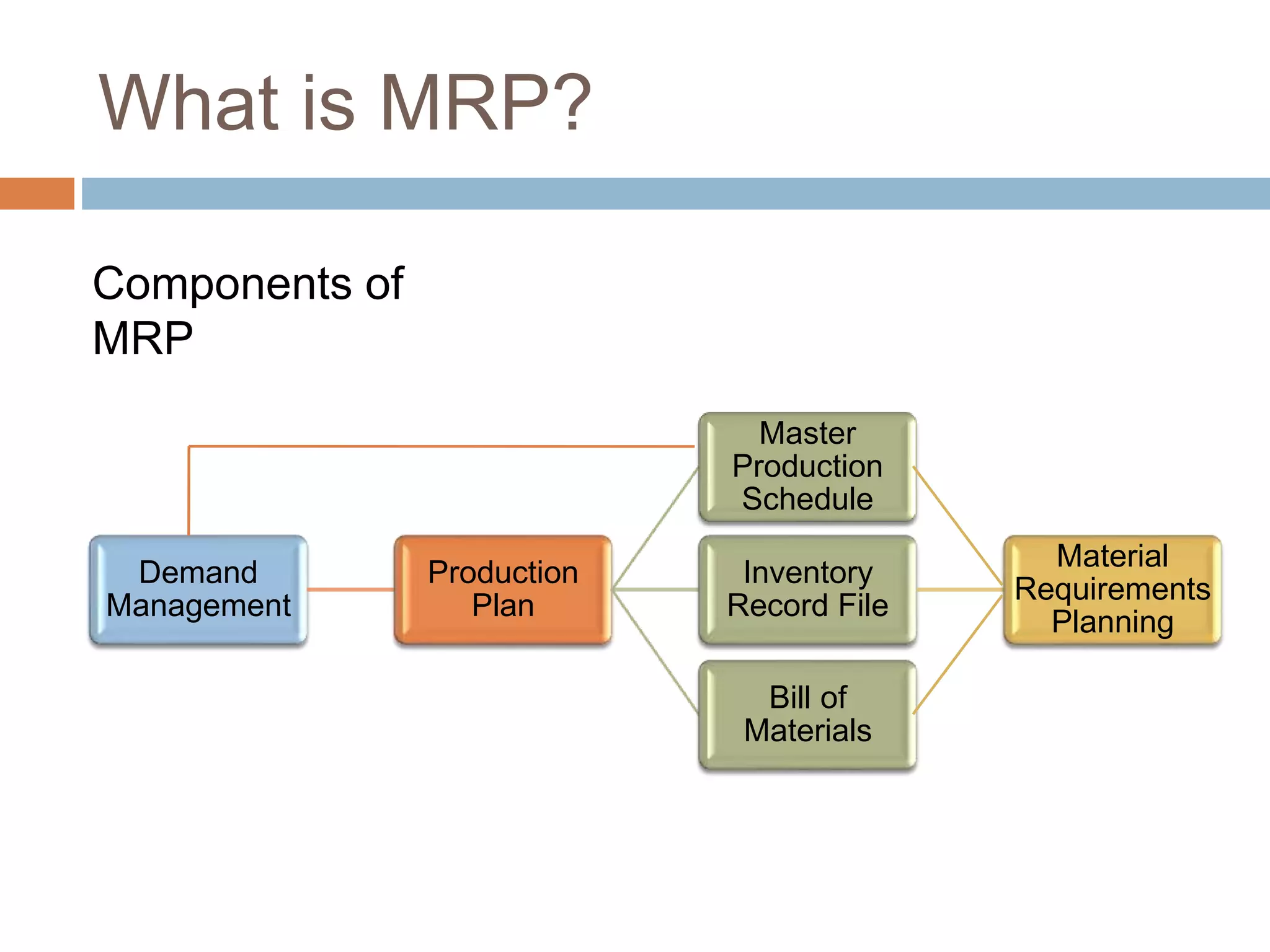
