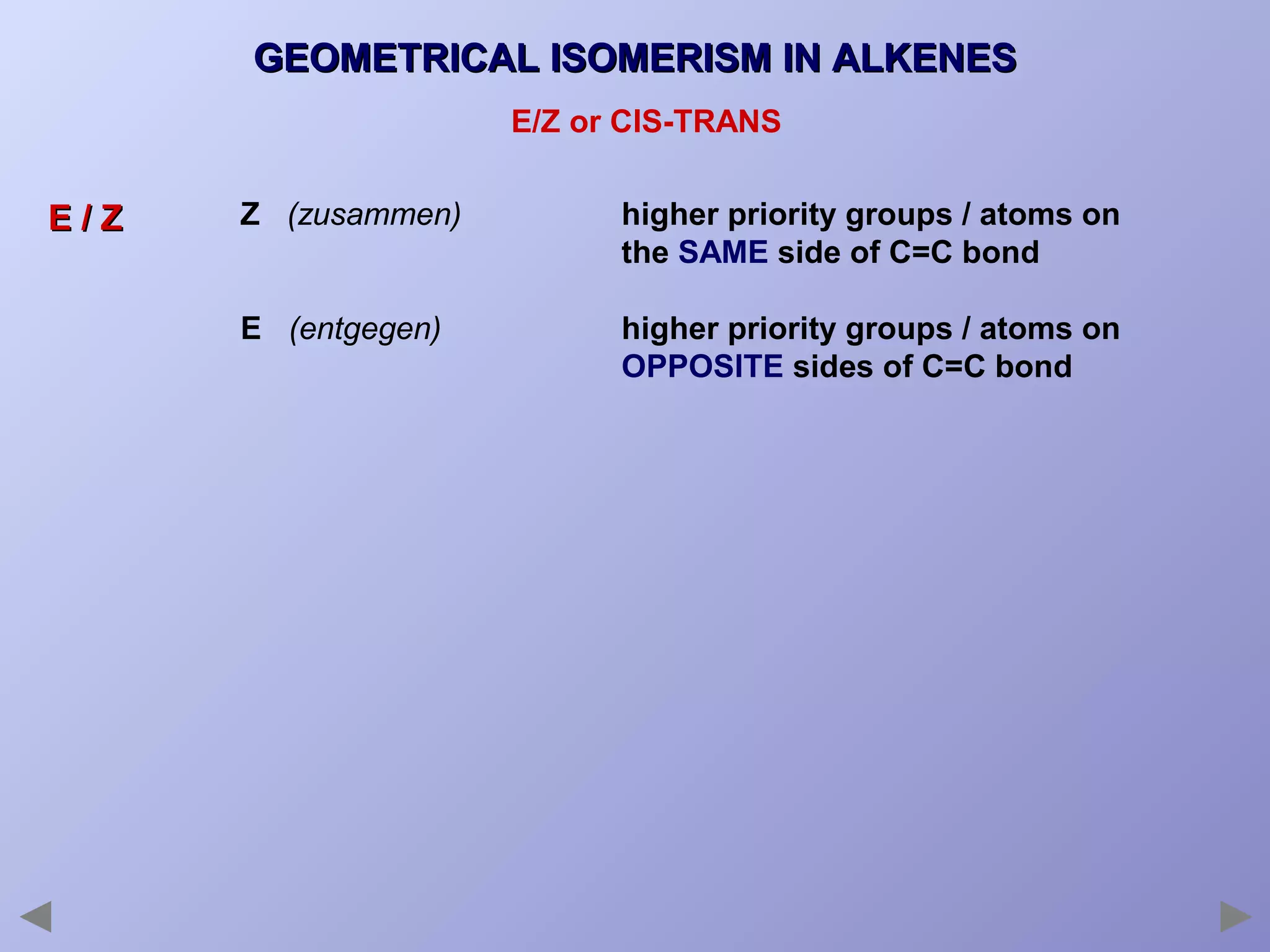
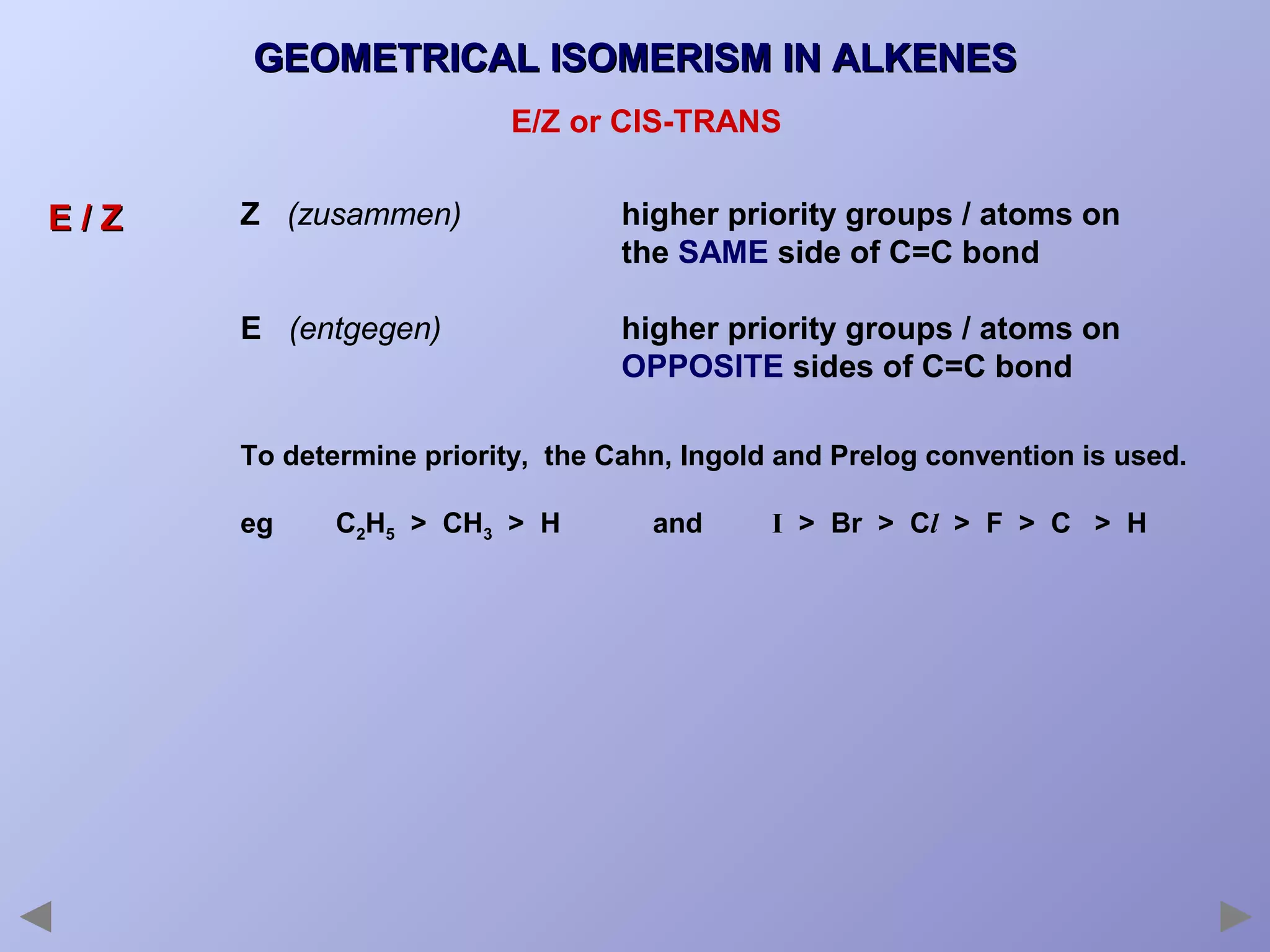
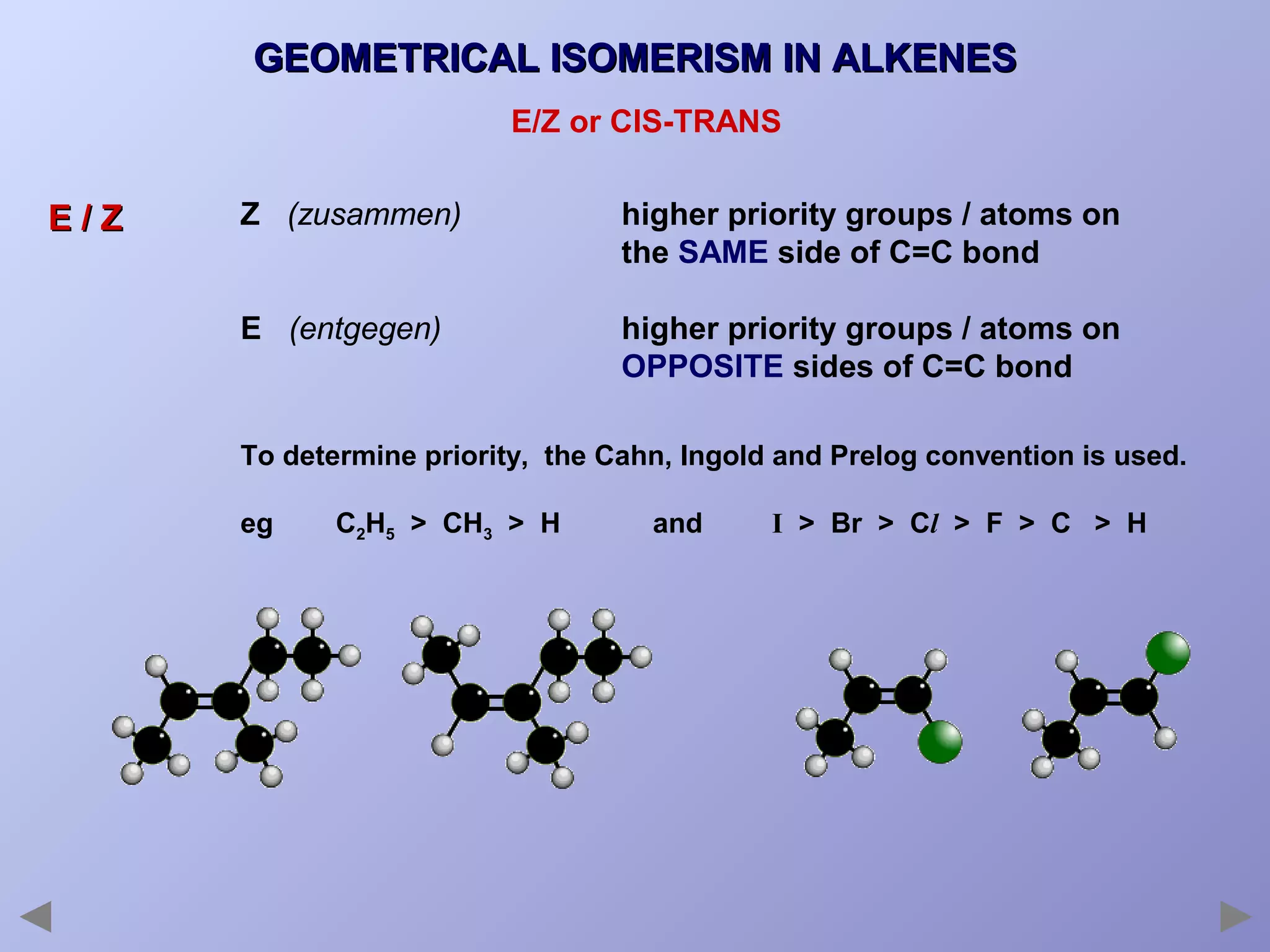
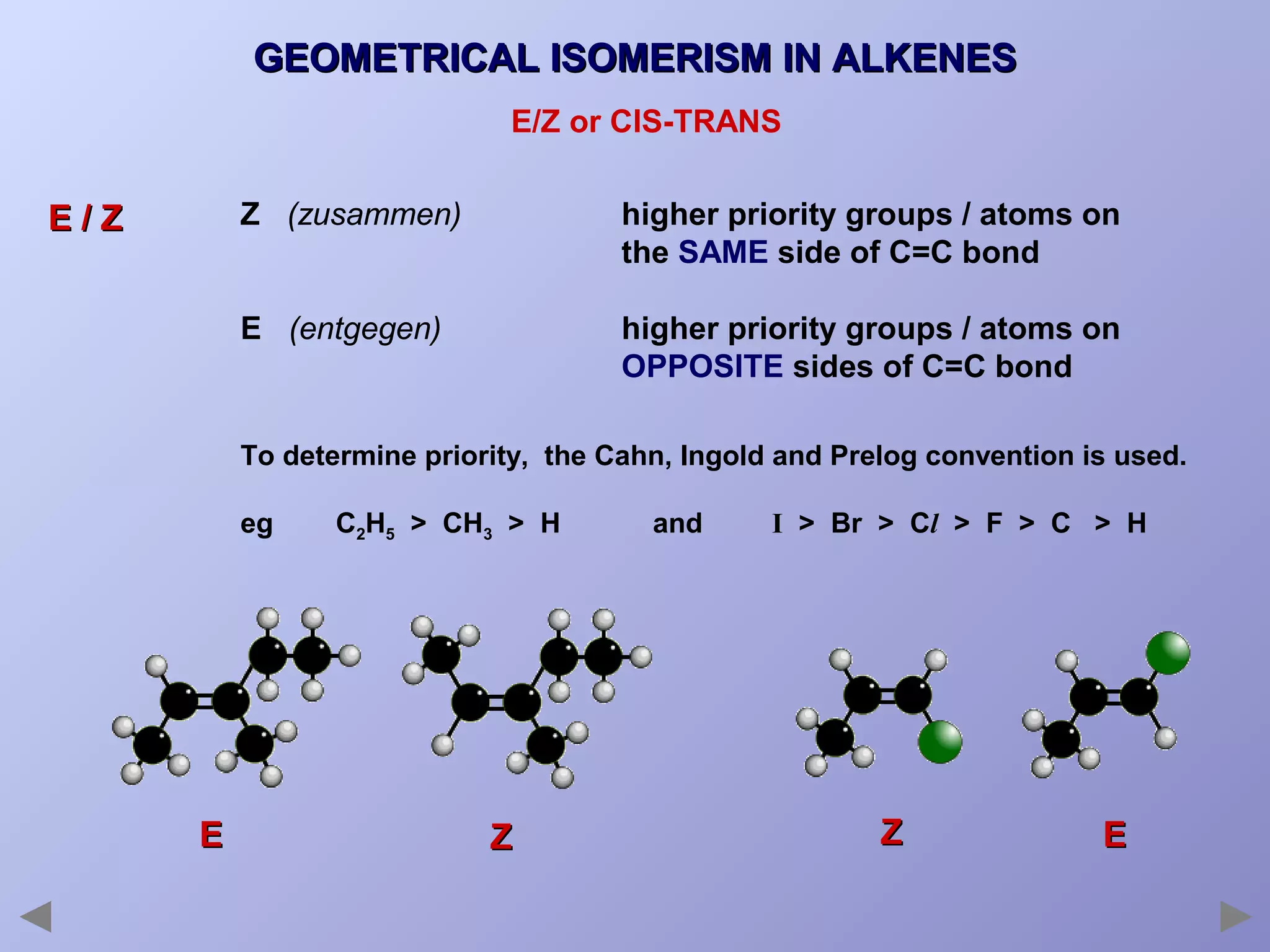
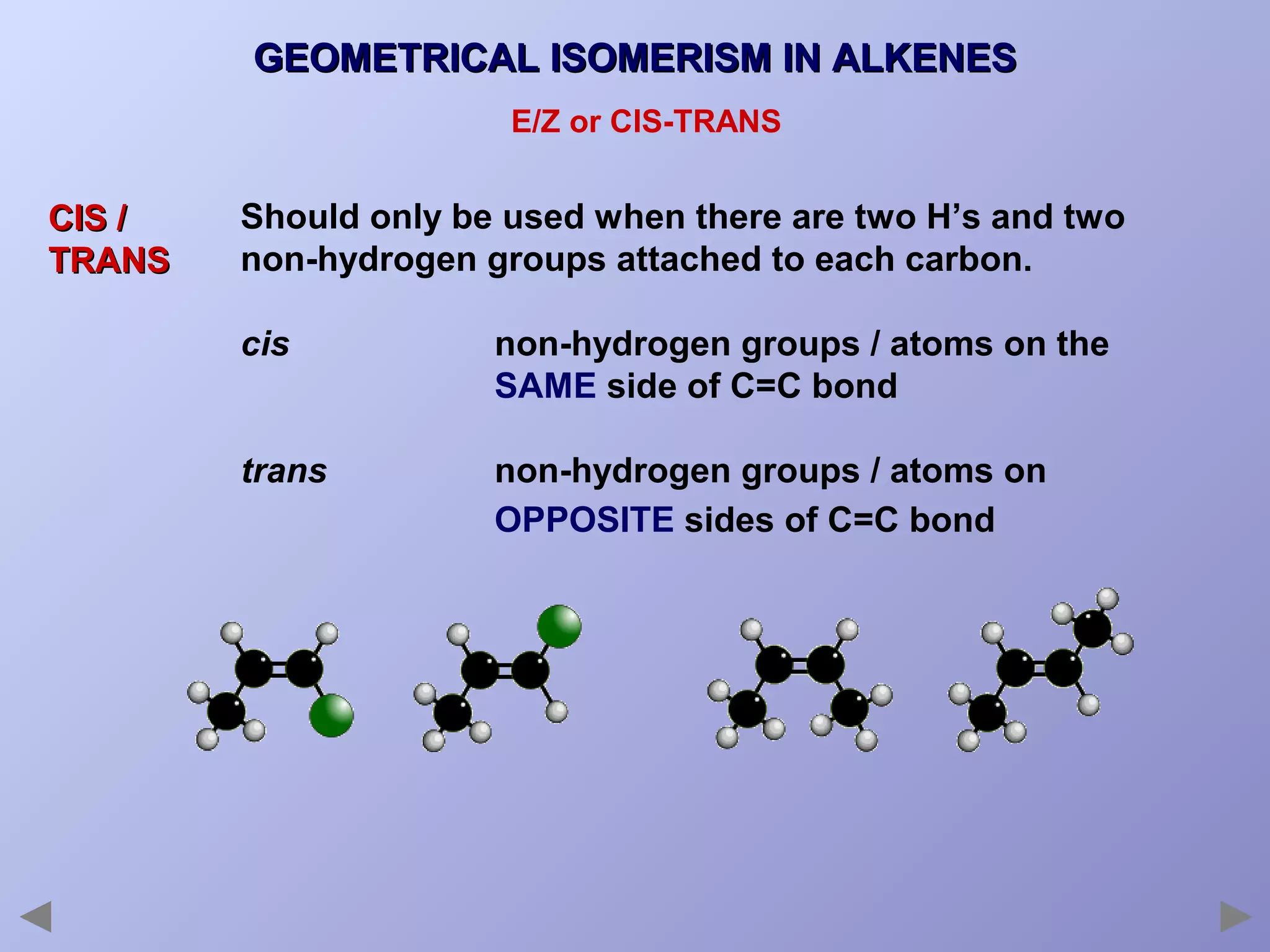
