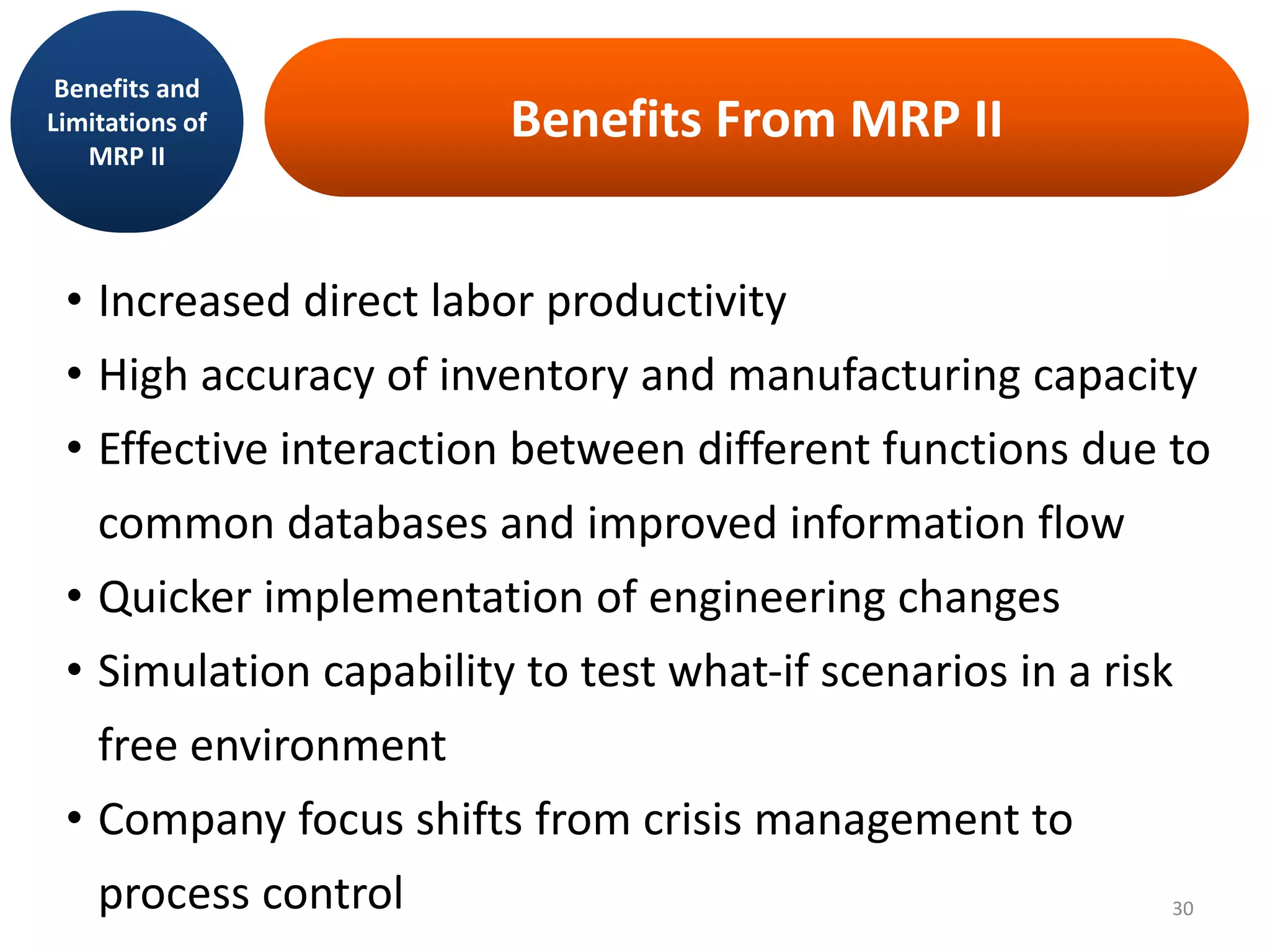
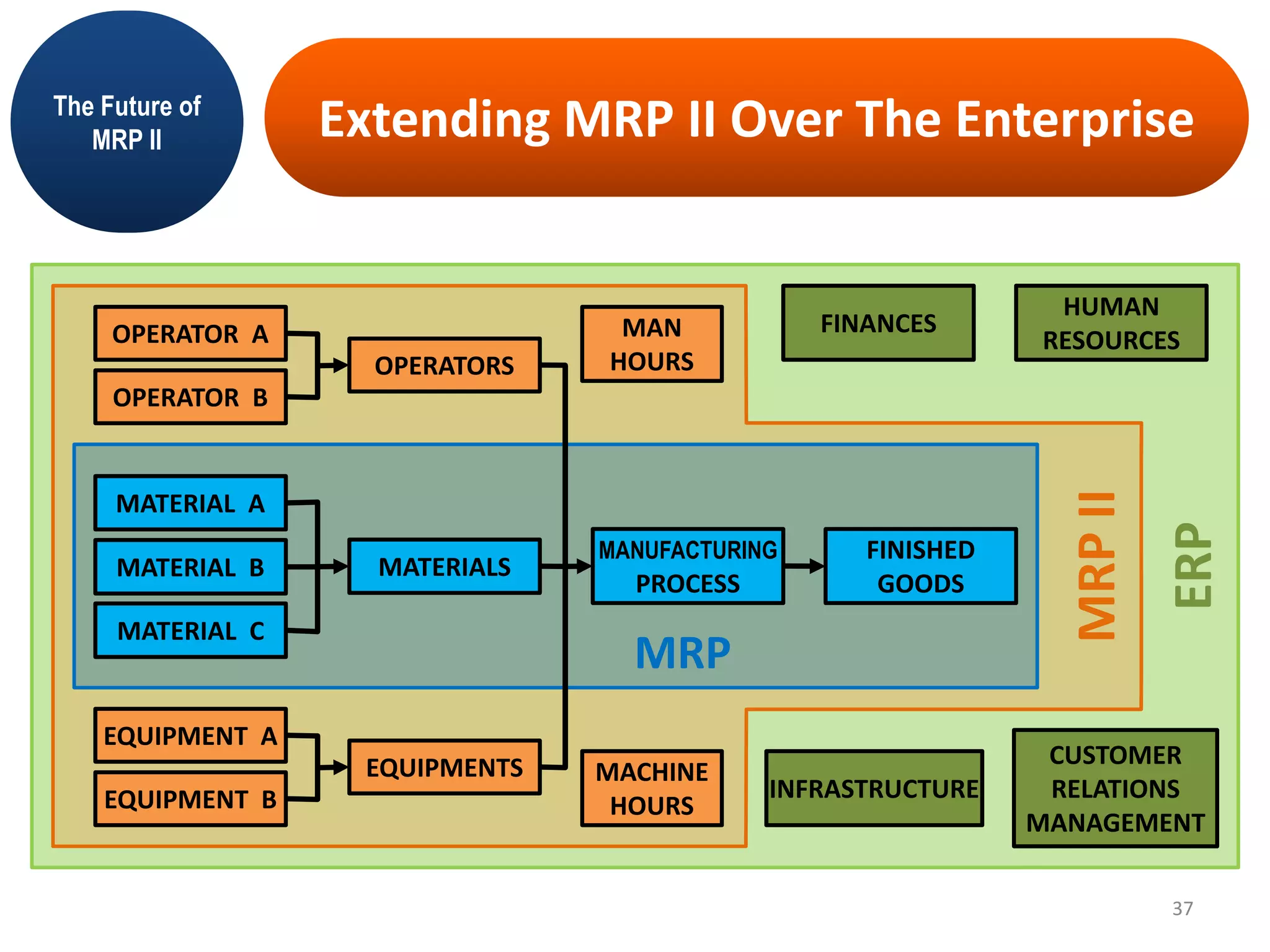
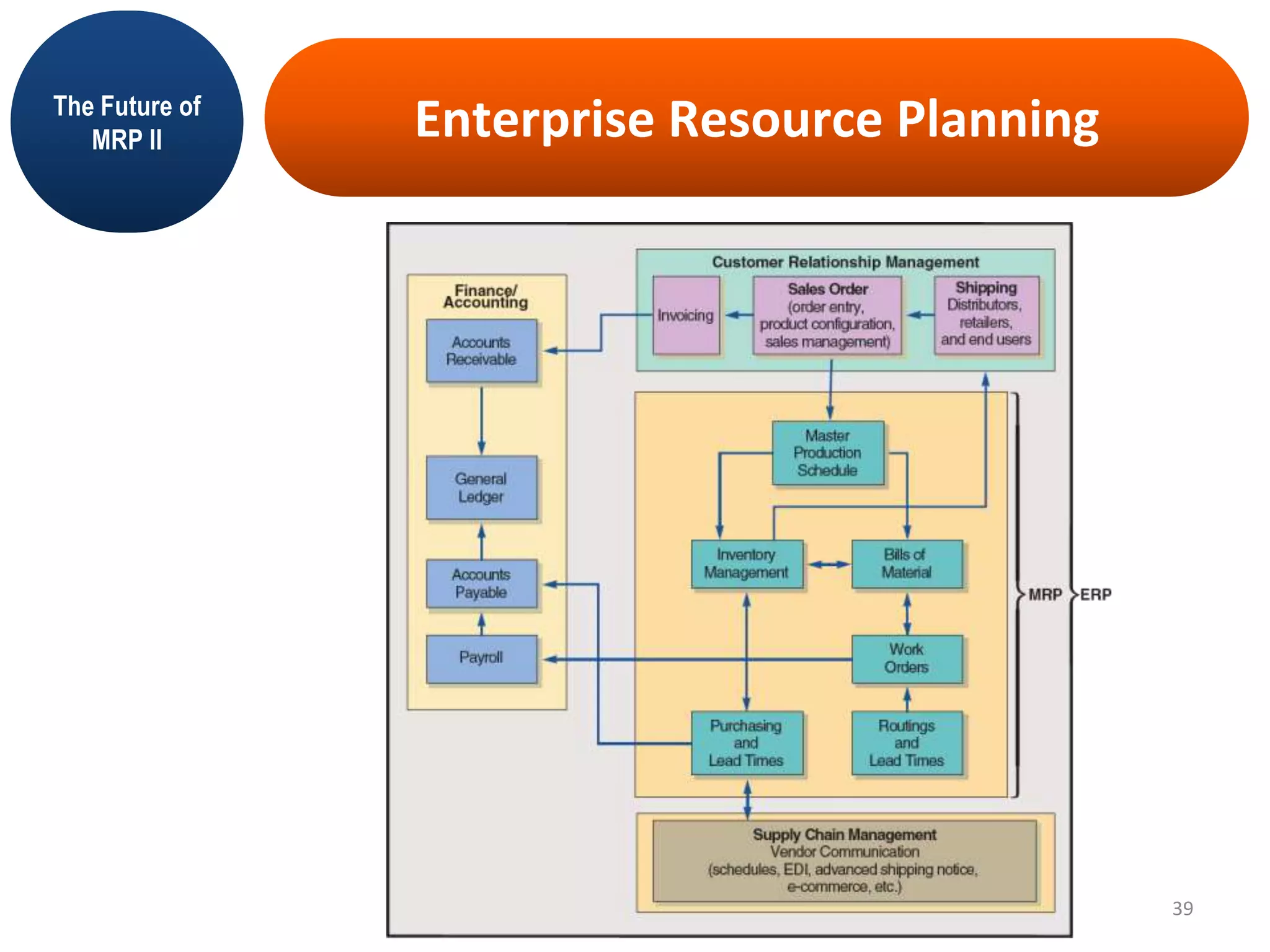
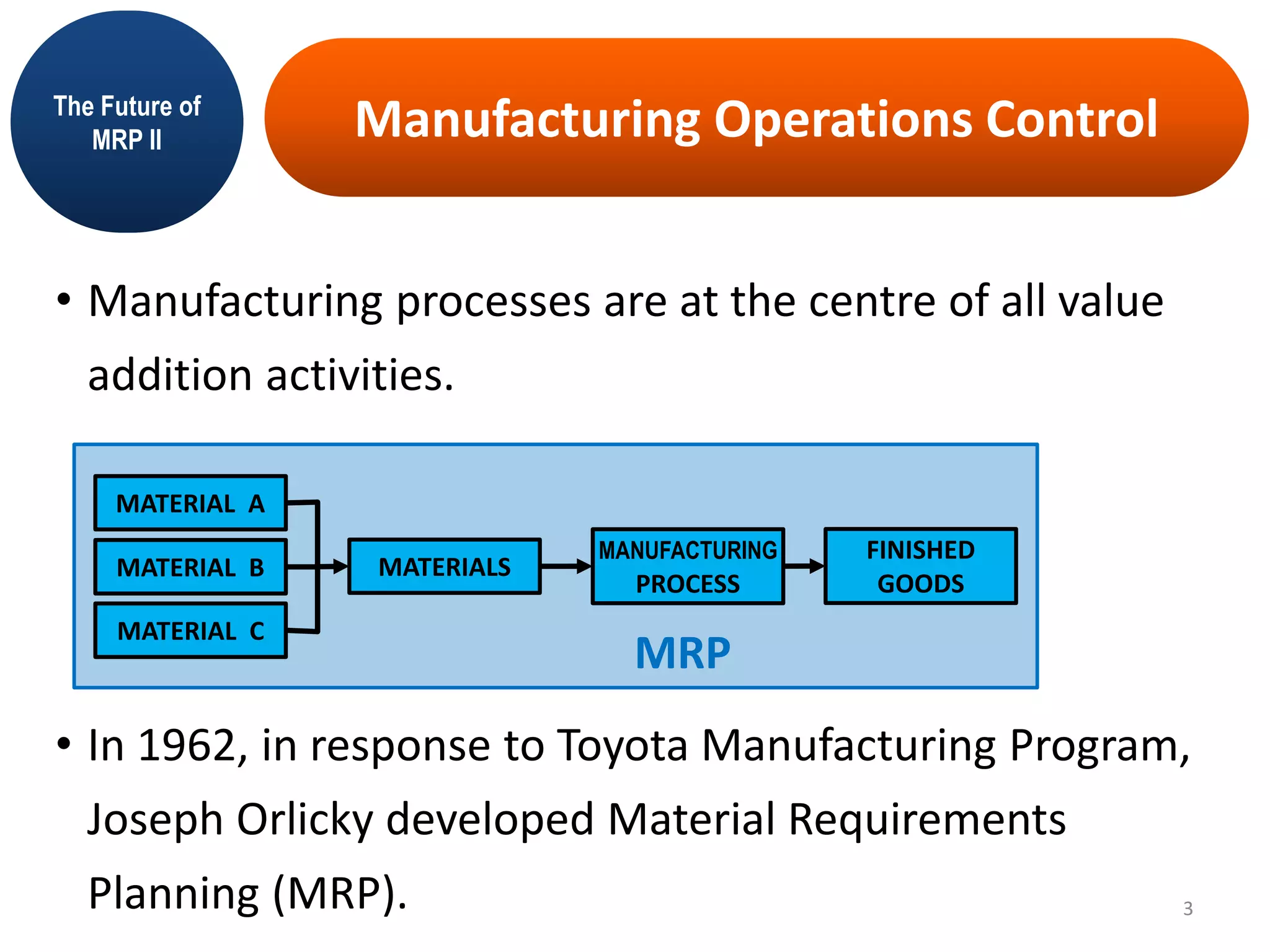
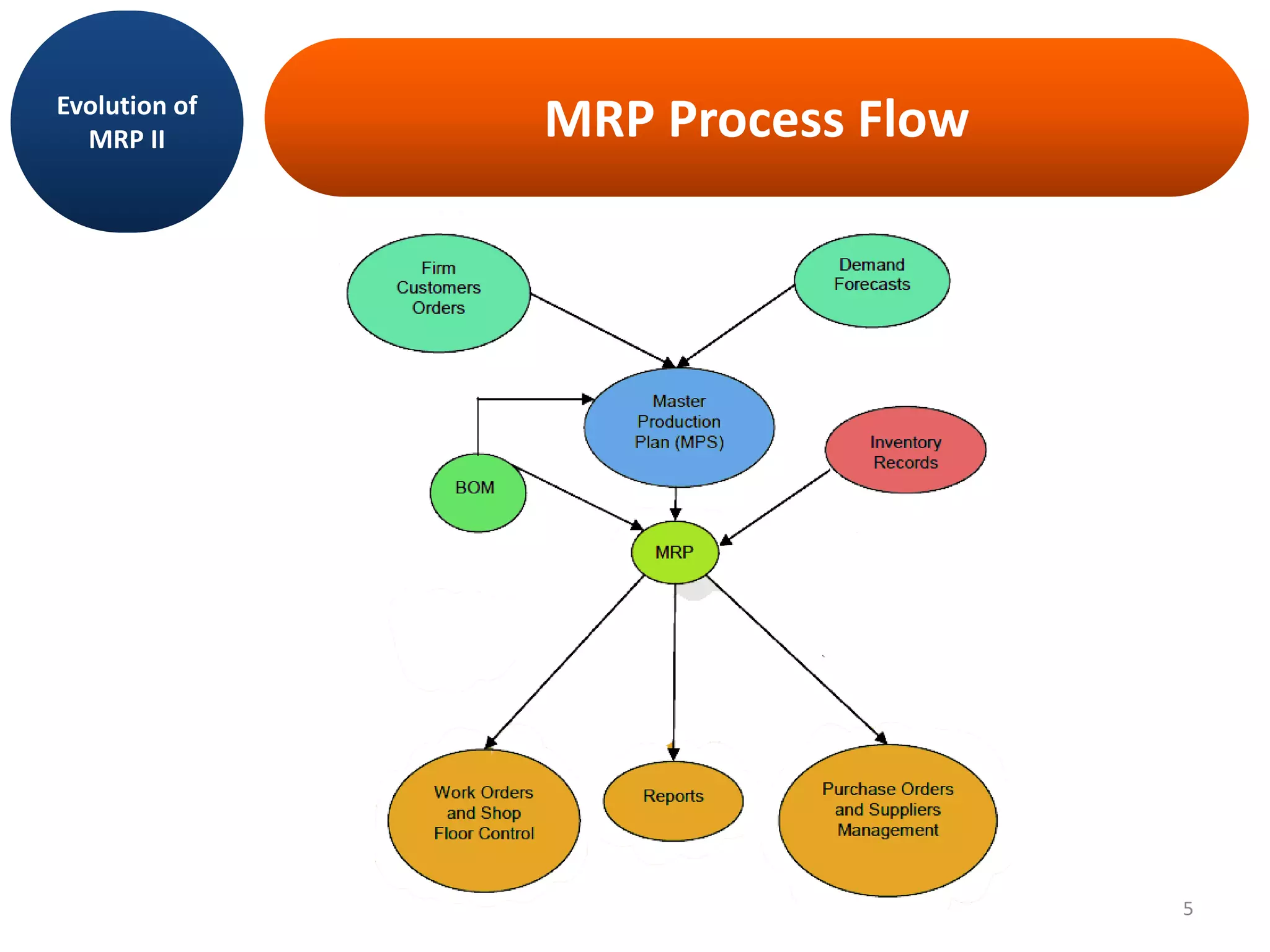
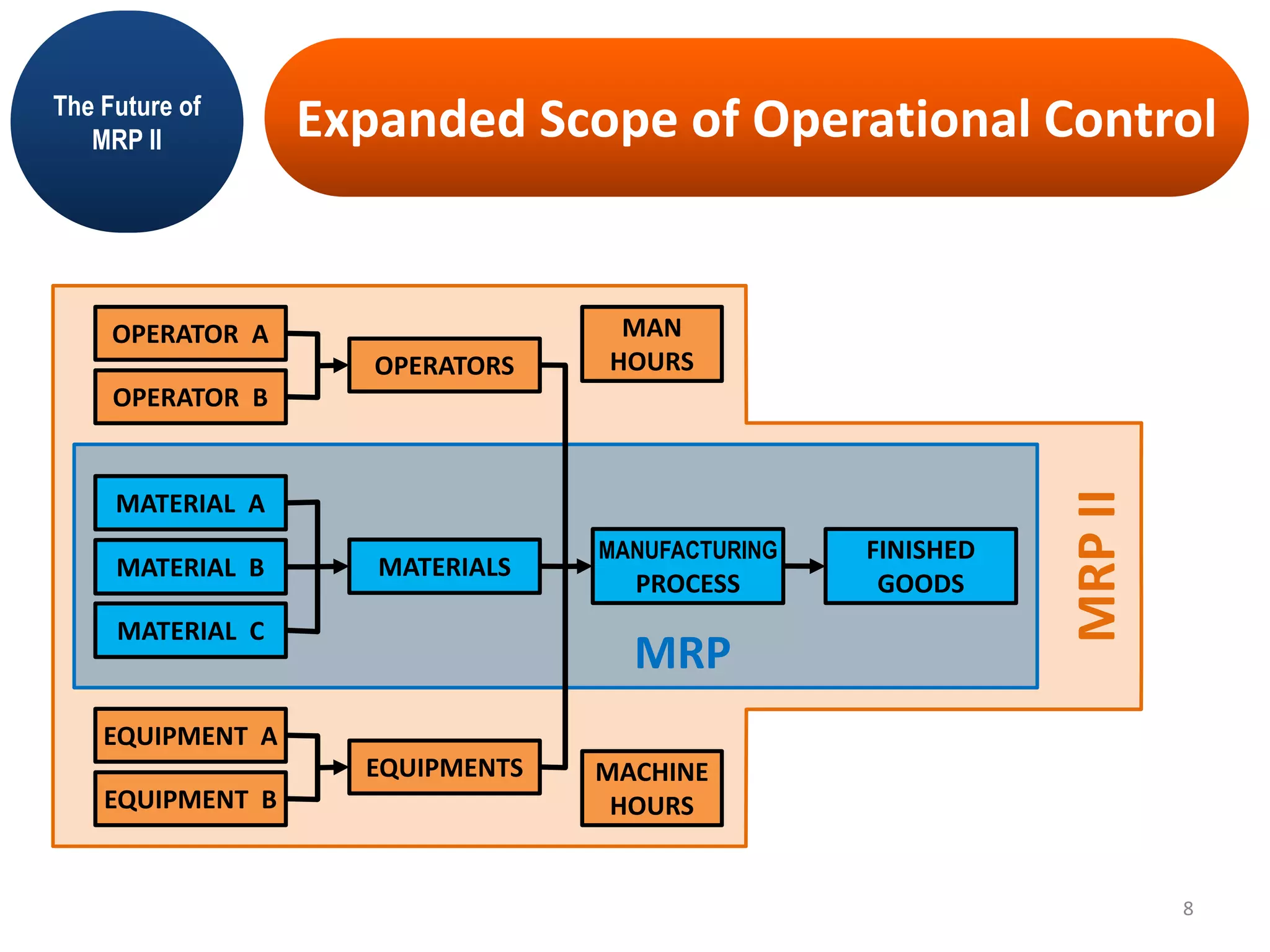