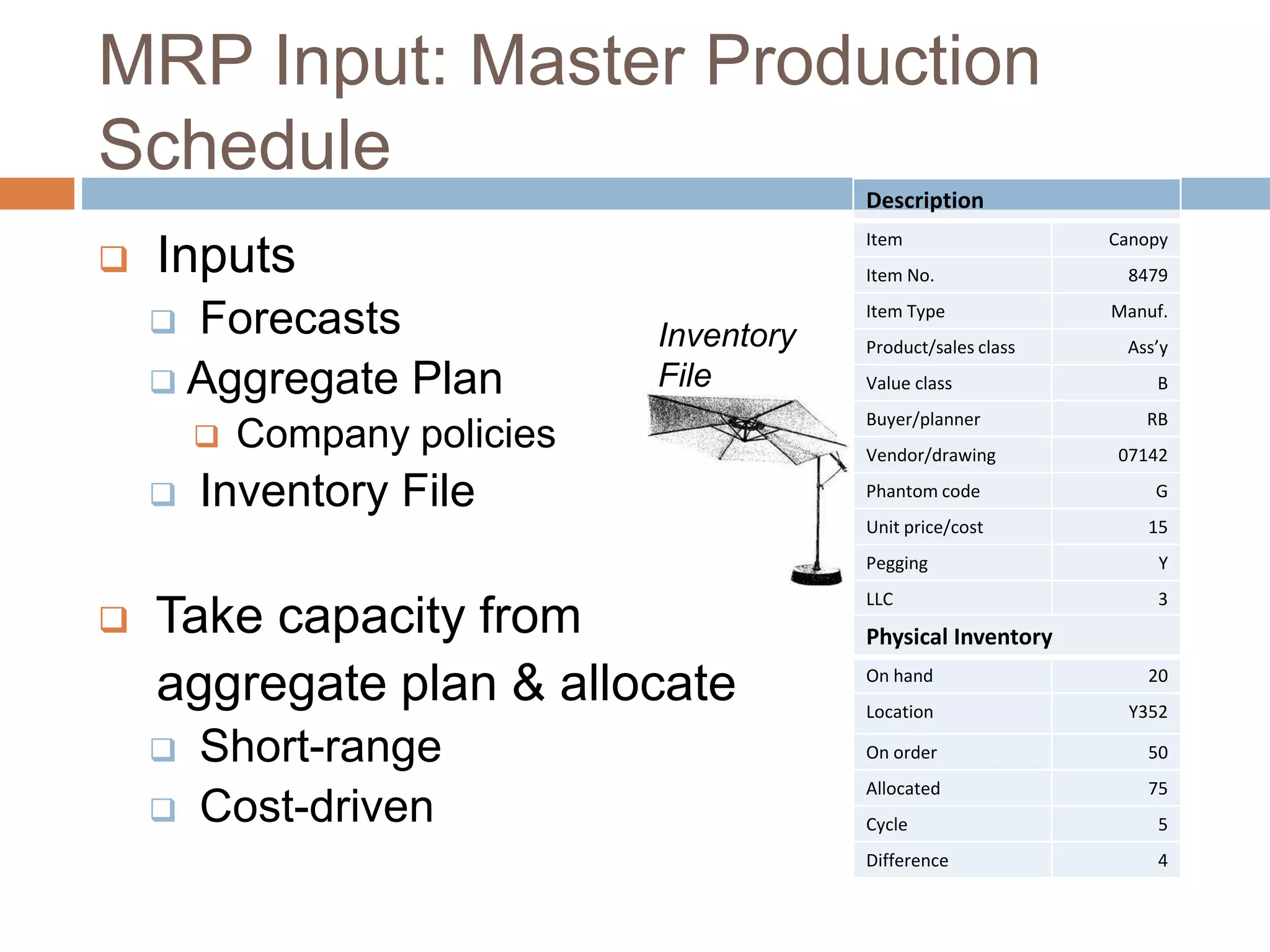