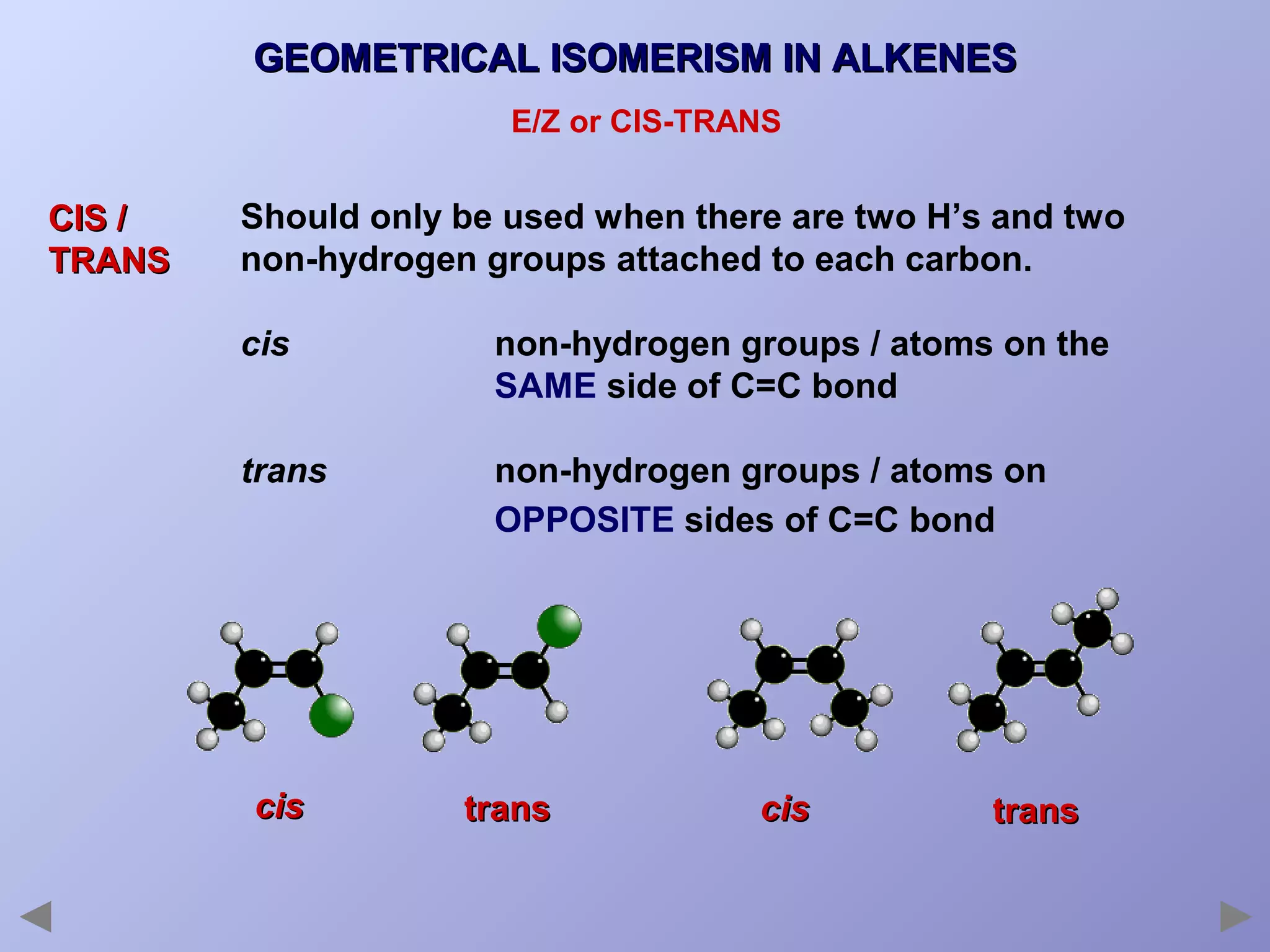
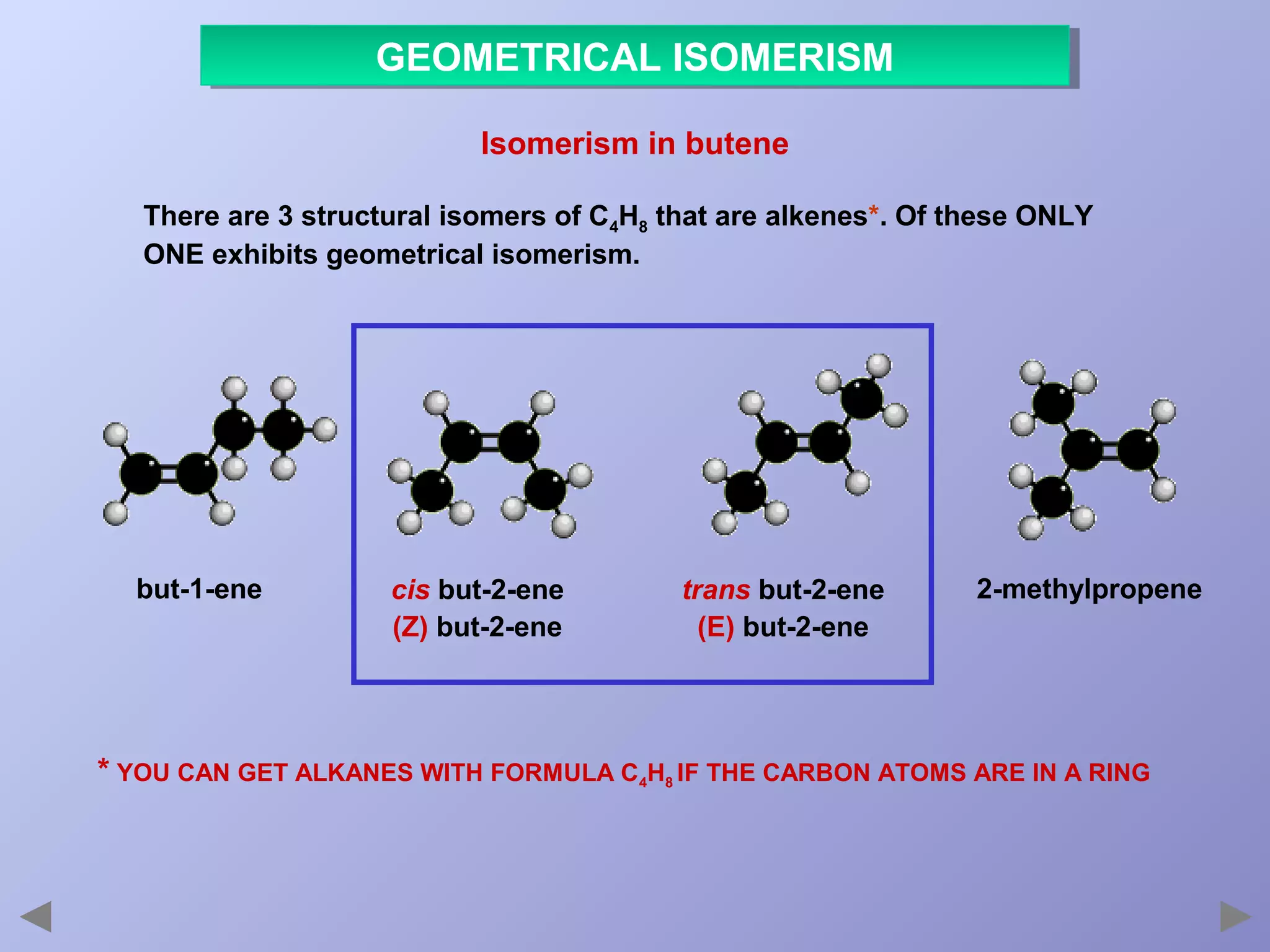
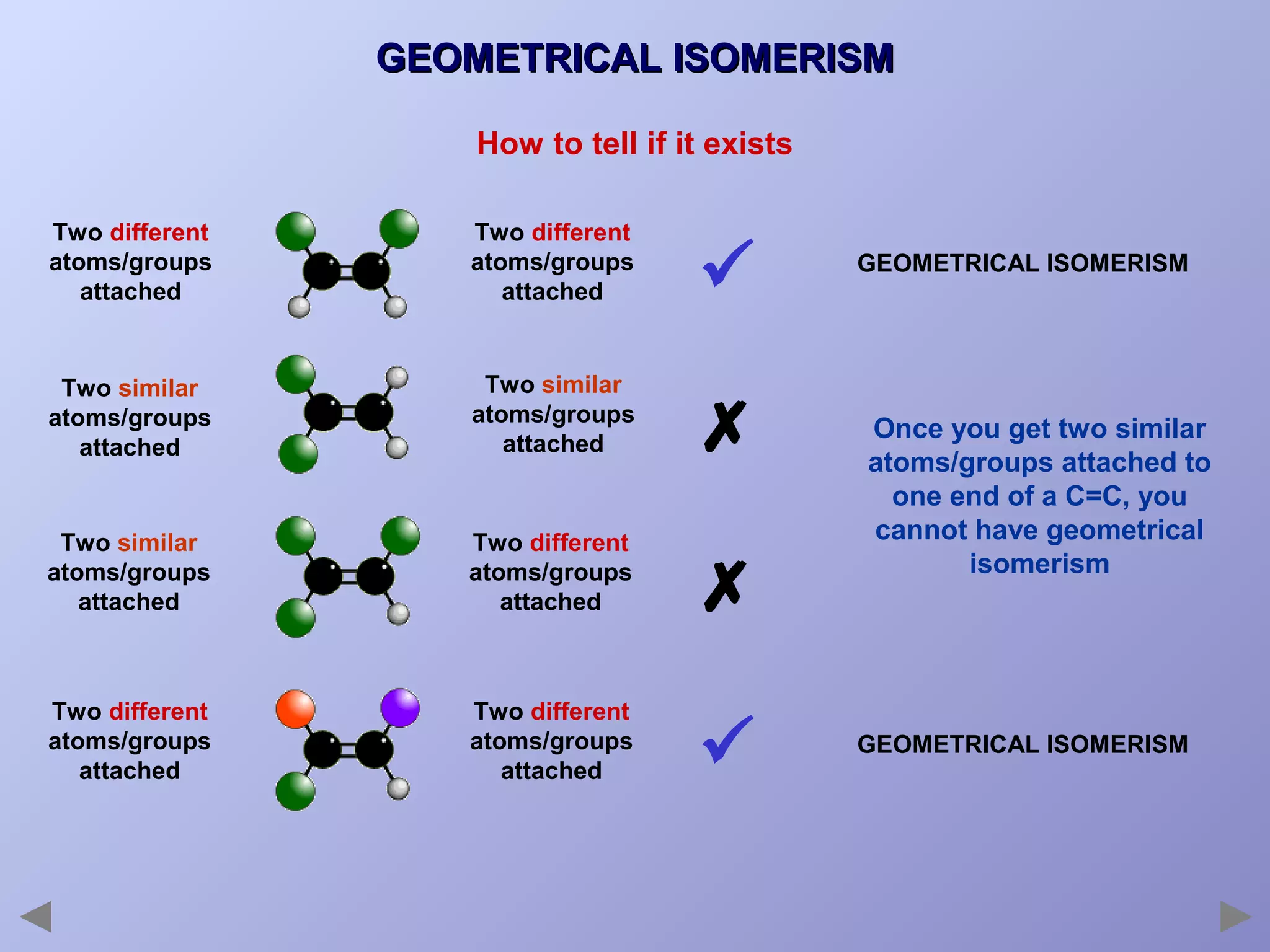
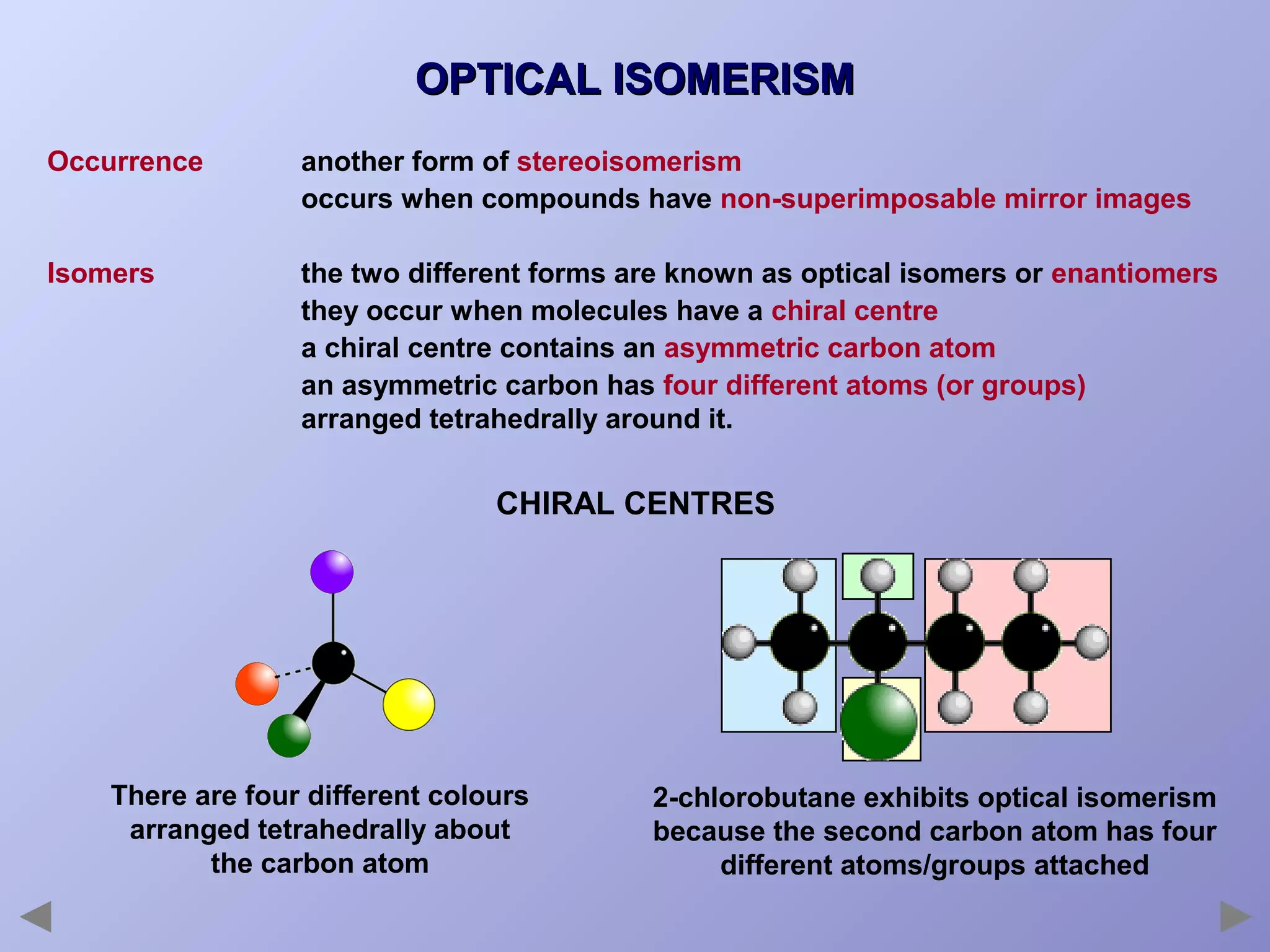
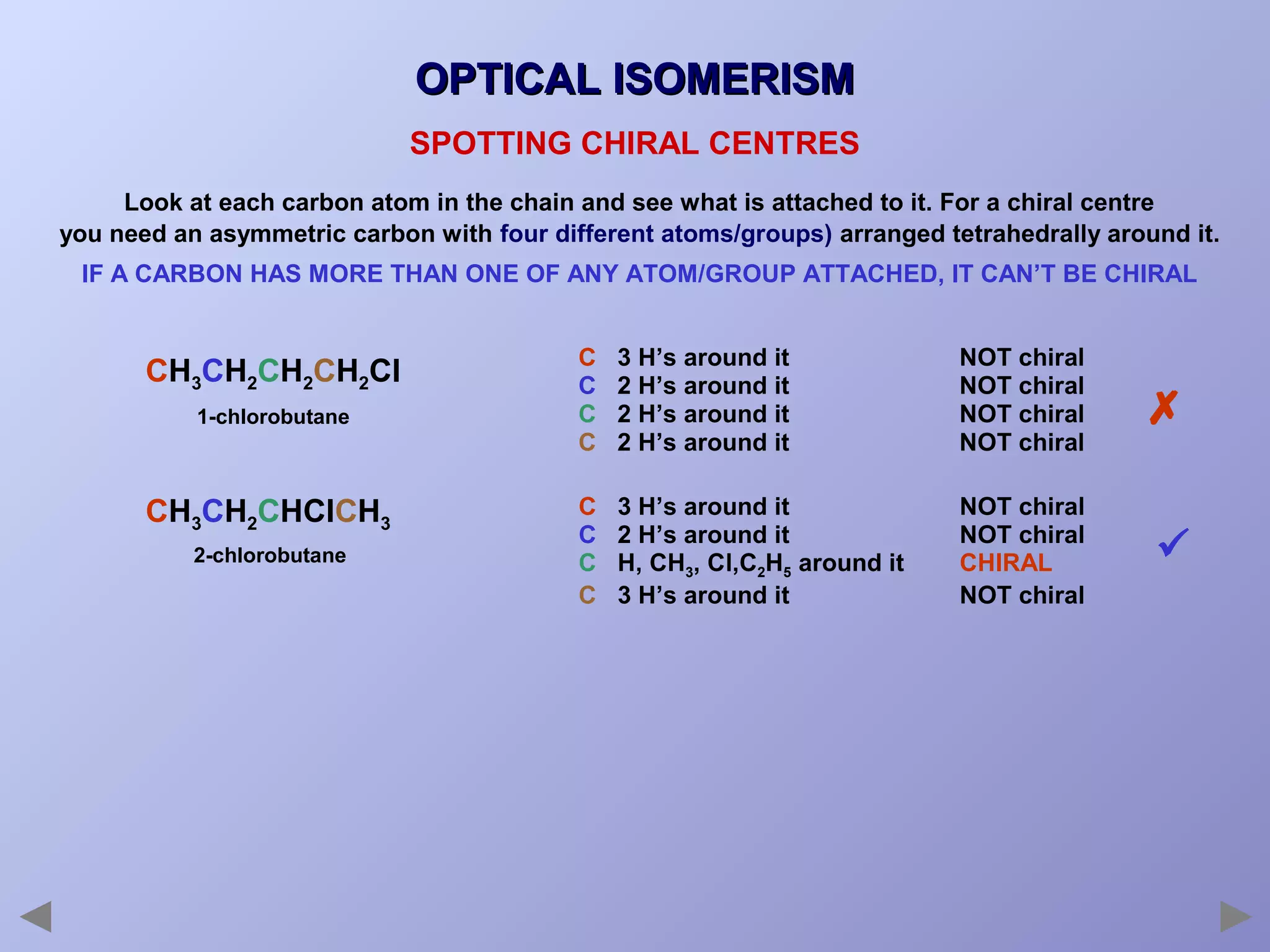