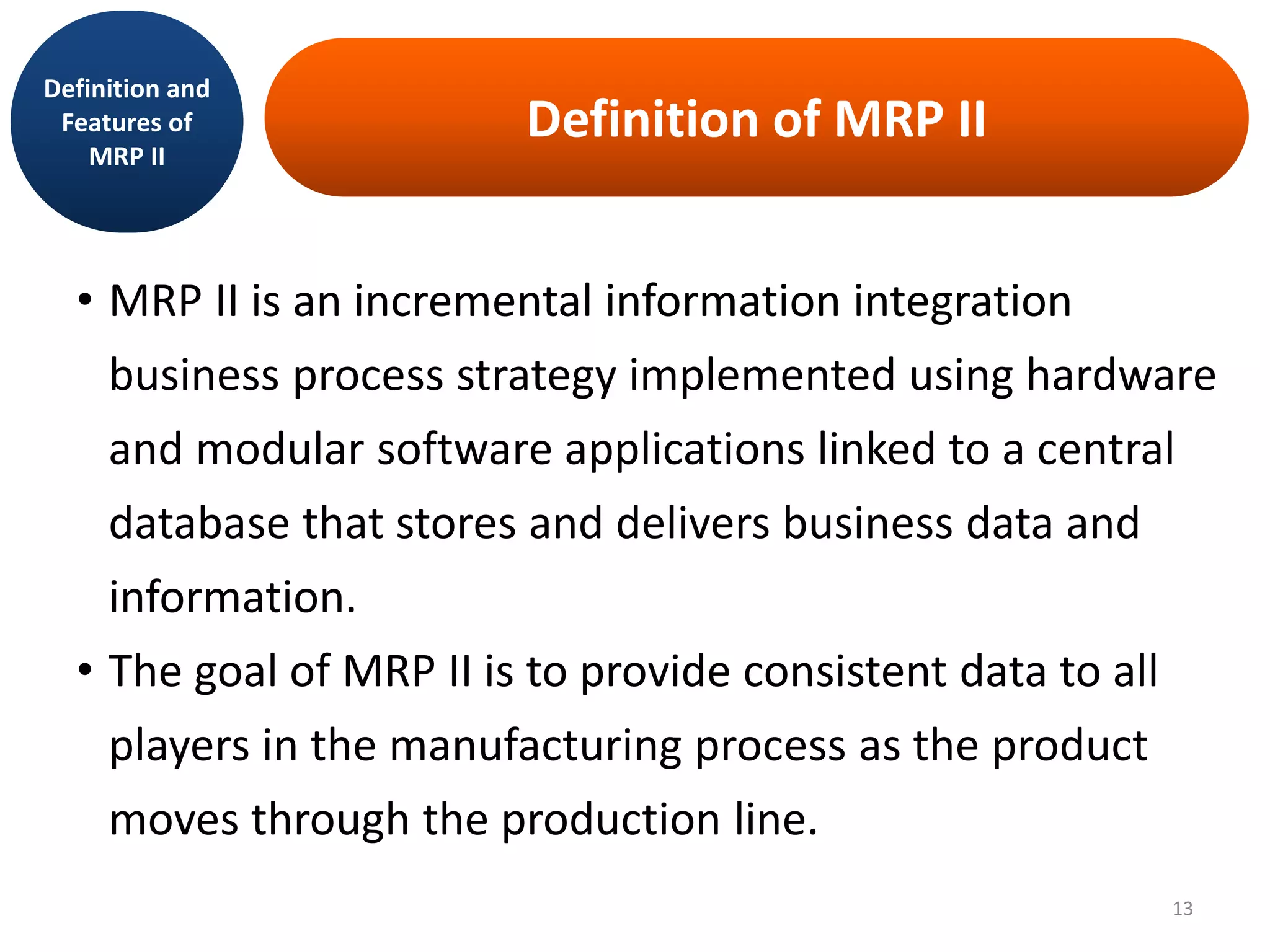
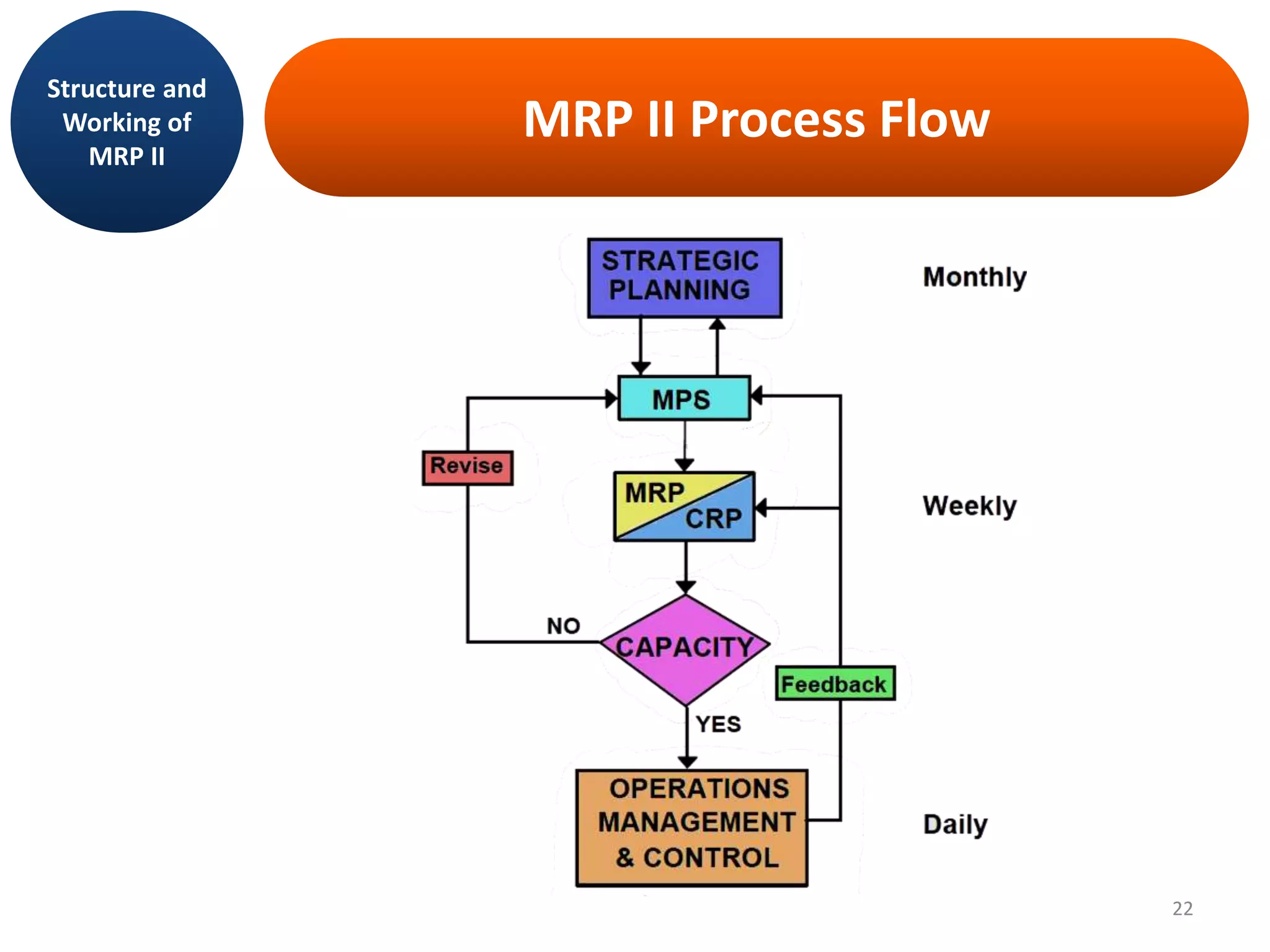
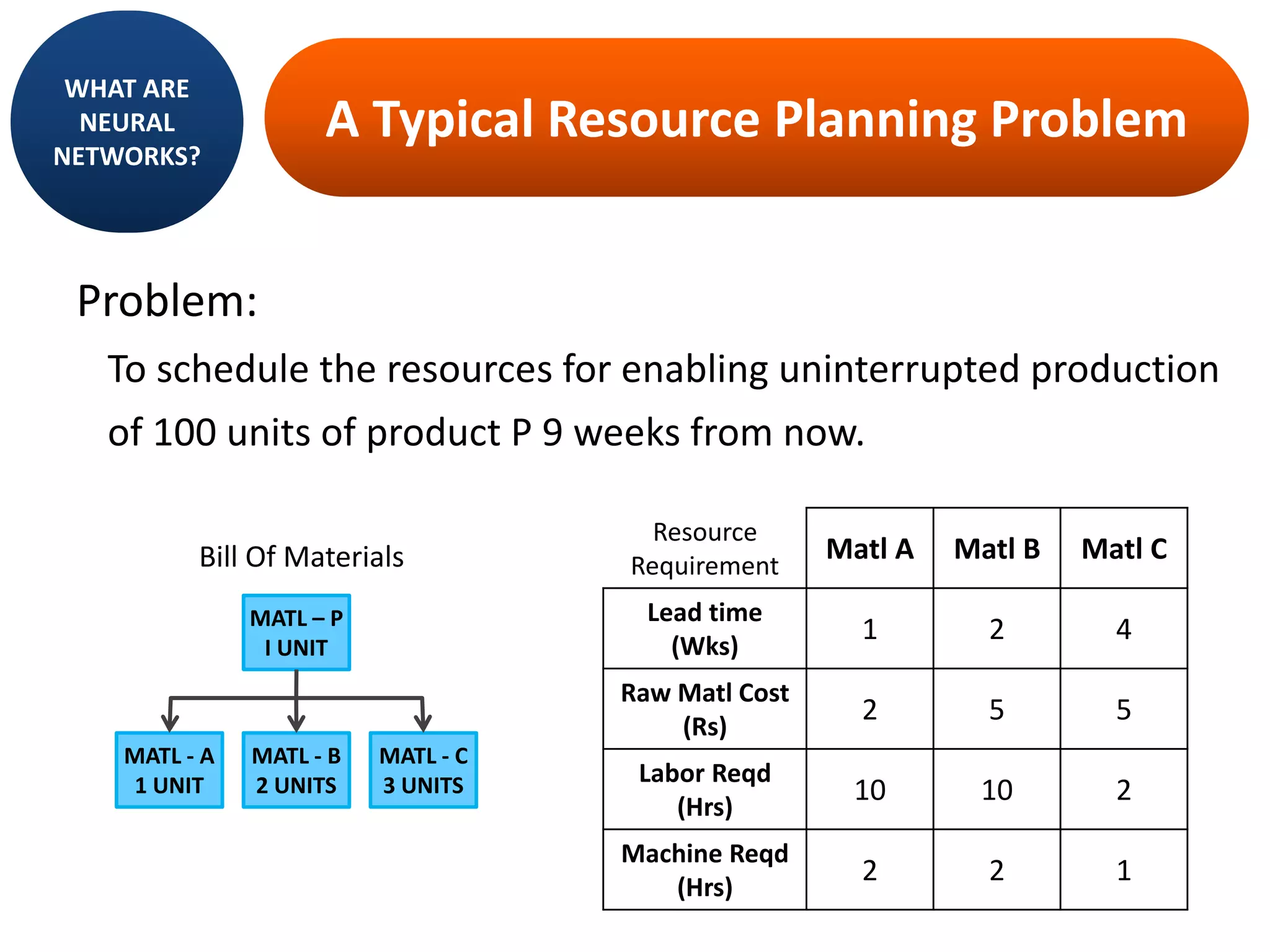
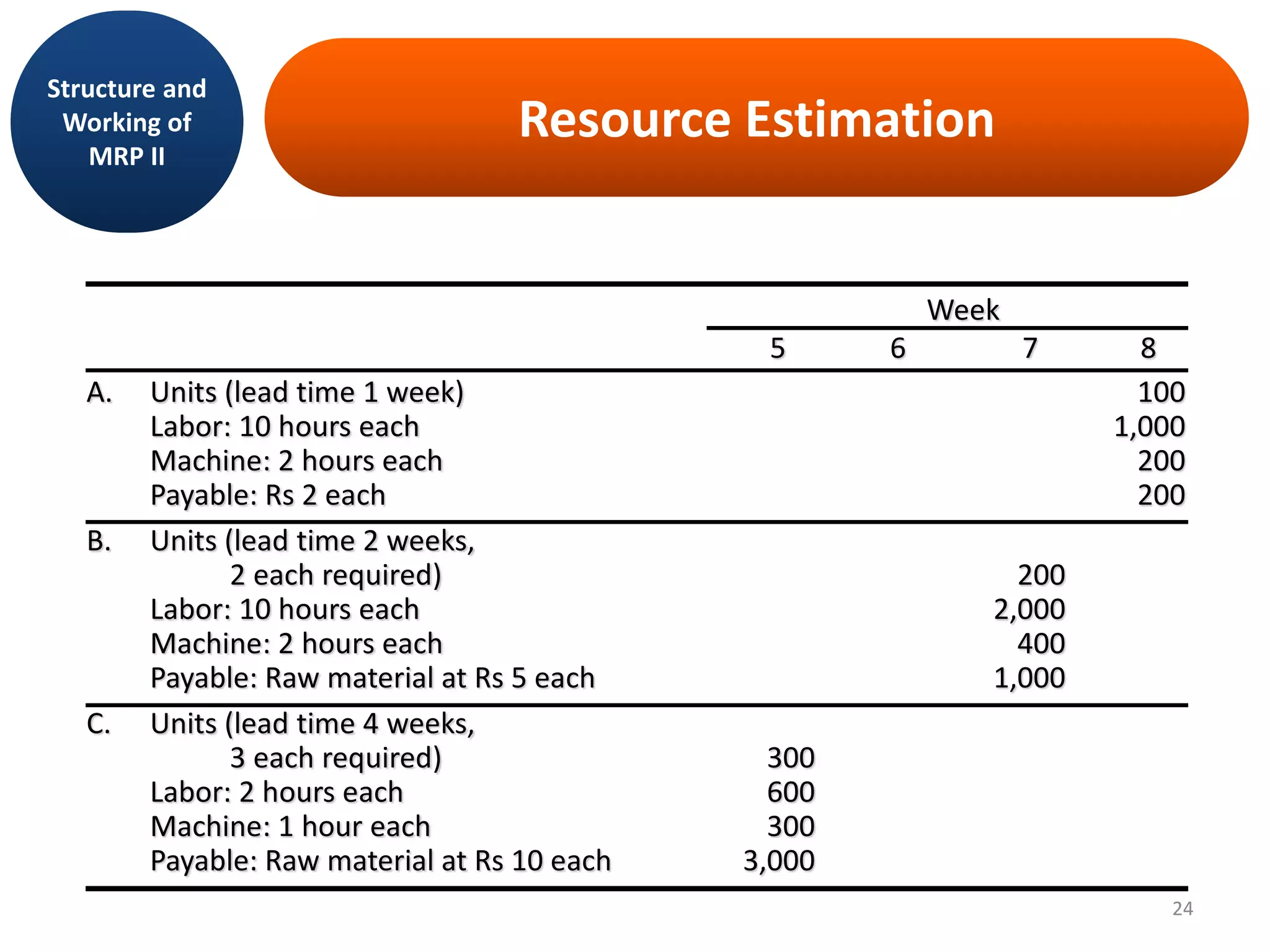
MRP II is an evolution of MRP that incorporates additional business functions like finance, accounting and human