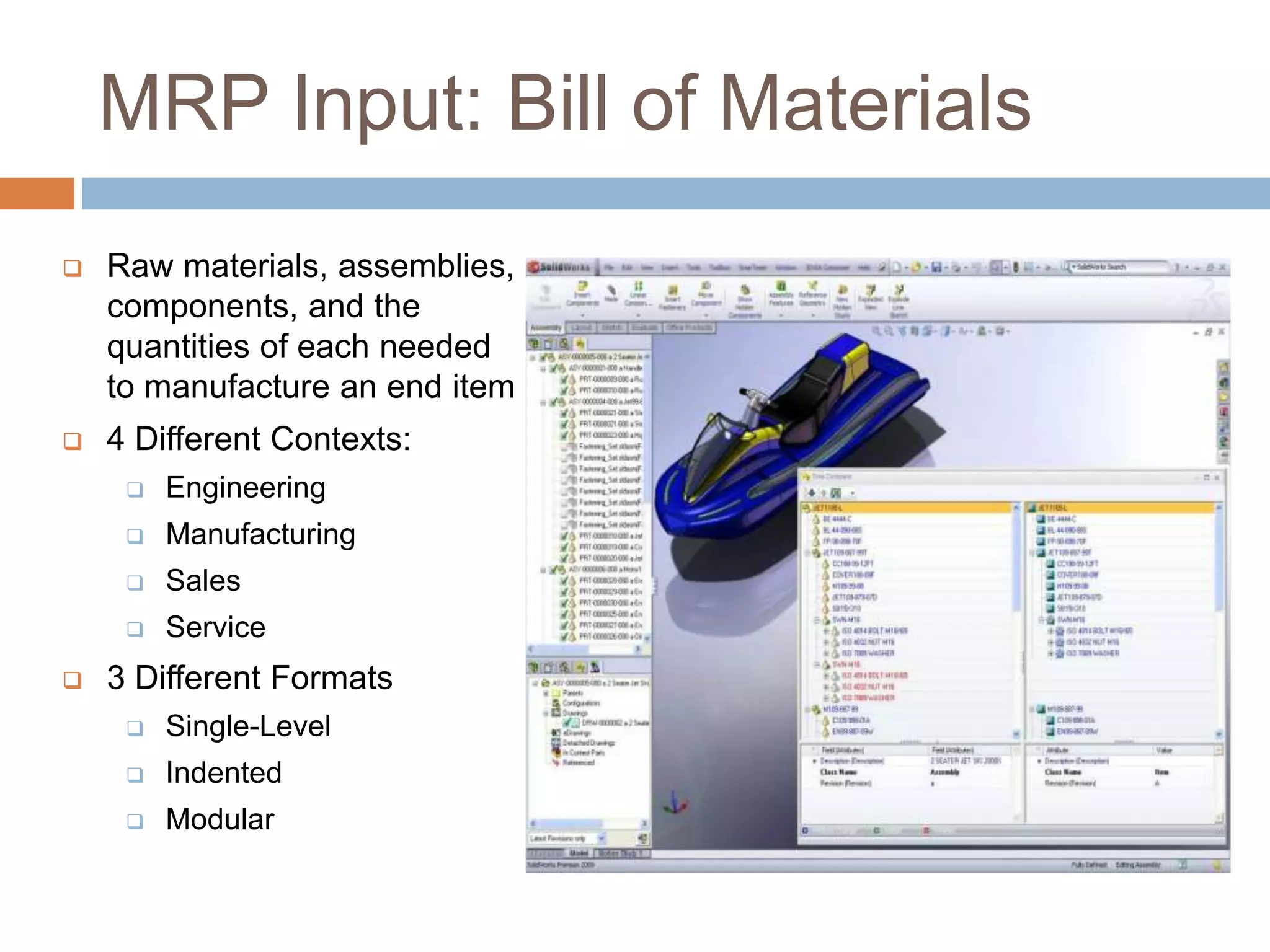
