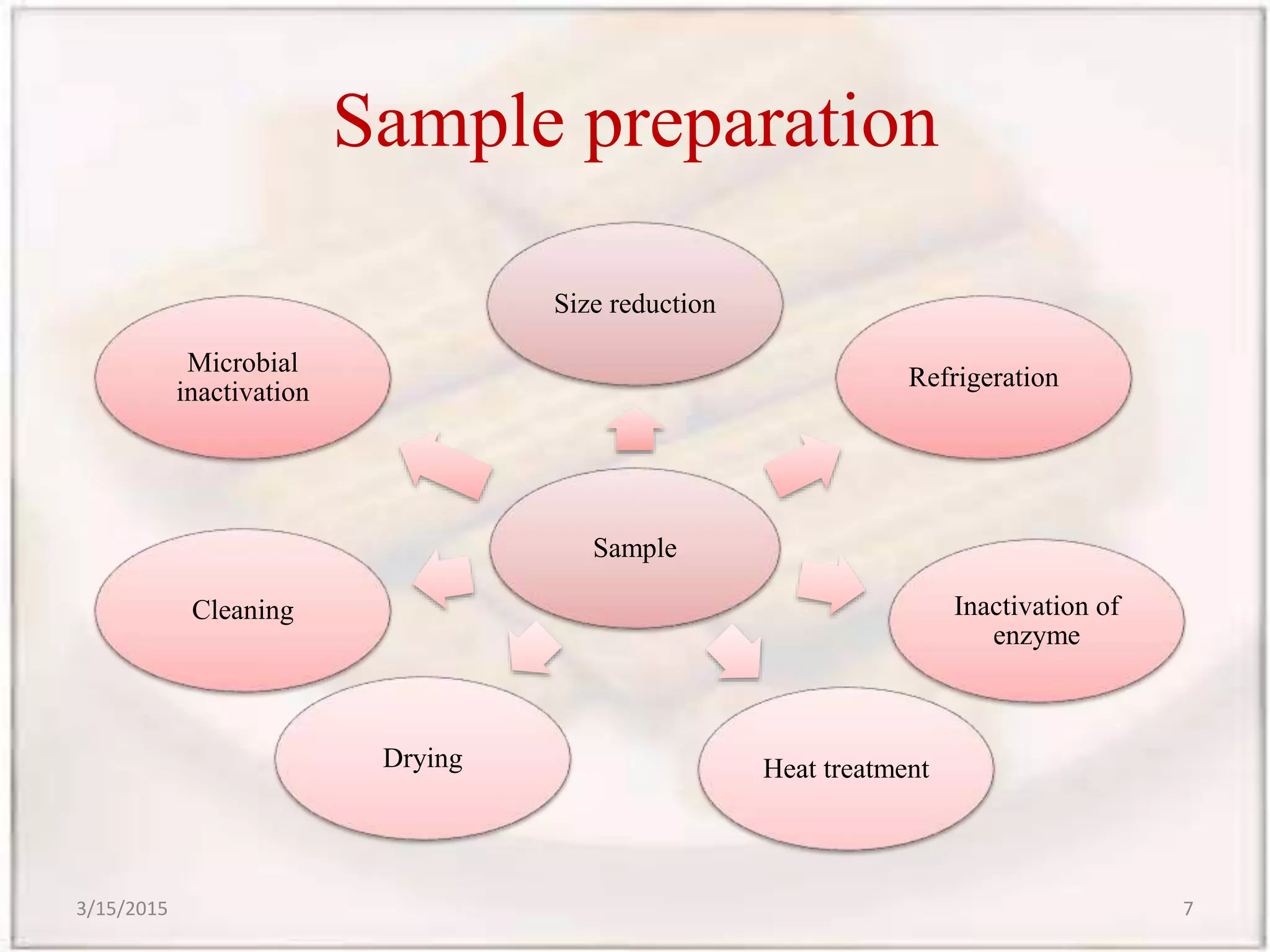
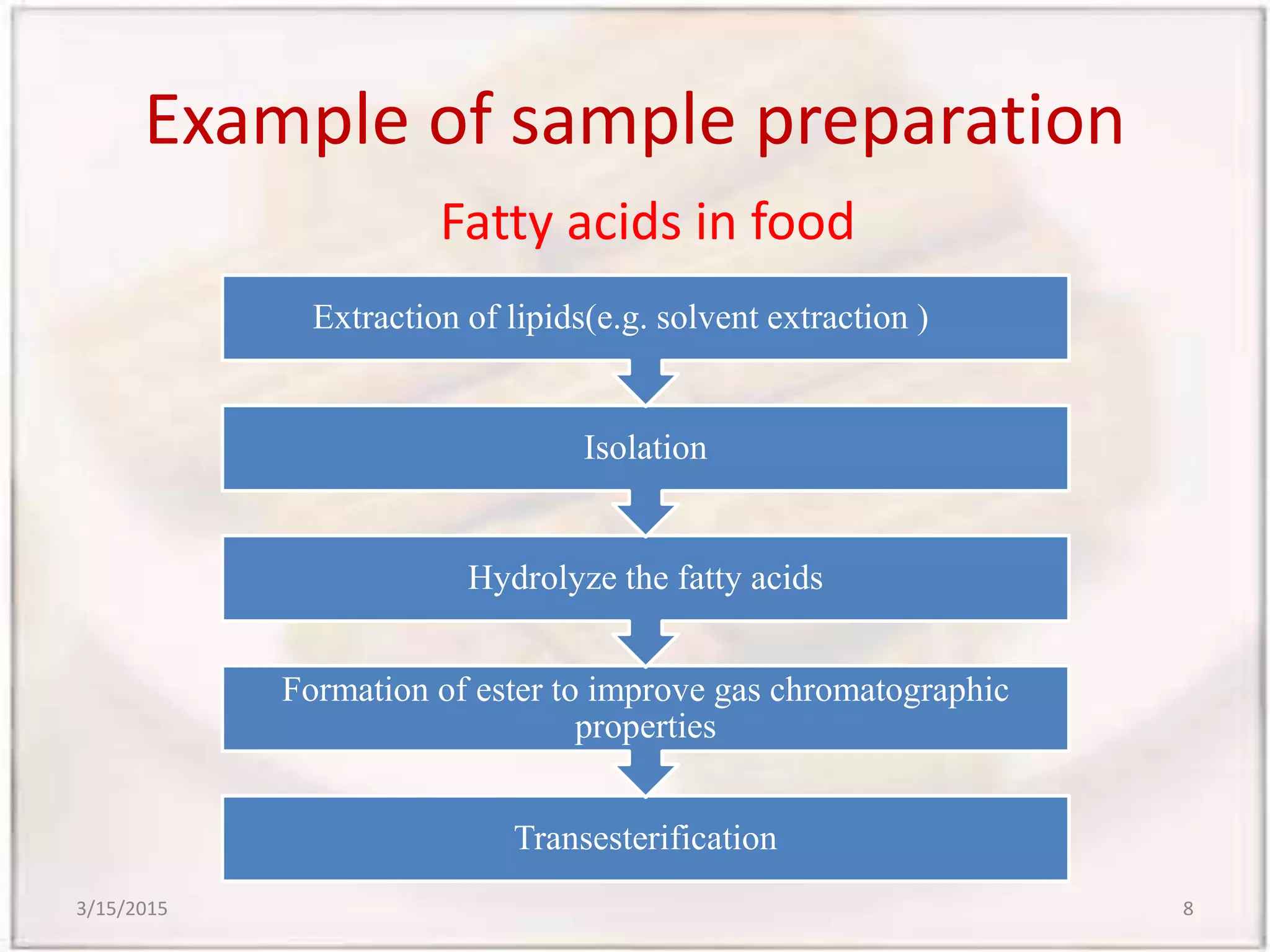
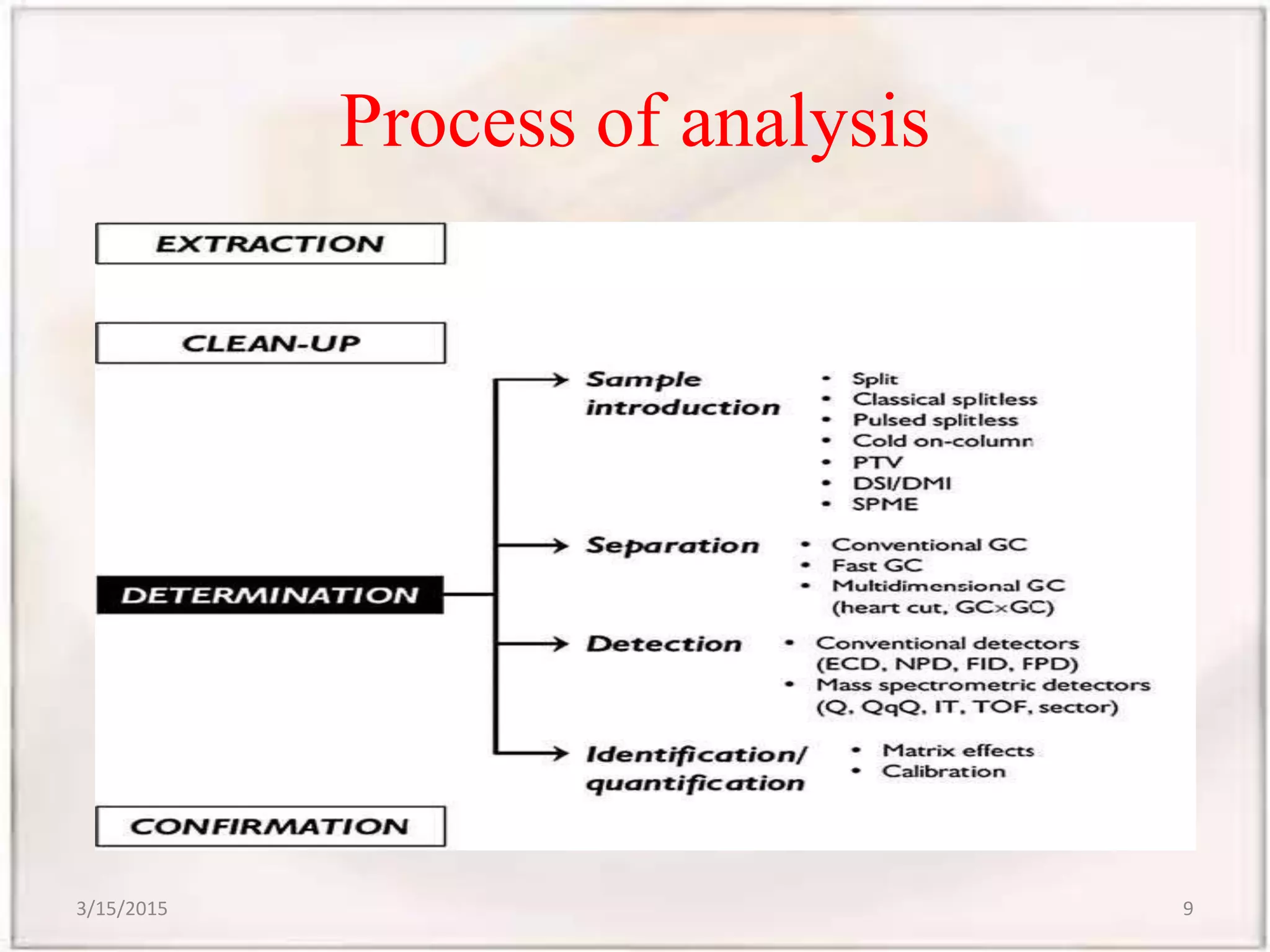
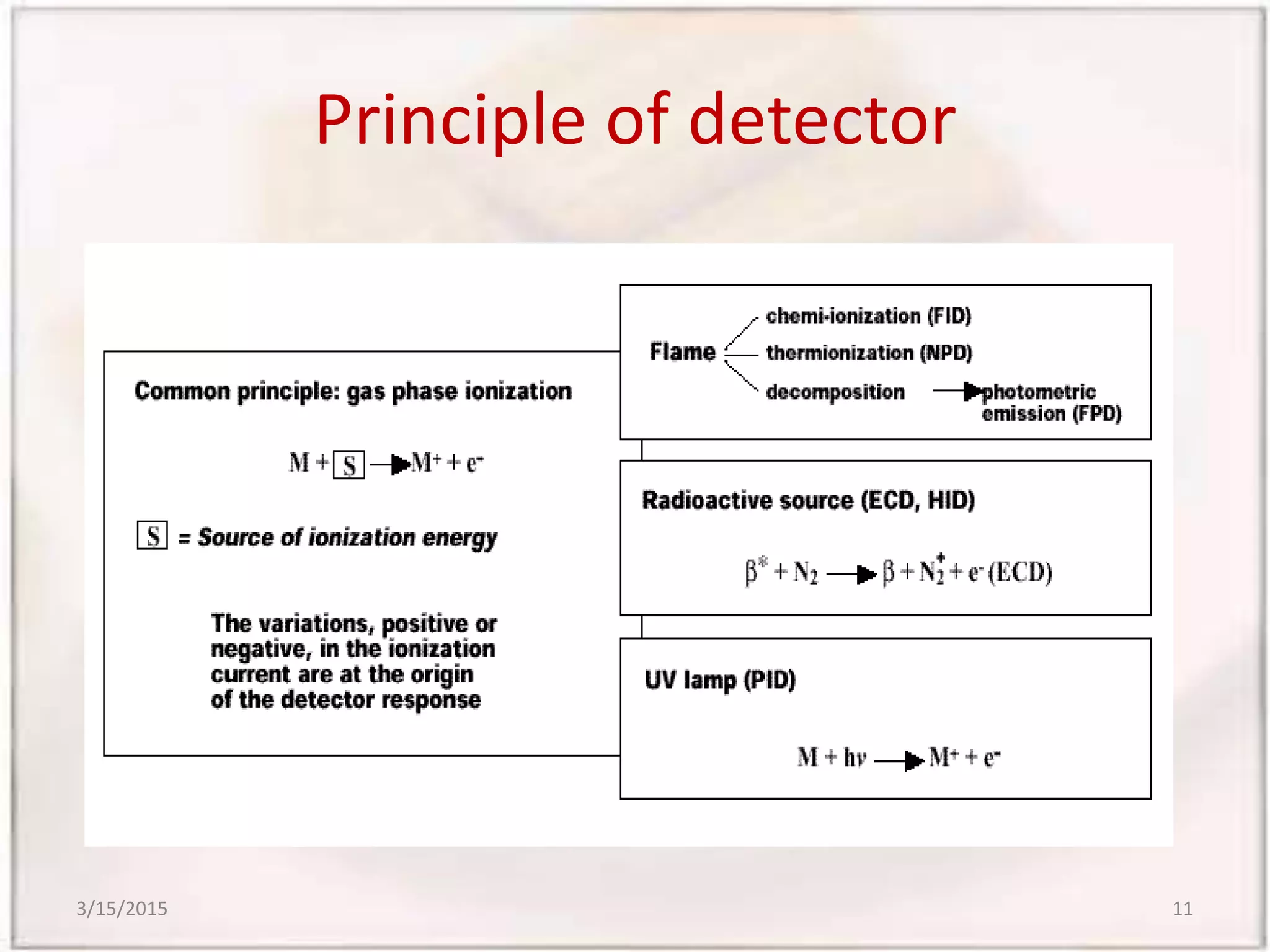
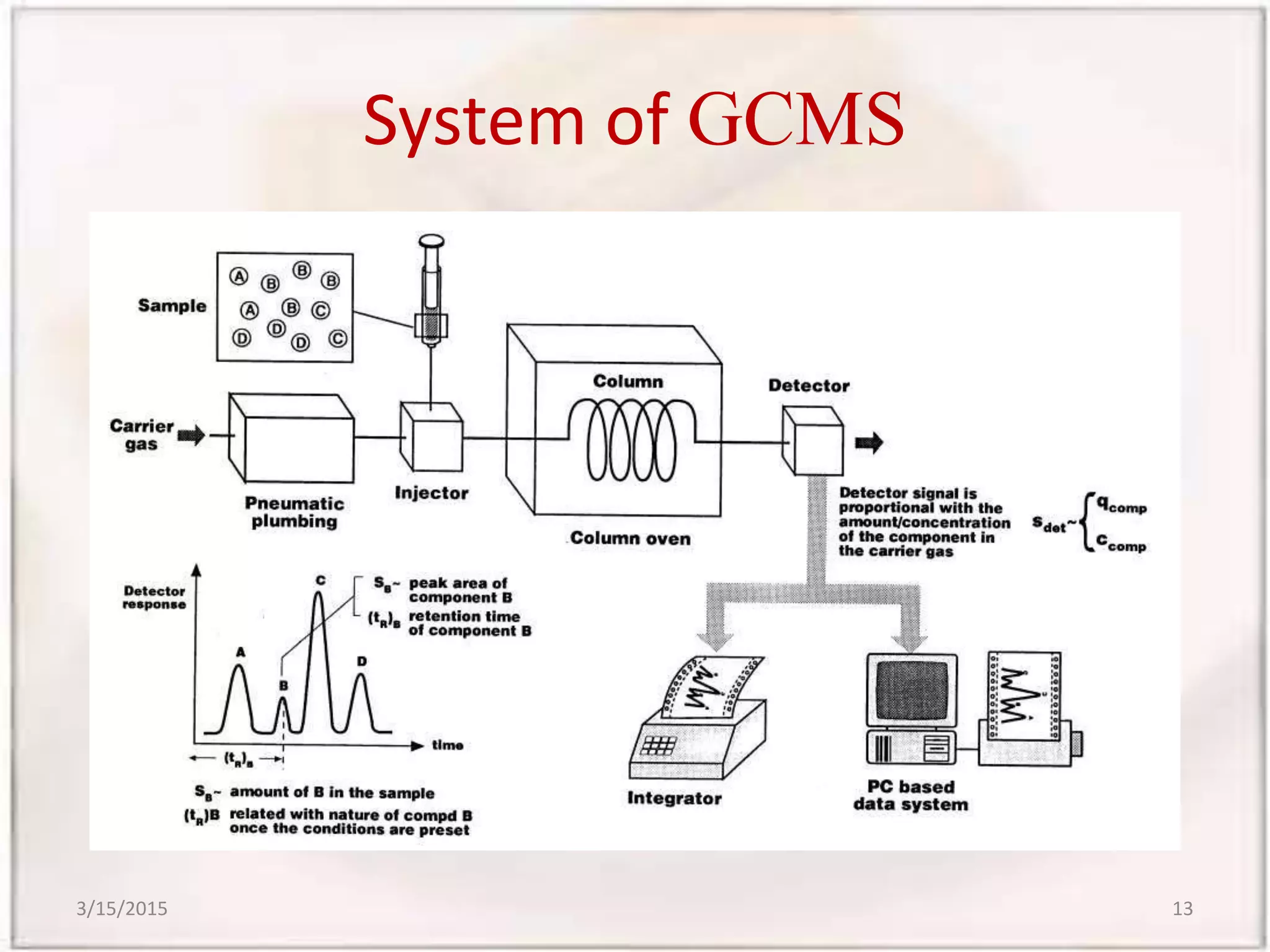
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GCMS) is an analytical technique that combines gas chromatography and mass spectrometry to identify different substances within a test sample. GCMS can be used for applications like drug detection, environmental analysis, and identifying unknown samples. It involves separating components of a sample via gas chromatography and then using mass spectrometry to identify the components based on their mass-to-charge ratios. GCMS provides advantages over traditional methods like simultaneous quantification and confirmation of targets as well as detection of non-target sample components. It has wide applications in food analysis including identification of fatty acids, sterols, flavors, and residues.