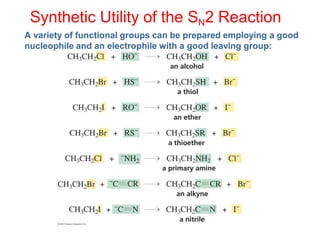
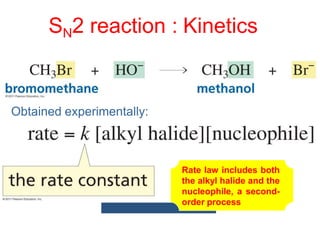
The document summarizes key aspects of SN2 reactions including reaction mechanism, kinetics, stereochemistry, and factors that affect the rate of the reaction. It describes the SN2 reaction as a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution where the nucleophile attacks the substrate simultaneously as the leaving group departs, resulting in an inversion of configuration. Rate depends on both the nucleophile and substrate concentrations. The stability of the transition state is affected by substrate structure, nucleophilicity, leaving group ability, solvent properties, and conjugation effects in allylic and benzylic systems. Cyclic substrates and those without available orbital overlap do not undergo SN2 reactions as easily.





























![SN2 or SN1?
Primary or methyl
Strong nucleophile
Polar aprotic
solvent
Rate = k [halide]
[Nuc]
Inversion
Tertiary
Weak nucleophile
(may also be solvent)
Polar protic solvent,
silver salts
Rate = k [halide]
Racemization
No rearrangements Rearranged products
=>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptsn2reaction-180416183044/85/Sn2-reaction-32-320.jpg)