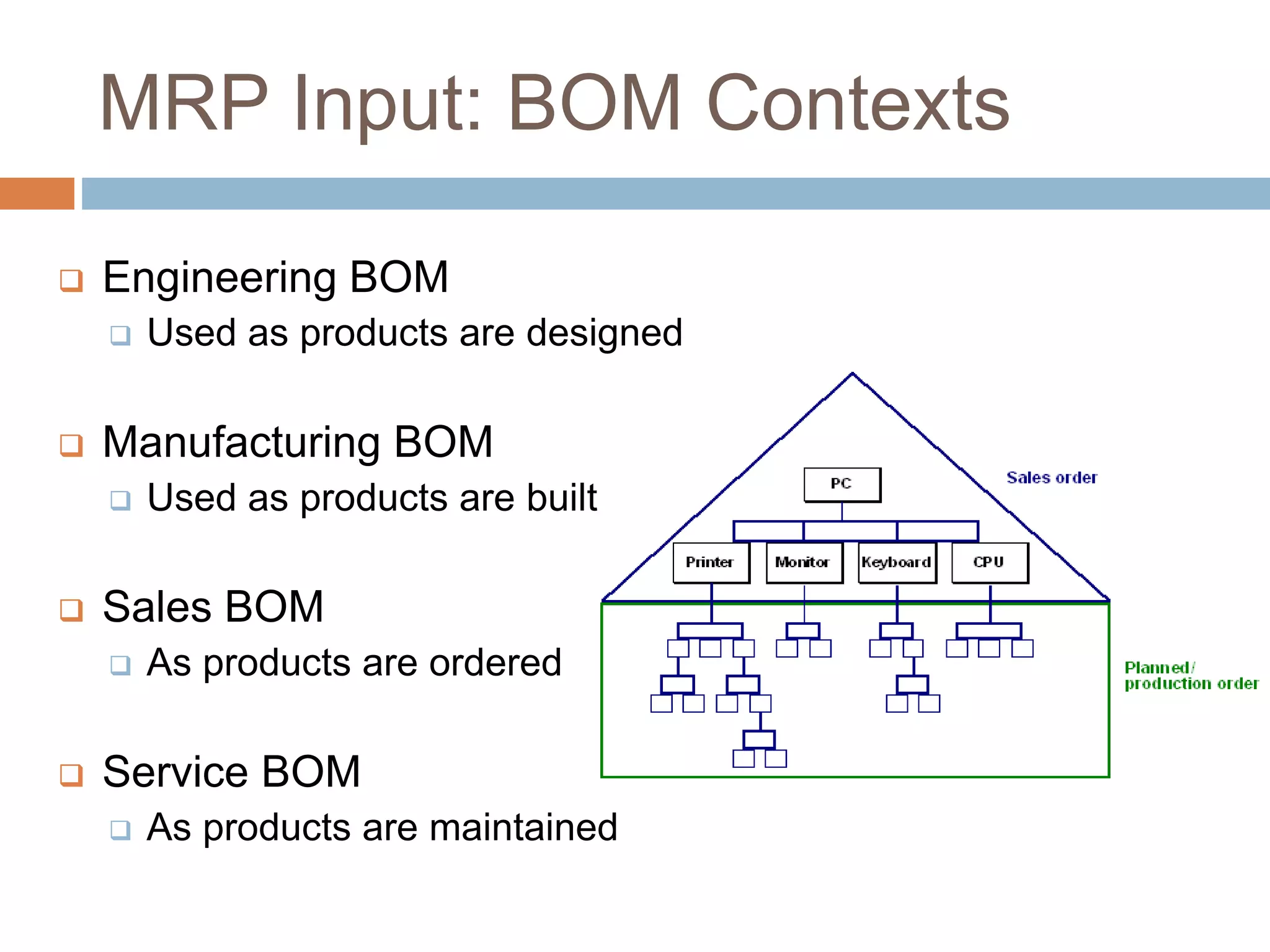