resources planning. It addresses both operational planning at the unit level as well as financial planning. MRP II systems integrate various modules like MRP, CRP, SFC etc. and use a common database to facilitate information sharing across functions. This helps achieve better coordination between different departments and improved control over resources like materials, labor and machines to efficiently meet production schedules. While MRP II provides several benefits, it also has some limitations like high implementation costs and difficulty in handling unexpected changes. Future developments involve further integration using ERP systems.


















![Ancillary Modules in a MRP II Software
• Business Planning
• Lot Traceability
• Contract Management
• Tool Management
• Engineering Change Control
• Configuration Management
• Shop Floor Data Collection
• Sales Analysis and Forecasting
• Finite Capacity Scheduling (FCS)
• General Ledger
• Accounts Payable (Purchase Ledger)
• Accounts Receivable (Sales Ledger)
• Sales Order Management
Structure and
Working of
MRP II
• Distribution Requirements Planning
• Distribution Resource Planning (DRP)
• [Automated] Warehouse Management
• Project Management
• Employee attendance
• Labour productivity
• Quality tracking tools
• Technical Records
• Estimating
• Computer-aided design/Computer-
aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM)
• Computer Aided Process Planning
(CAPP) 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14-150401234044-conversion-gate01/75/mohsin-dalvi-mrp-ii-presentation-27-2048.jpg)