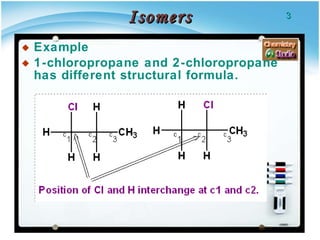
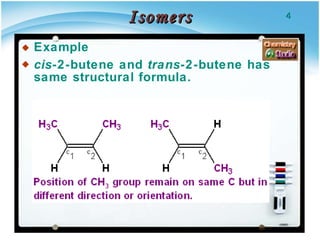
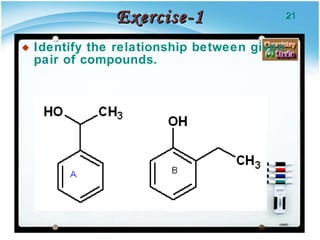
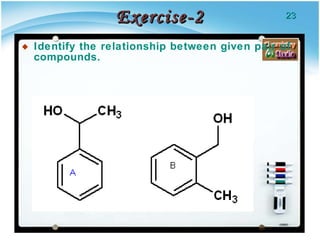
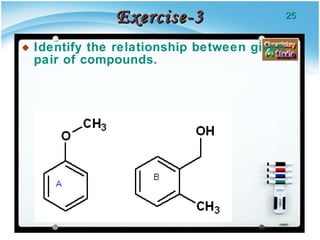
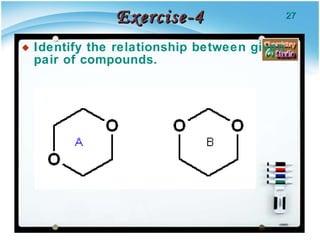
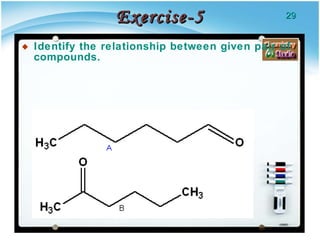
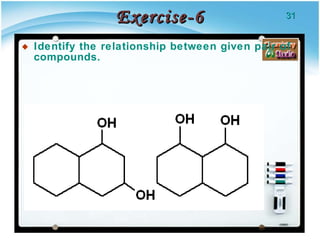
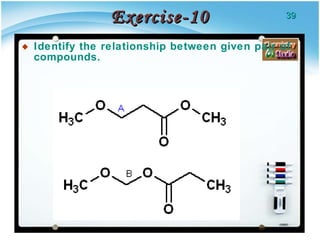
1. Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas, meaning different bond arrangements or connectivity of atoms.
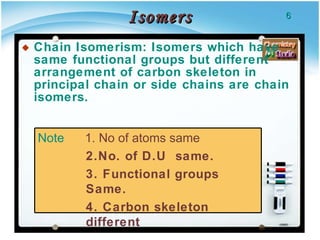
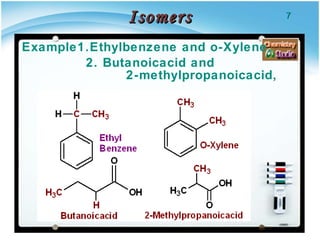
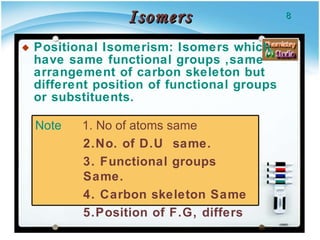
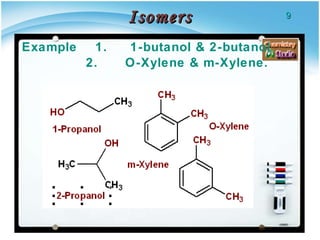
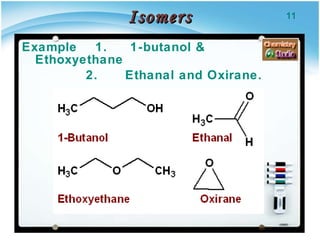
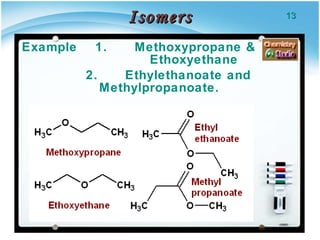
2. There are several types of structural isomers including chain isomers, positional isomers, functional isomers, metamers, and tautomers.
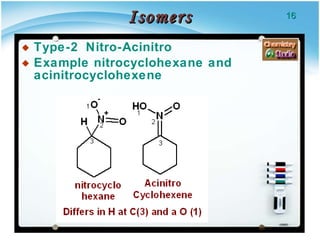
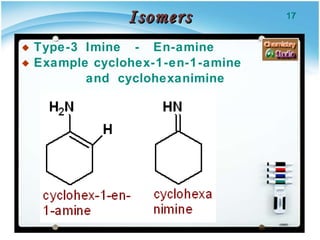
3. Tautomers are a type of functional isomer that can interconvert in solution through the rapid movement of hydrogen atoms or other groups between functional groups.























![Concept Developed by K.Chandana. [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structuralisomerism-100910145014-phpapp01/85/Structural-isomerism-41-320.jpg)
