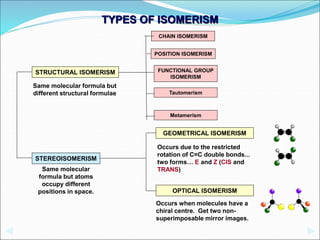
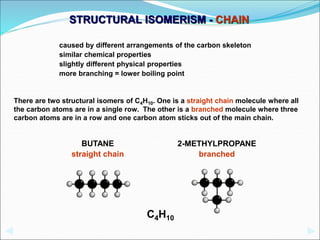
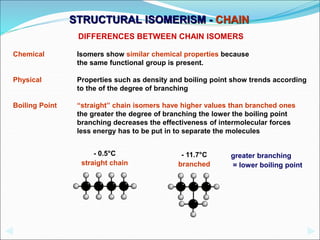
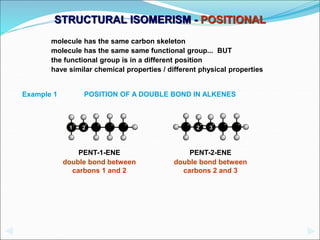
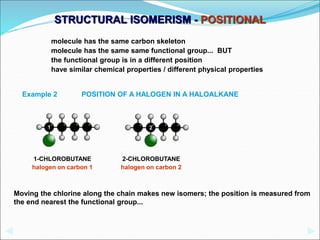
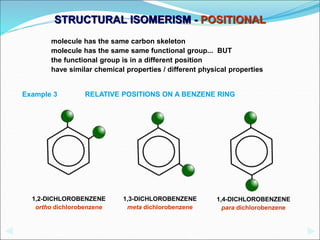
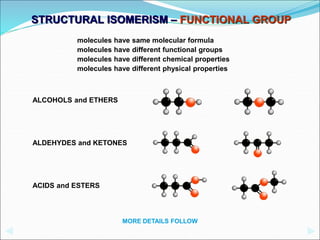
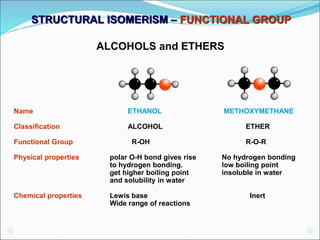
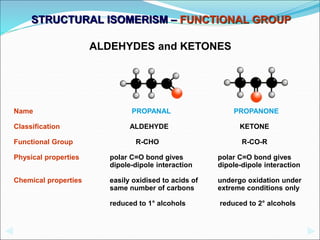
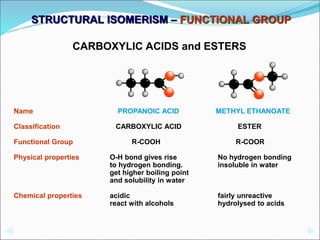
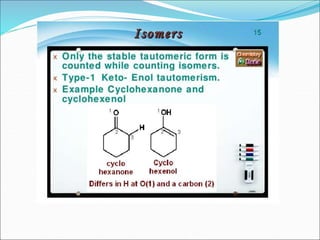
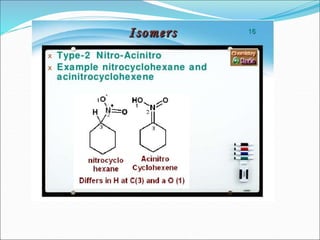
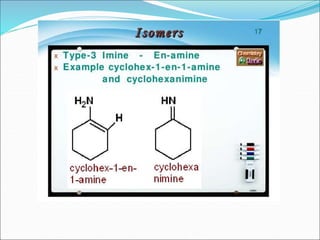
This document discusses different types of isomerism including structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. Structural isomerism occurs when compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Types of structural isomerism include chain isomerism, positional isomerism, and functional group isomerism. Chain isomerism involves compounds having the same molecular formula but different carbon chain structures. Positional isomerism involves compounds having functional groups at different positions. Functional group isomerism involves compounds having different functional groups. Stereoisomerism occurs when compounds have the same connectivity of atoms but different arrangements in space.