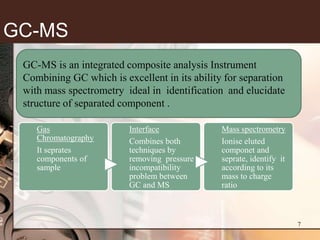
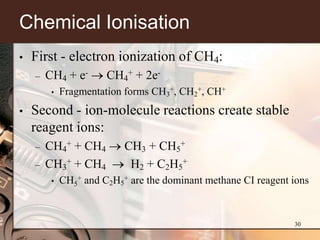
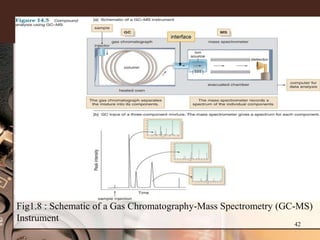
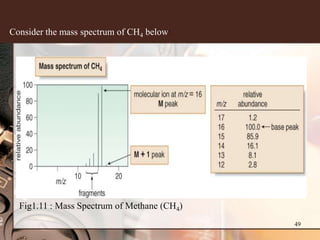
1. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) is a hyphenated analytical technique that combines gas chromatography and mass spectrometry to identify different substances within a test sample.
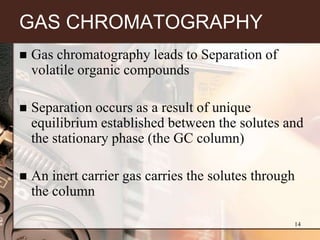
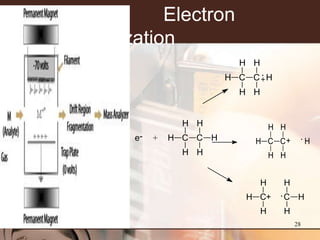
2. GC separates the chemical components in a sample, while MS identifies the compounds by measuring their mass-to-charge ratios. This allows both qualitative and quantitative analysis of a sample in a single run.
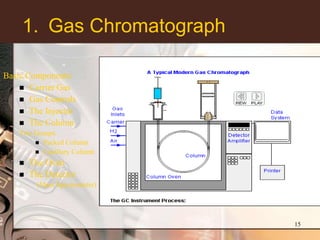
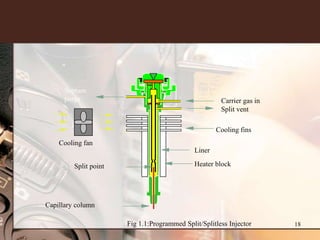
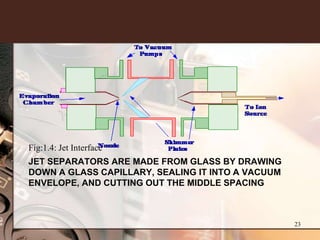
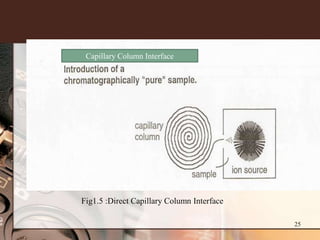
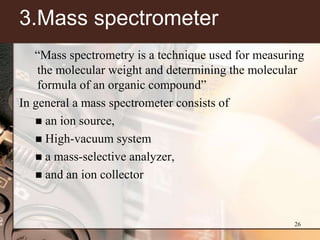
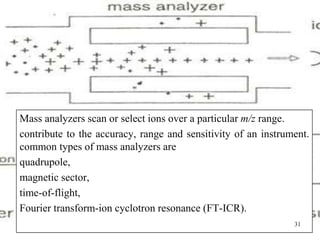
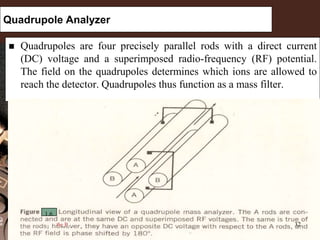
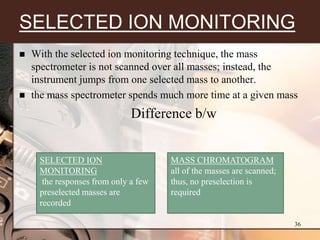
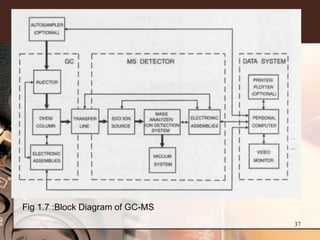
3. Key components of a GC-MS system include the gas chromatograph, interface, mass spectrometer, and data system. The gas chromatograph uses a carrier gas to separate compounds which are then ionized and detected by the mass spectrometer before being analyzed by the data system.