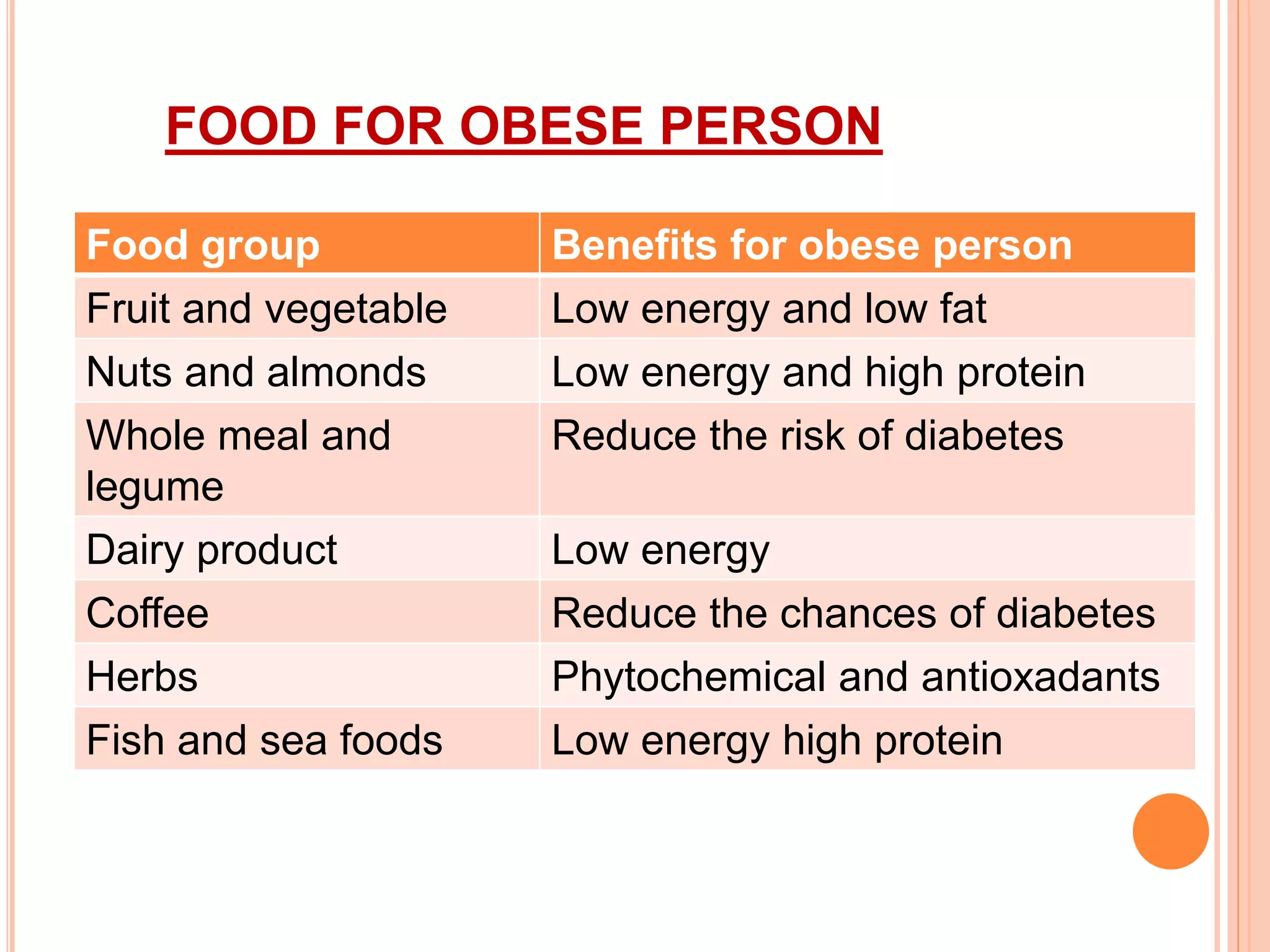
This document discusses various types of specialized diets for different medical conditions. It defines obesity and provides dietary recommendations for obese individuals, including low-calorie meal replacement products and high-protein diets. It also discusses dietary guidelines for cancer, low-fat, low-cholesterol, gluten-free, non-dairy, sugar-free diets. Foods and food groups are recommended for each type of specialized diet. References are provided at the end.