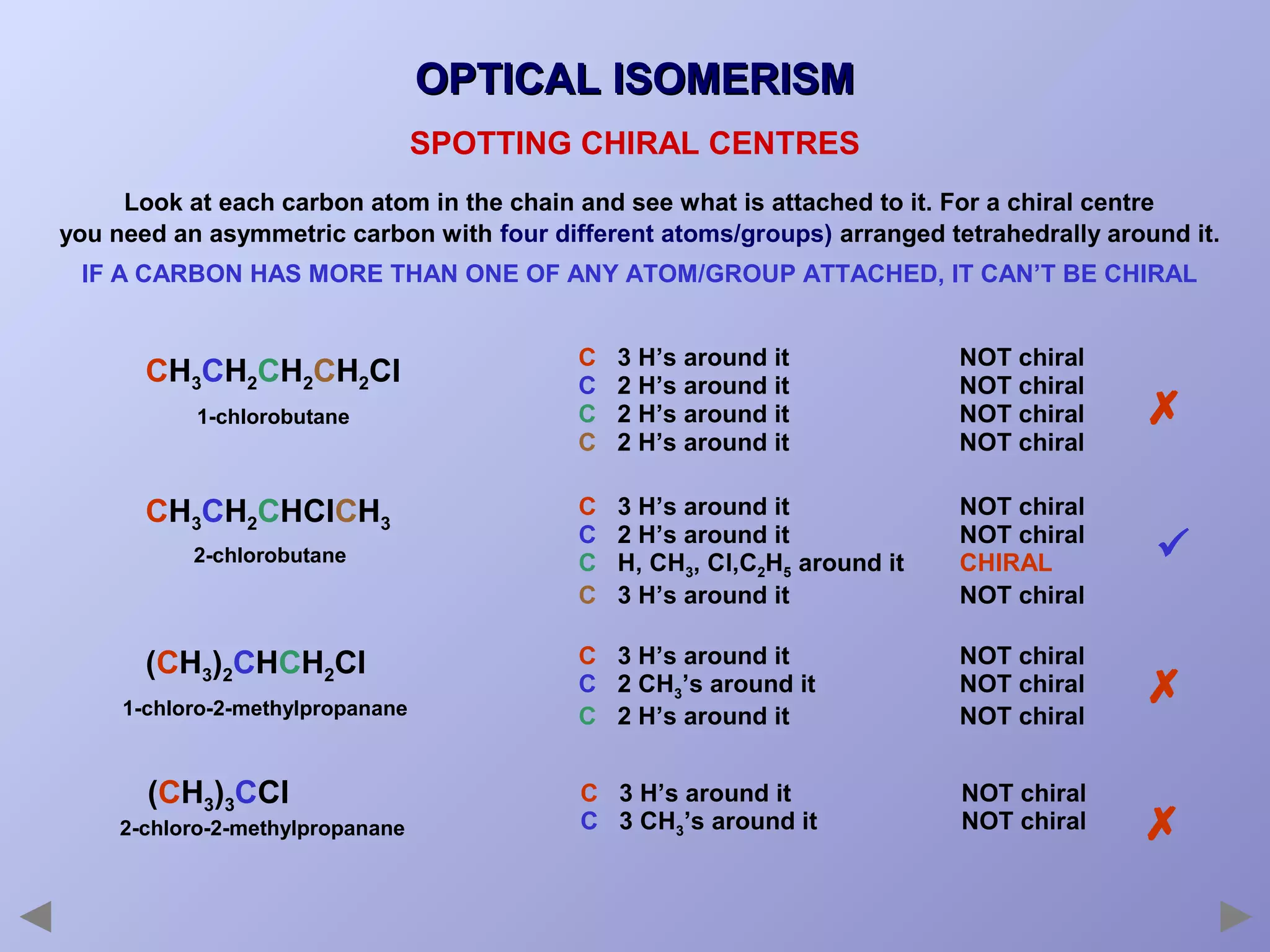
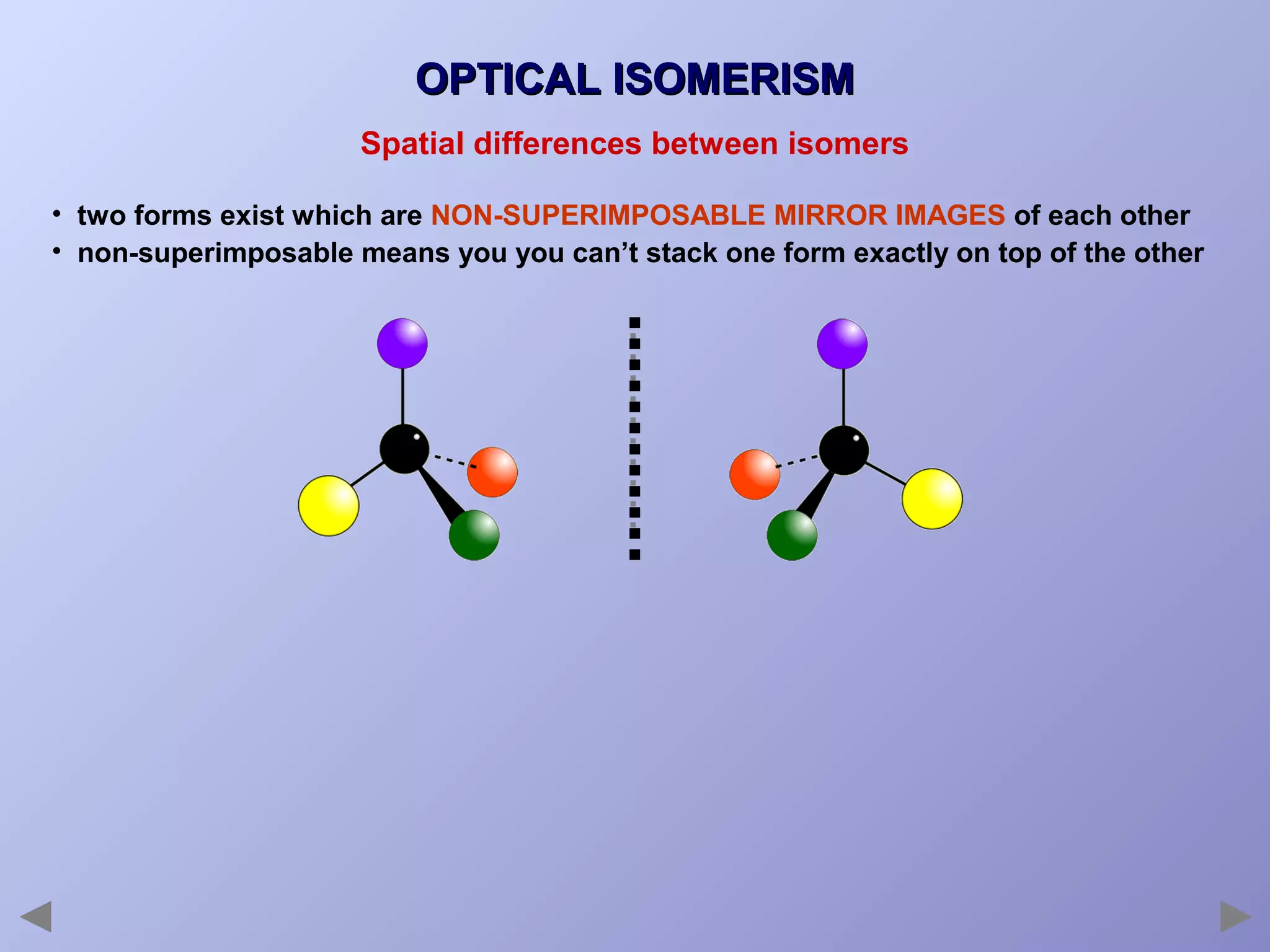
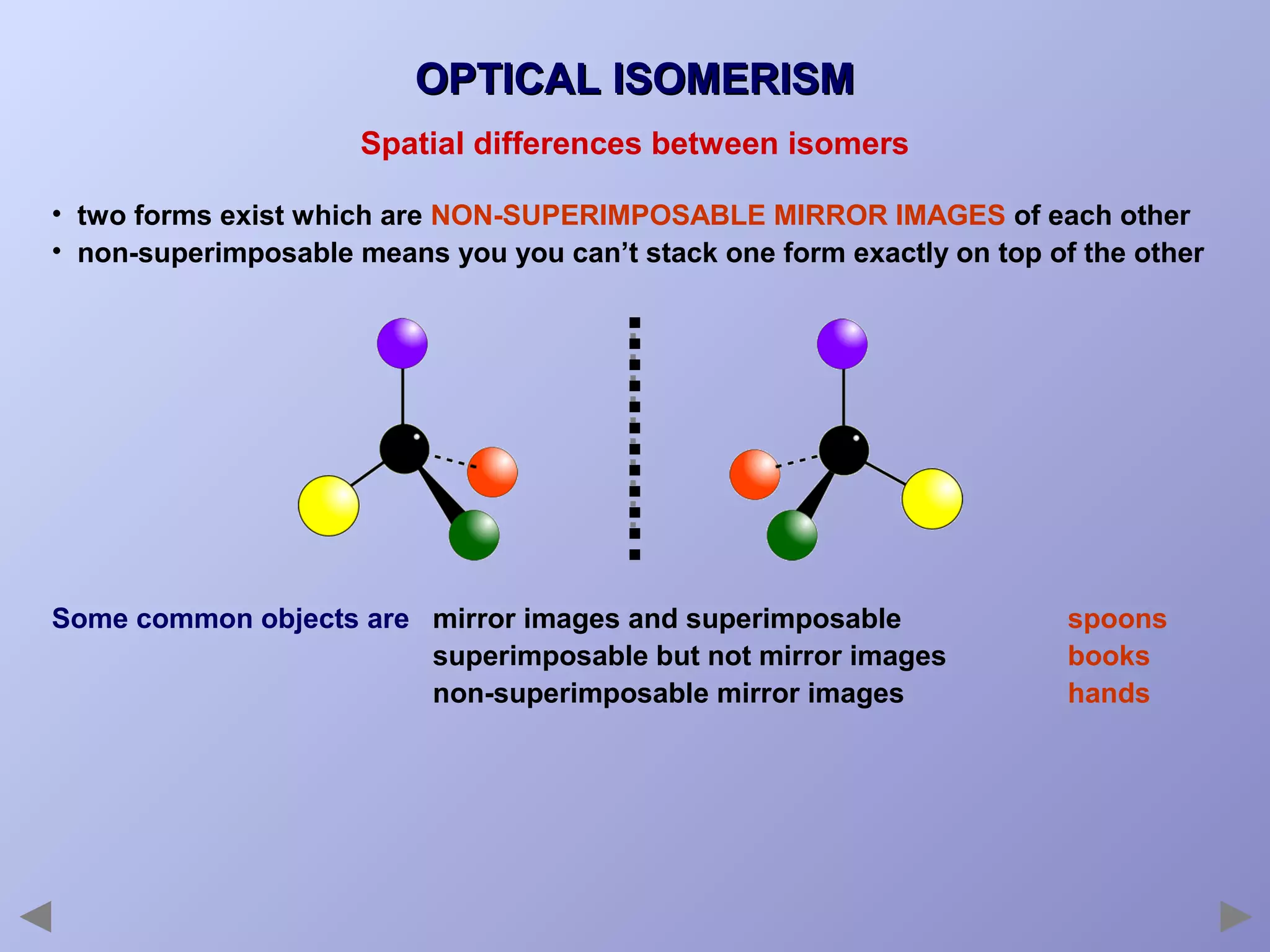
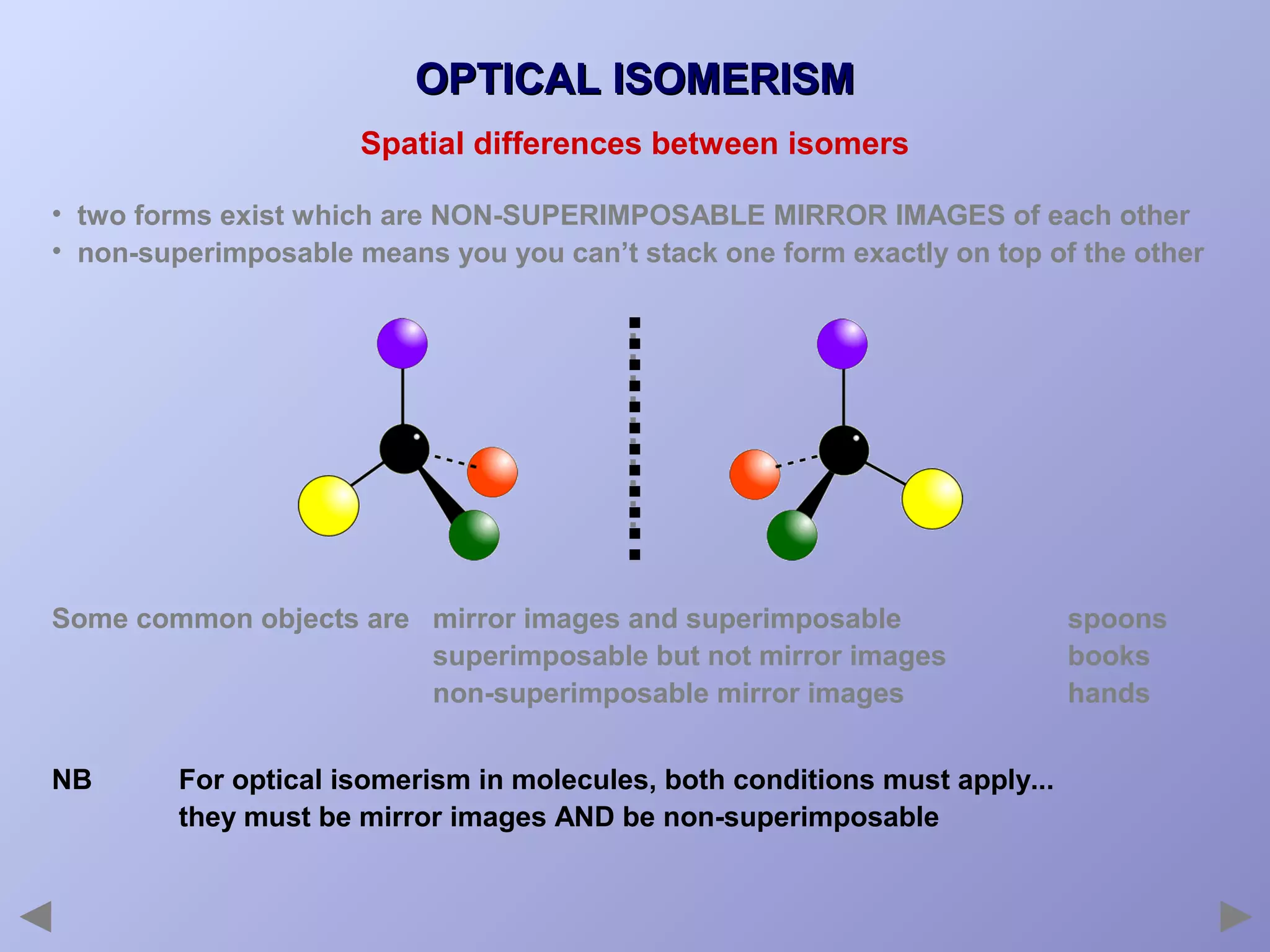
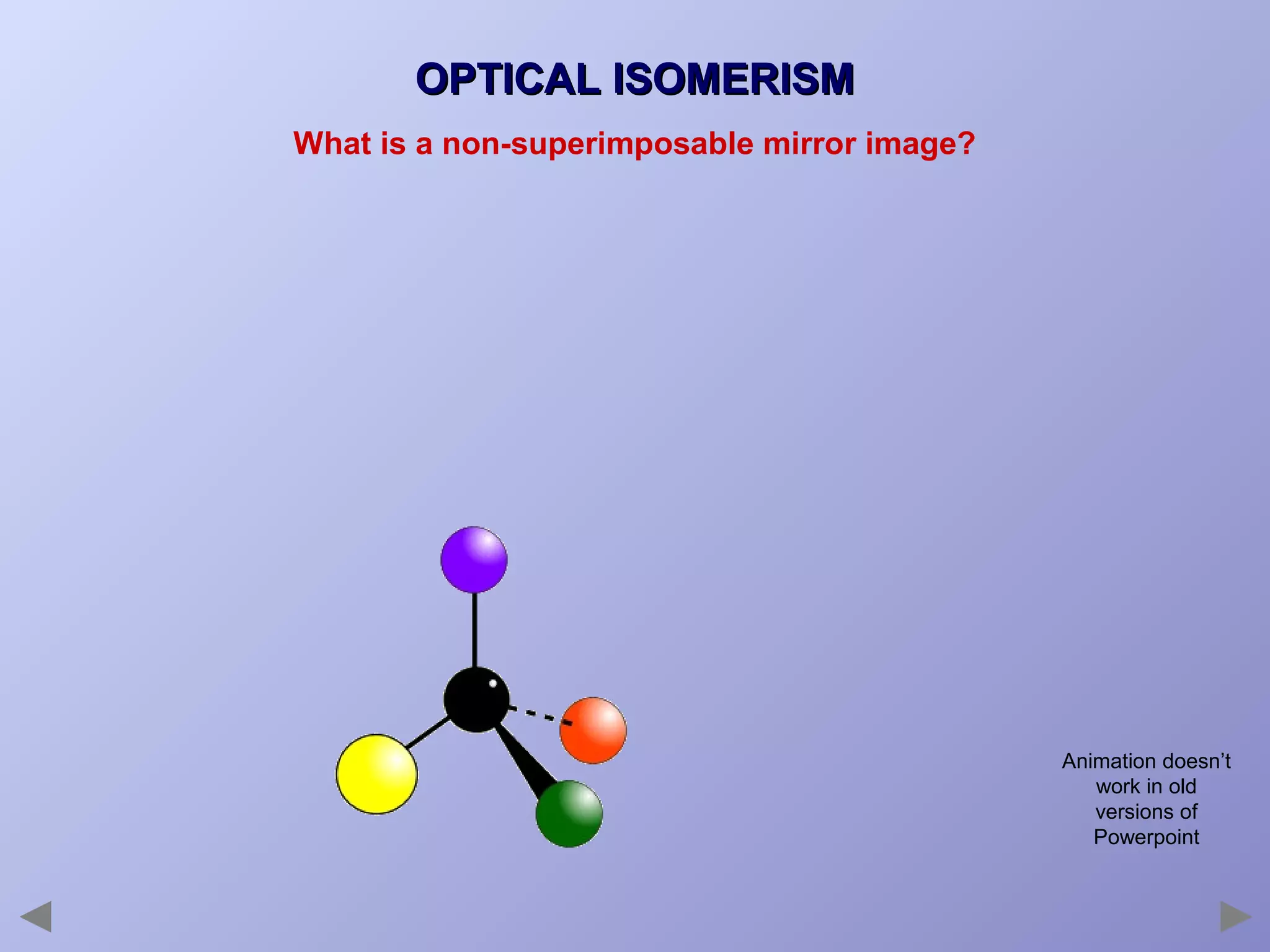
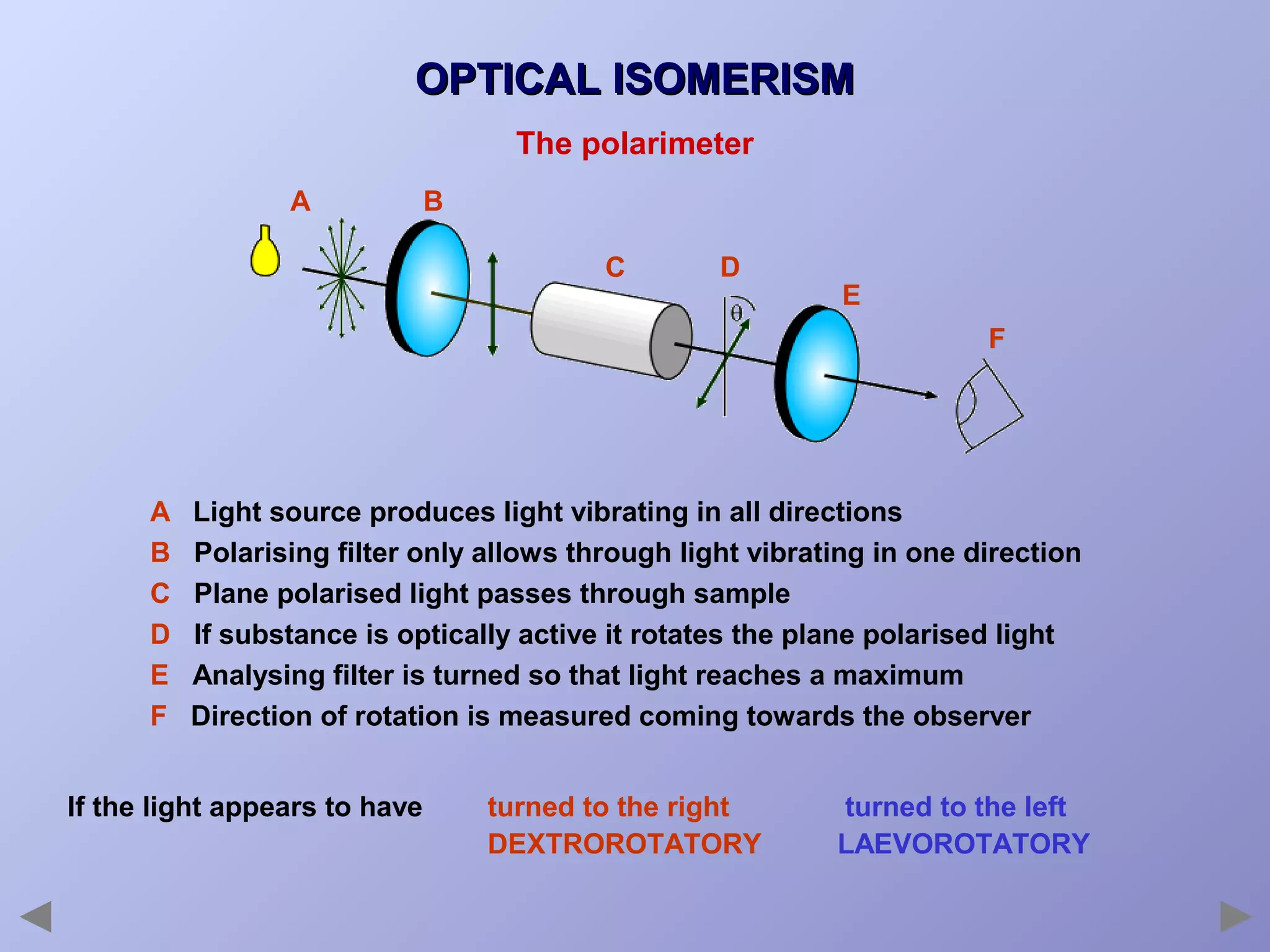
