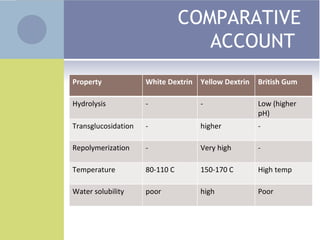
1. Isomerization is the process of converting a carbohydrate like glucose into another with the same molecular formula but different structure. Glucose isomerase catalyzes the conversion of glucose into fructose, which is used to produce high fructose corn syrup.
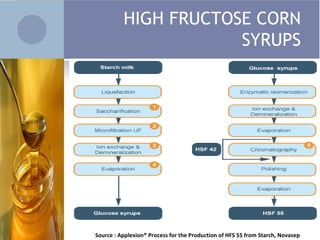
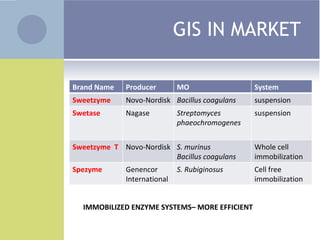
2. High fructose corn syrup is composed of 42% or 55% fructose and is sweeter and cheaper than sucrose, making it widely used as a sweetener in foods and beverages. It is produced through the isomerization of glucose into fructose using immobilized glucose isomerase enzymes.
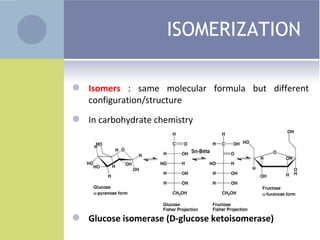
3. Dextrinization is the breakdown of starch into smaller carbohydrate molecules called dextrins through enzymatic


![DEXTRINIZATION Browning Reaction in Food material : Reasons : Caramelization [ at High Temp, sugar/starch breakdown] Dextrinization [Starch in Dry conditions] Enzymatic Browning [at low/moderate temp] Sugar-Amine Browning [usually at cooking temp]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isomerizationanddextrinizations-12994366609138-phpapp01/85/Isomerization-And-Dextrinization-S-6-320.jpg)