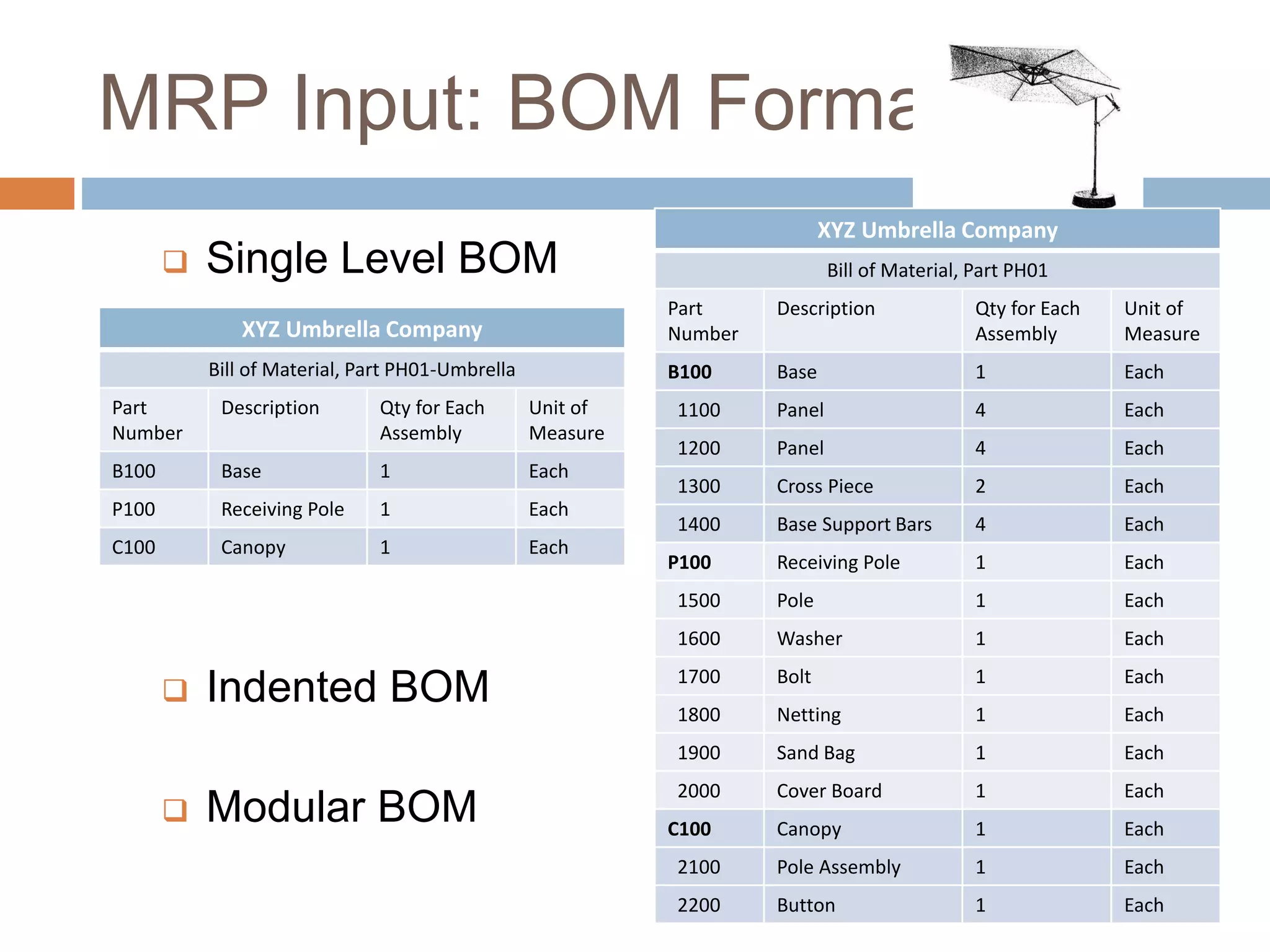