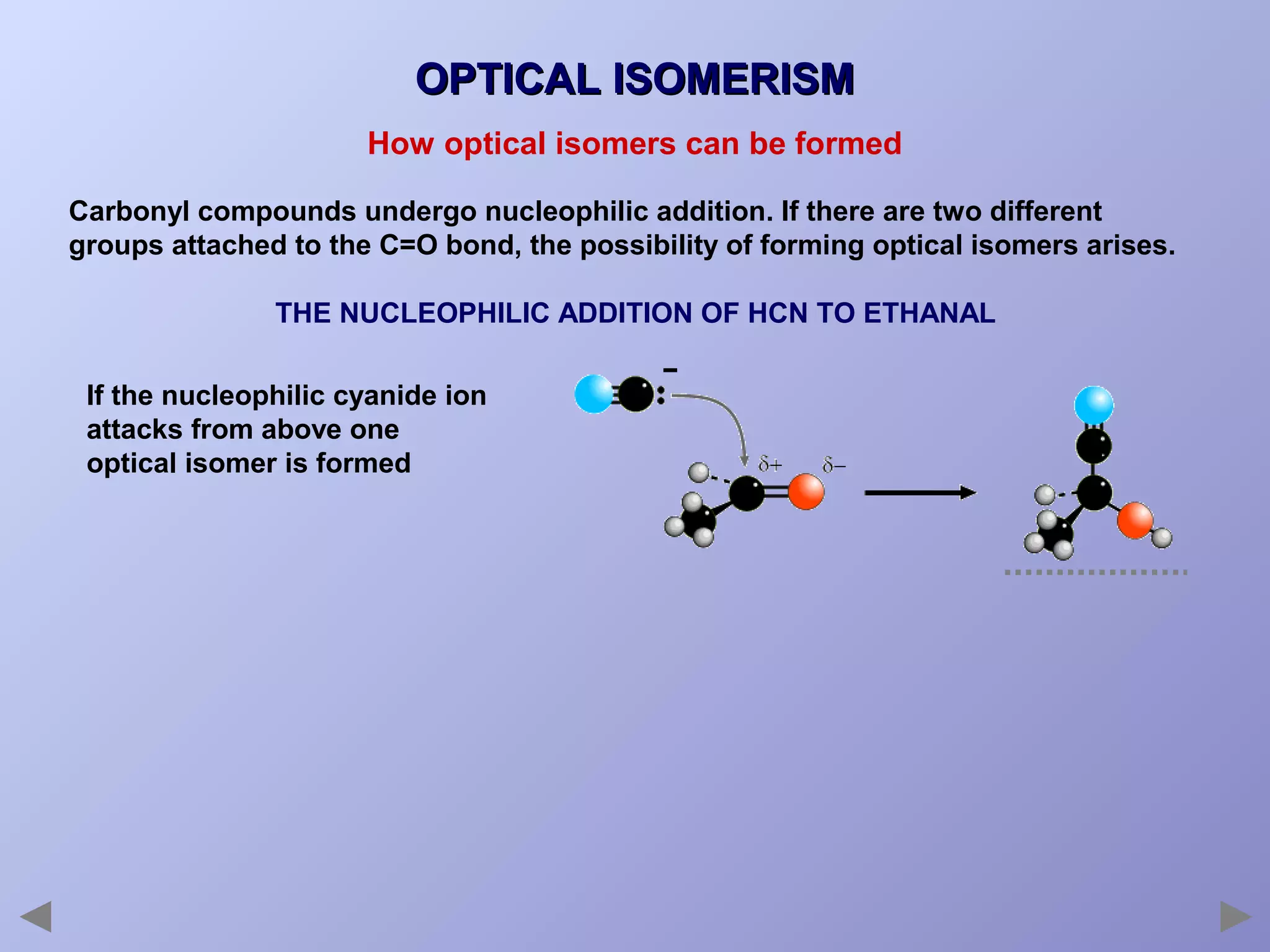
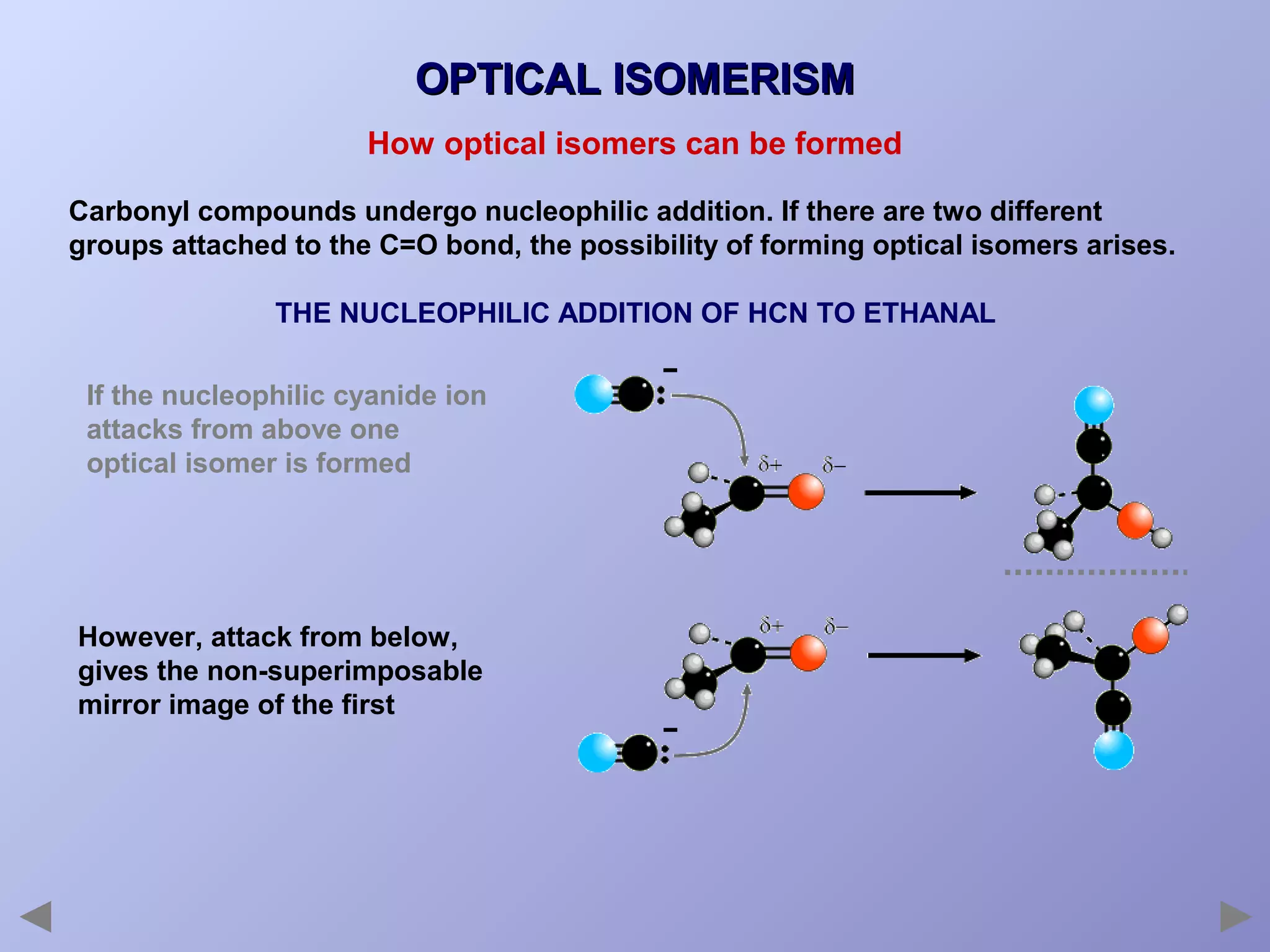
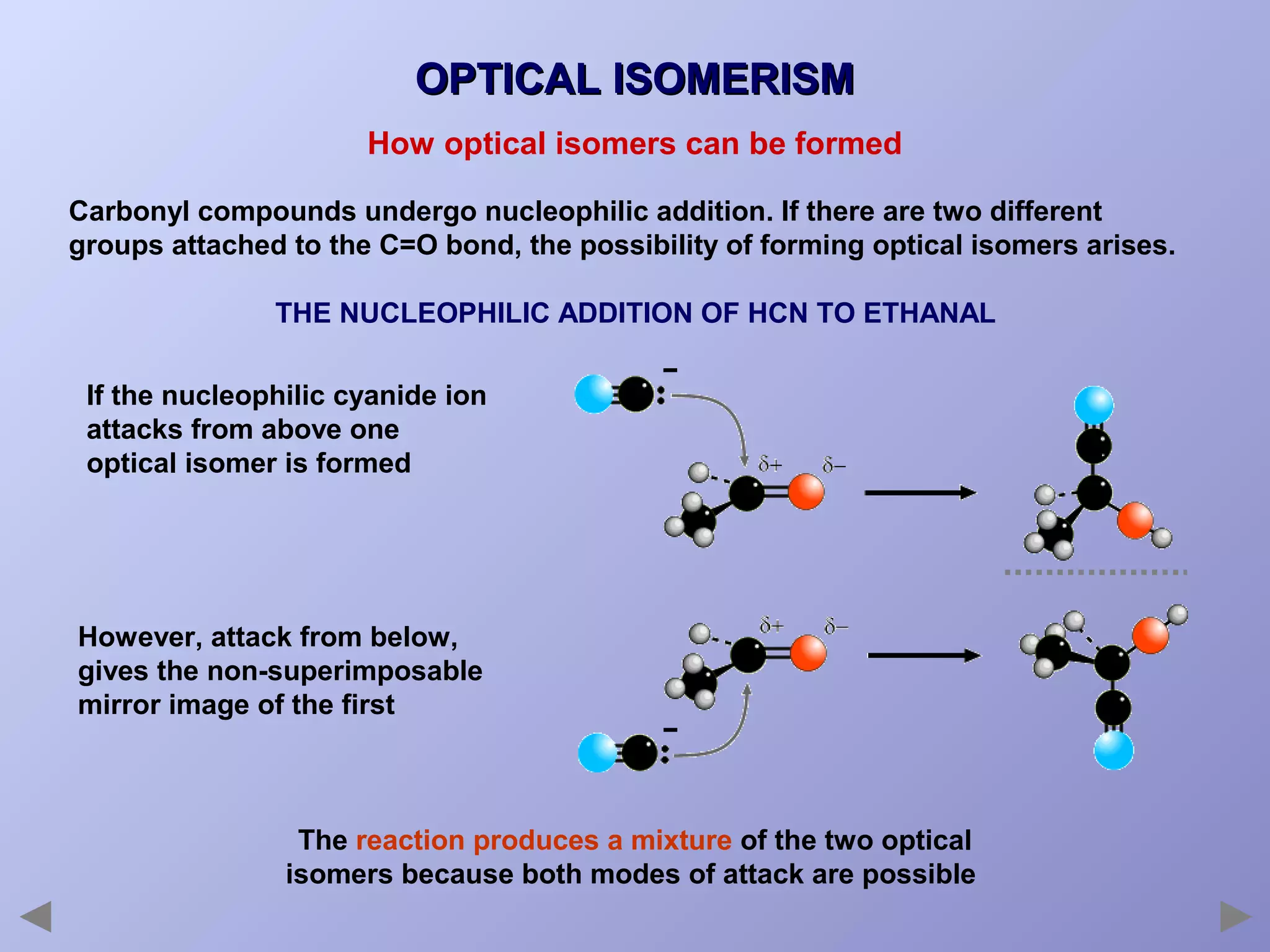
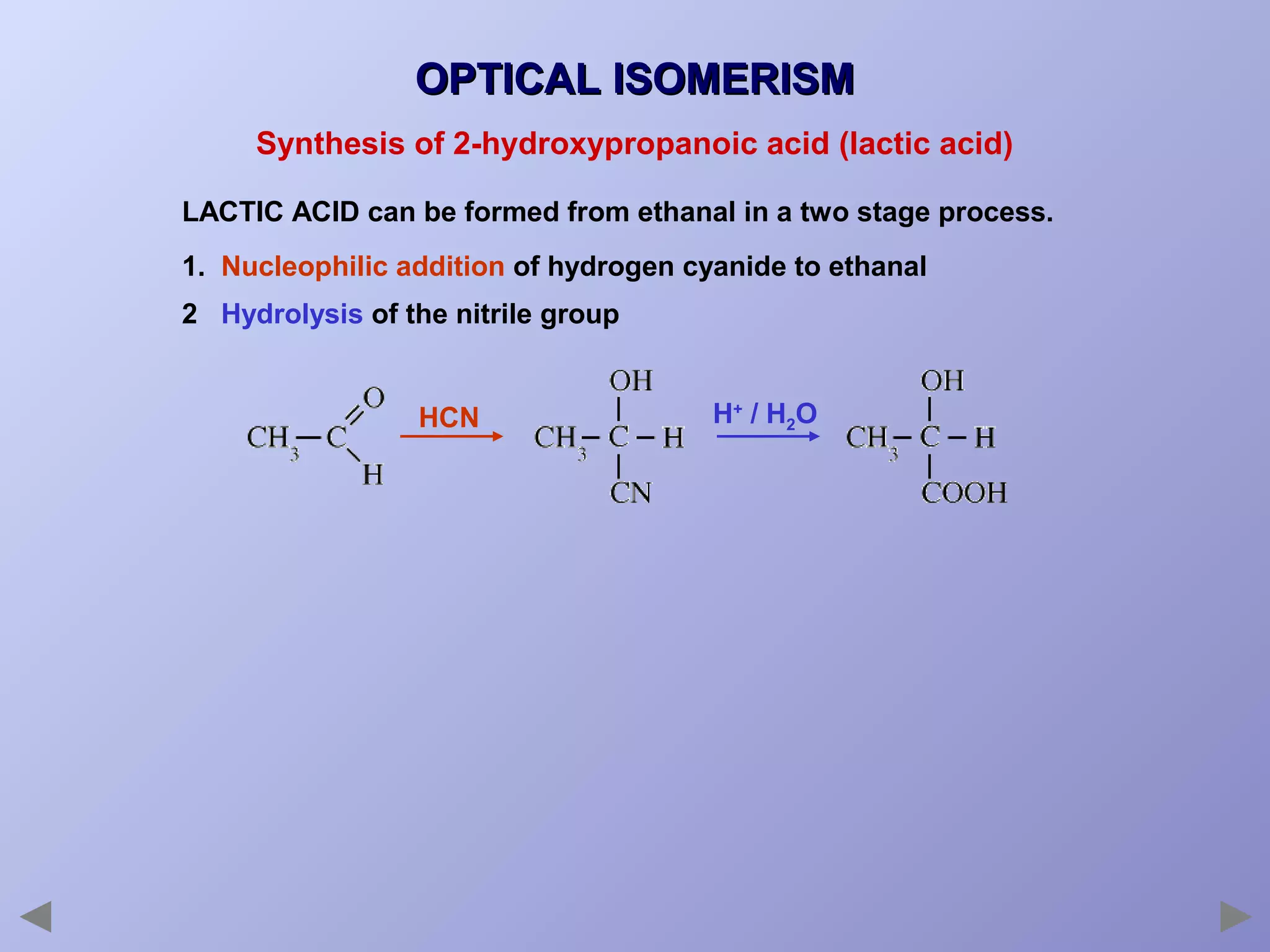
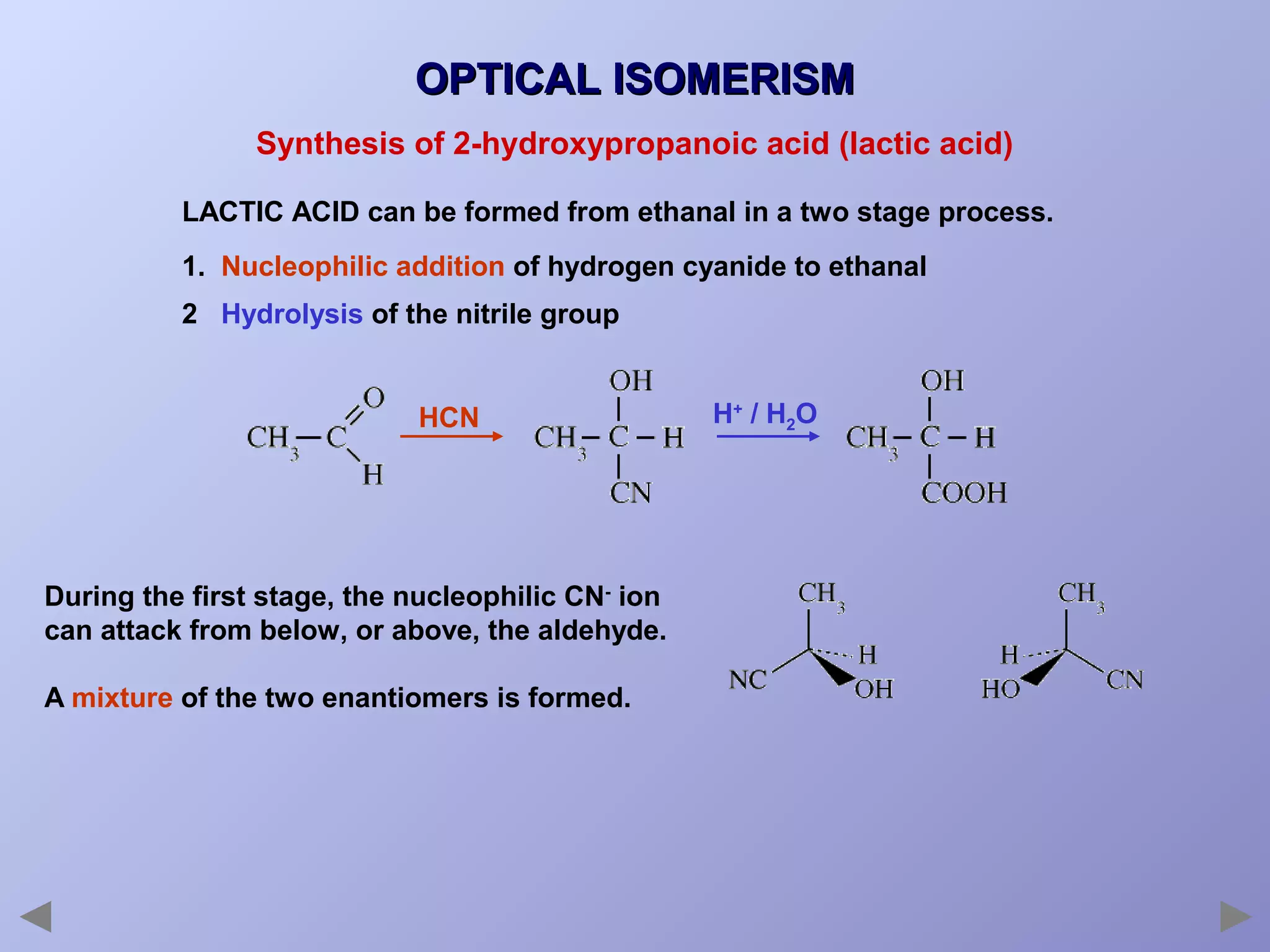
