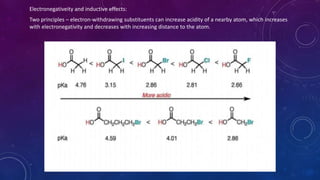
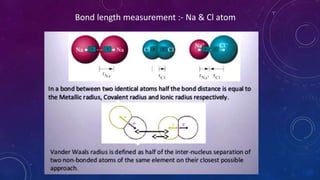
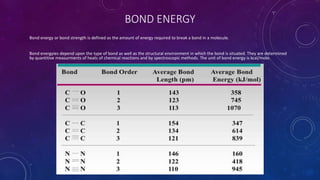
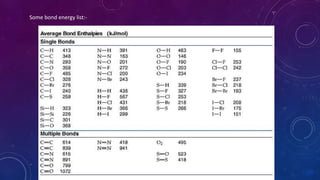
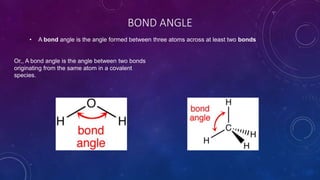
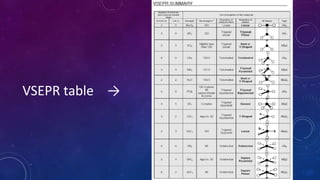
The document is a presentation on topics related to organic pharmacy, including inductive effects, bond lengths, bond energies, and bond angles. It defines the inductive effect and its types, discusses the relationship between electronegativity and acidity, and explains bond characteristics and measurements. The presentation is intended for a classroom setting and includes references to various sources.