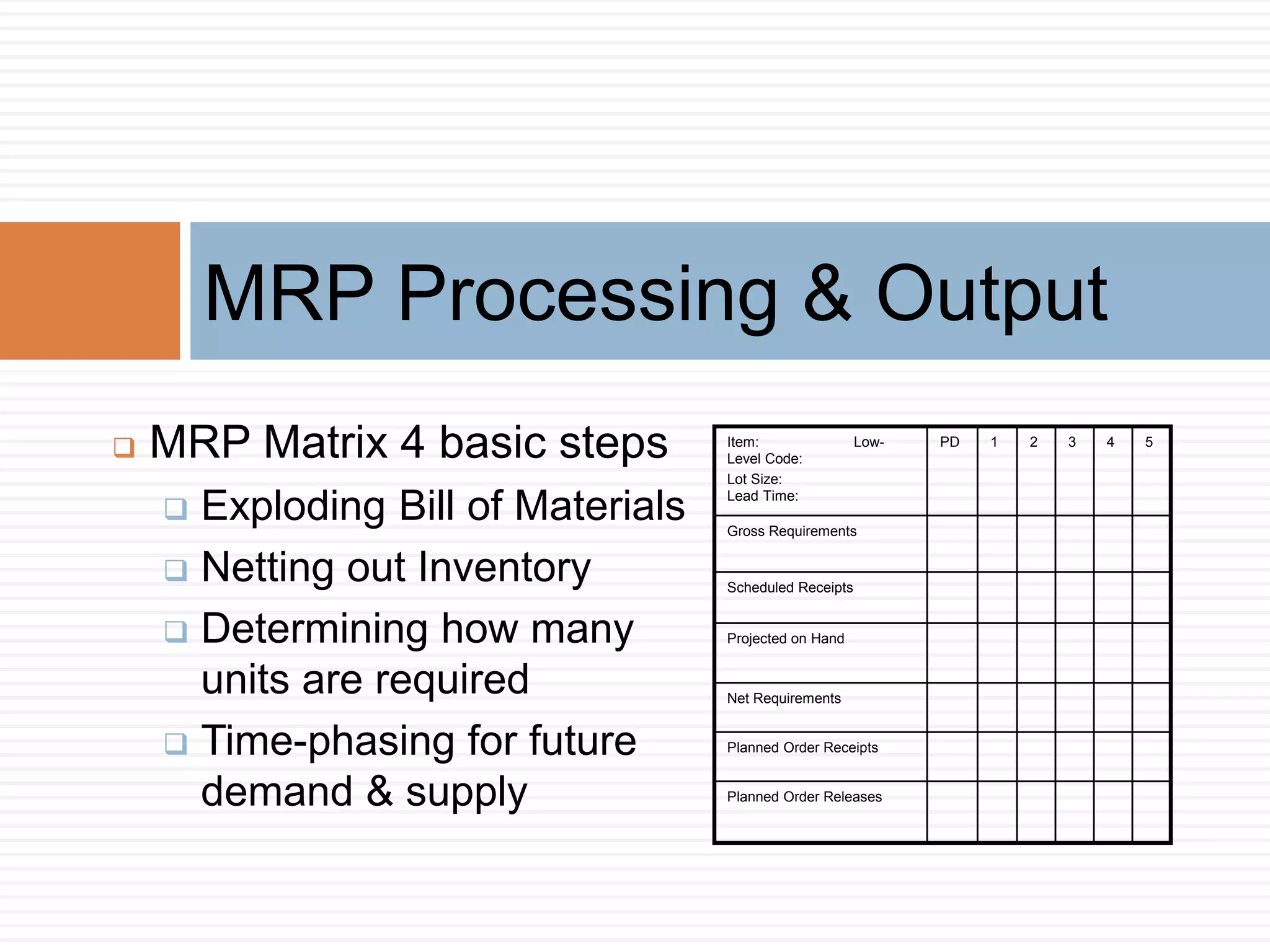