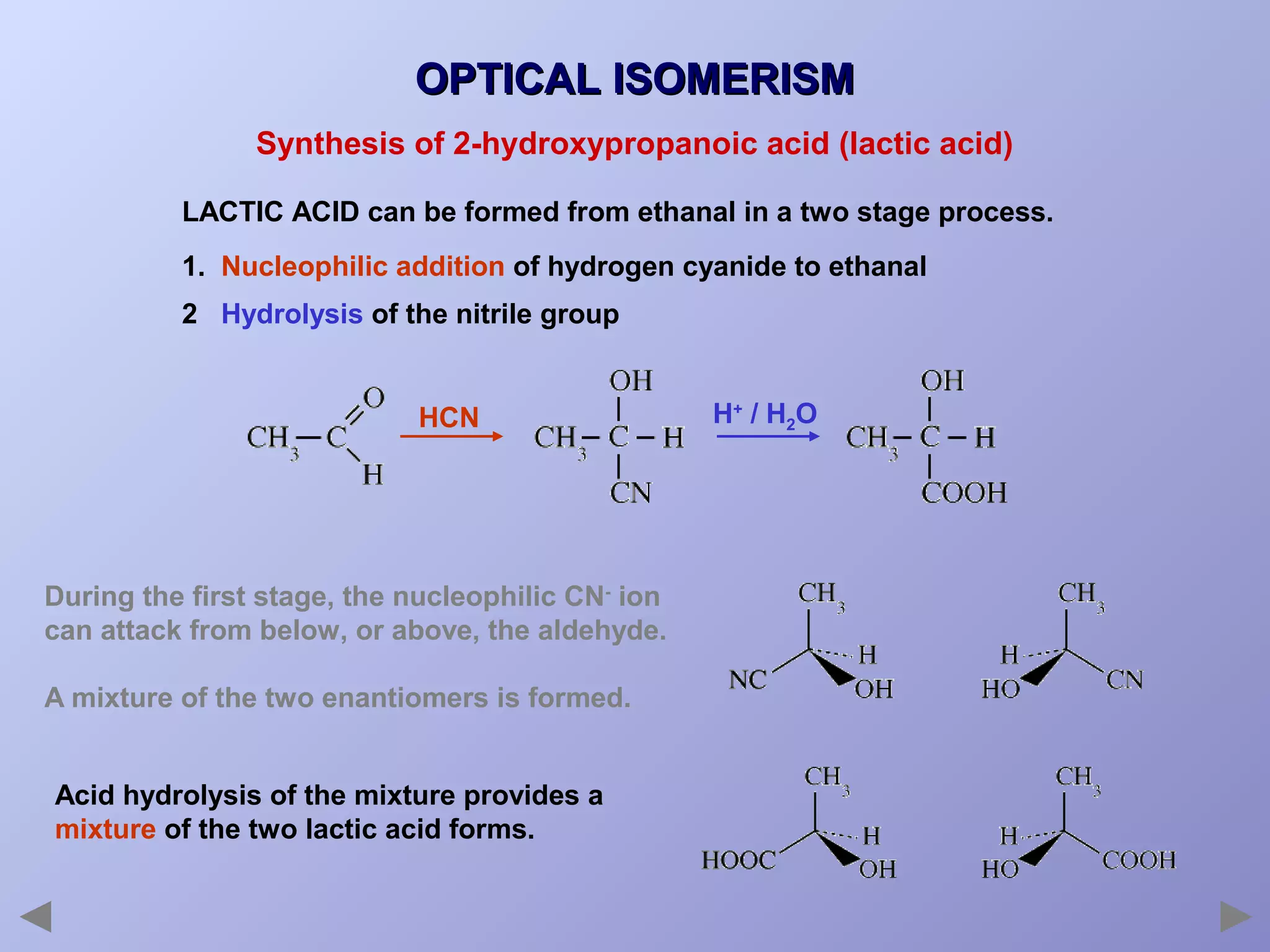
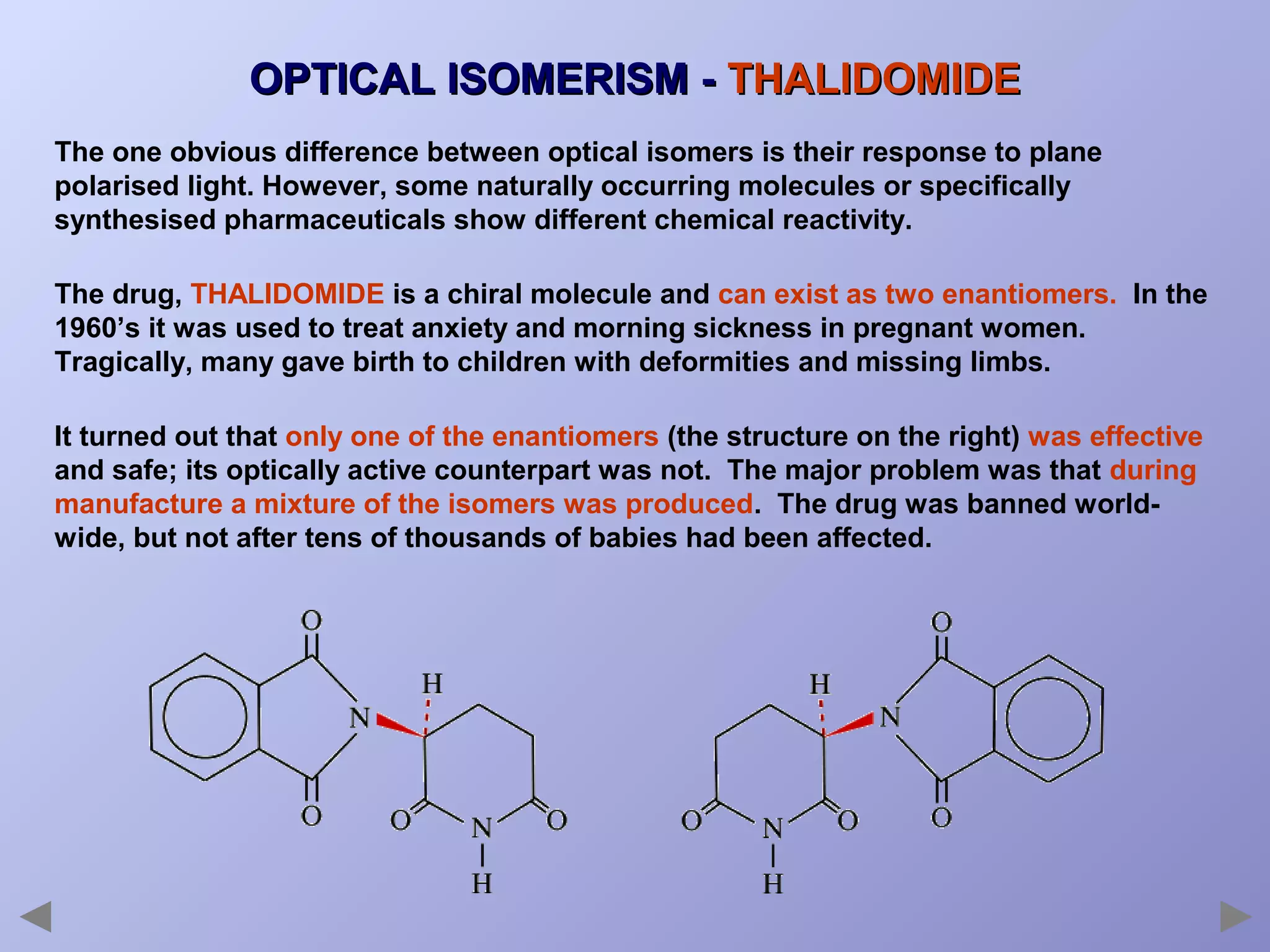
This document provides an overview of isomerism for students. It begins by outlining the prior knowledge needed to understand isomerism and then defines the main types: structural isomerism, stereoisomerism, geometrical isomerism, and optical isomerism. For each type, examples are given to illustrate key concepts like different arrangements of carbon skeletons or functional groups (structural), restricted double bond rotation causing cis/trans forms (geometrical), and chiral centers producing non-superimposable mirror images (optical). Checklists are provided to identify isomerism possibilities in different molecules. The document aims to clearly define and differentiate the various isomerism types through detailed explanations, diagrams, and molecular