The document discusses biscuits and cookies, including their definitions, types, ingredients, and manufacturing processes. Some key points:
- Biscuits are cereal-based products with less than 5% moisture that have a crisp crust and tender layers.
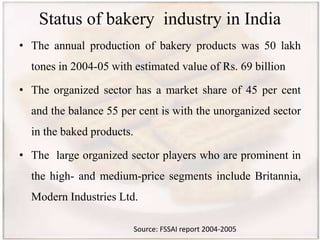
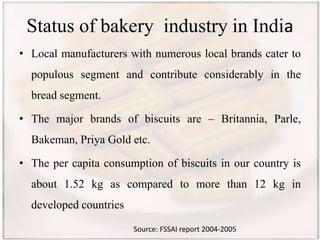
- India's annual bakery production in 2004-2005 was 50 lakh tones worth Rs. 69 billion, with organized players having 45% market share. Major biscuit brands include Britannia, Parle, and Bakeman.
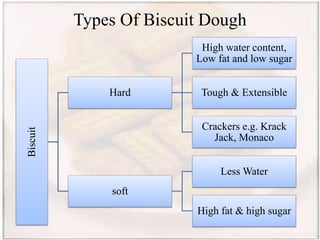
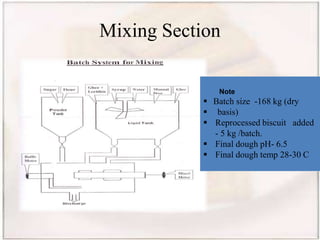
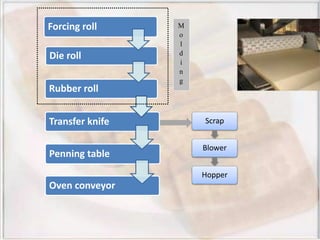
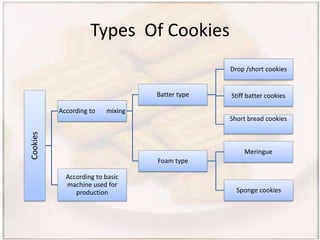
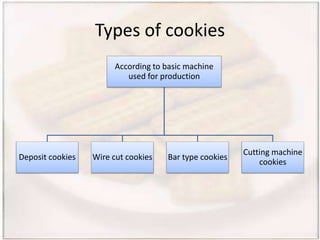
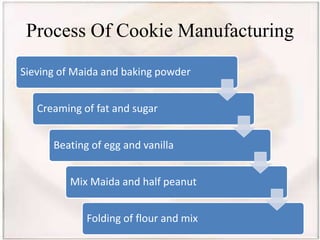
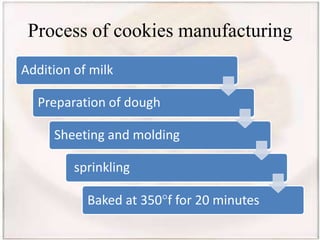
- Biscuits can be classified by dough (hard, semi-hard, soft) and shaping method (embossing, rotary cutting). The manufacturing process involves ingredient preparation, mixing, molding, baking, cooling