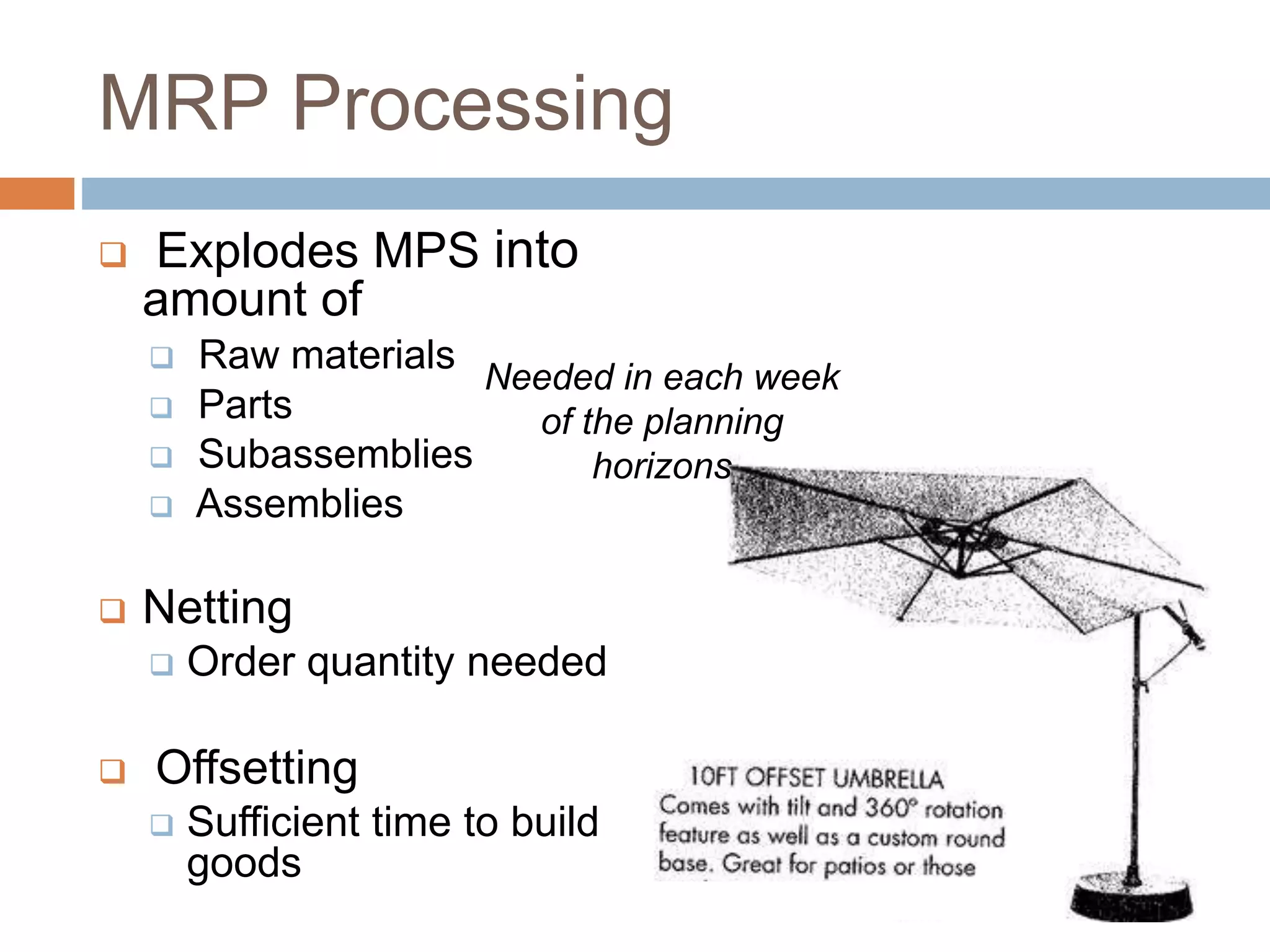
