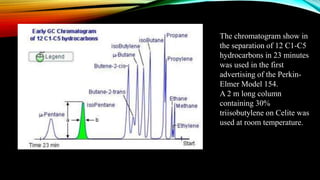
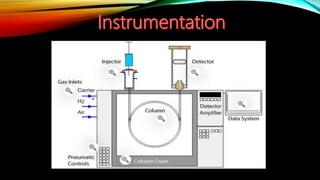
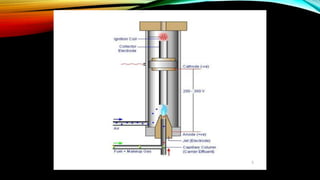
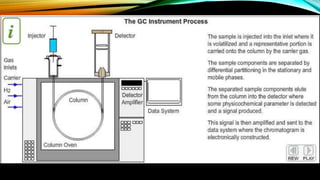
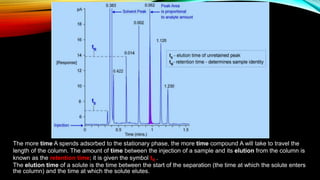
Gas chromatography is an analytical technique used to separate mixtures by vaporizing the components and passing them through a column with a mobile gas phase and a stationary liquid phase. It was pioneered in the 1940s and the first gas chromatograph was developed in 1951. A typical gas chromatography system consists of a gas inlet, injector, column inside an oven, detector, and data system. The sample is injected and separated in the column based on interactions between the phases, then detected and analyzed to produce a chromatogram showing the composition of the original mixture.