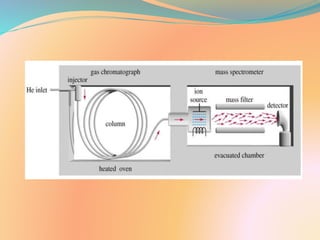
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) is an analytical technique that combines gas chromatography and mass spectrometry to identify different substances within a test sample. It works by separating chemical mixtures using gas chromatography and then analyzing the components at a molecular level using mass spectrometry. The GC-MS instrument is composed of a gas chromatograph to separate molecules and a mass spectrometer to capture, ionize, accelerate, deflect, and detect the ionized molecules to identify compounds by their mass. It has various applications including environmental monitoring, pharmaceutical analysis, drug metabolism studies, food analysis, and medical diagnosis.