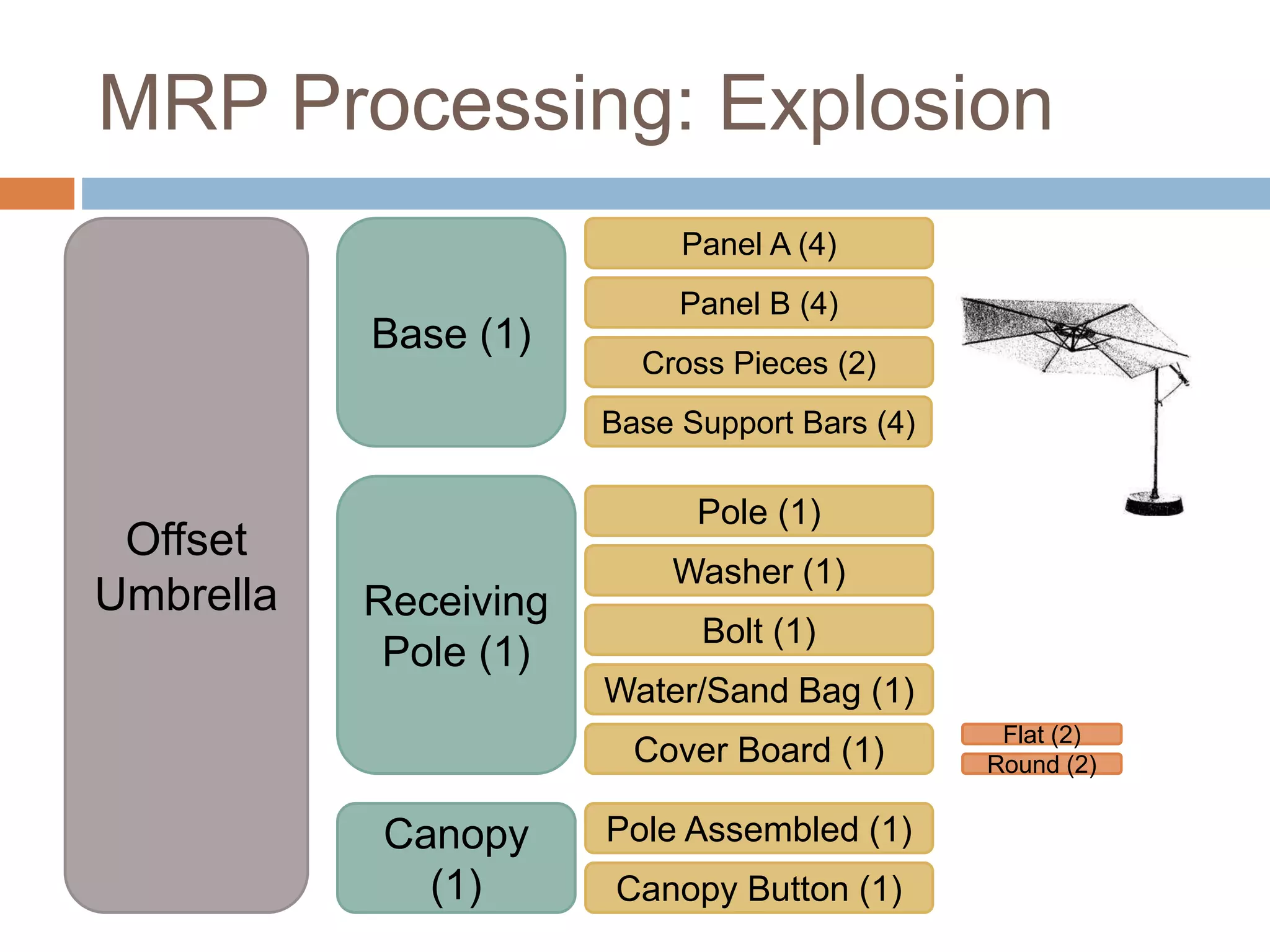
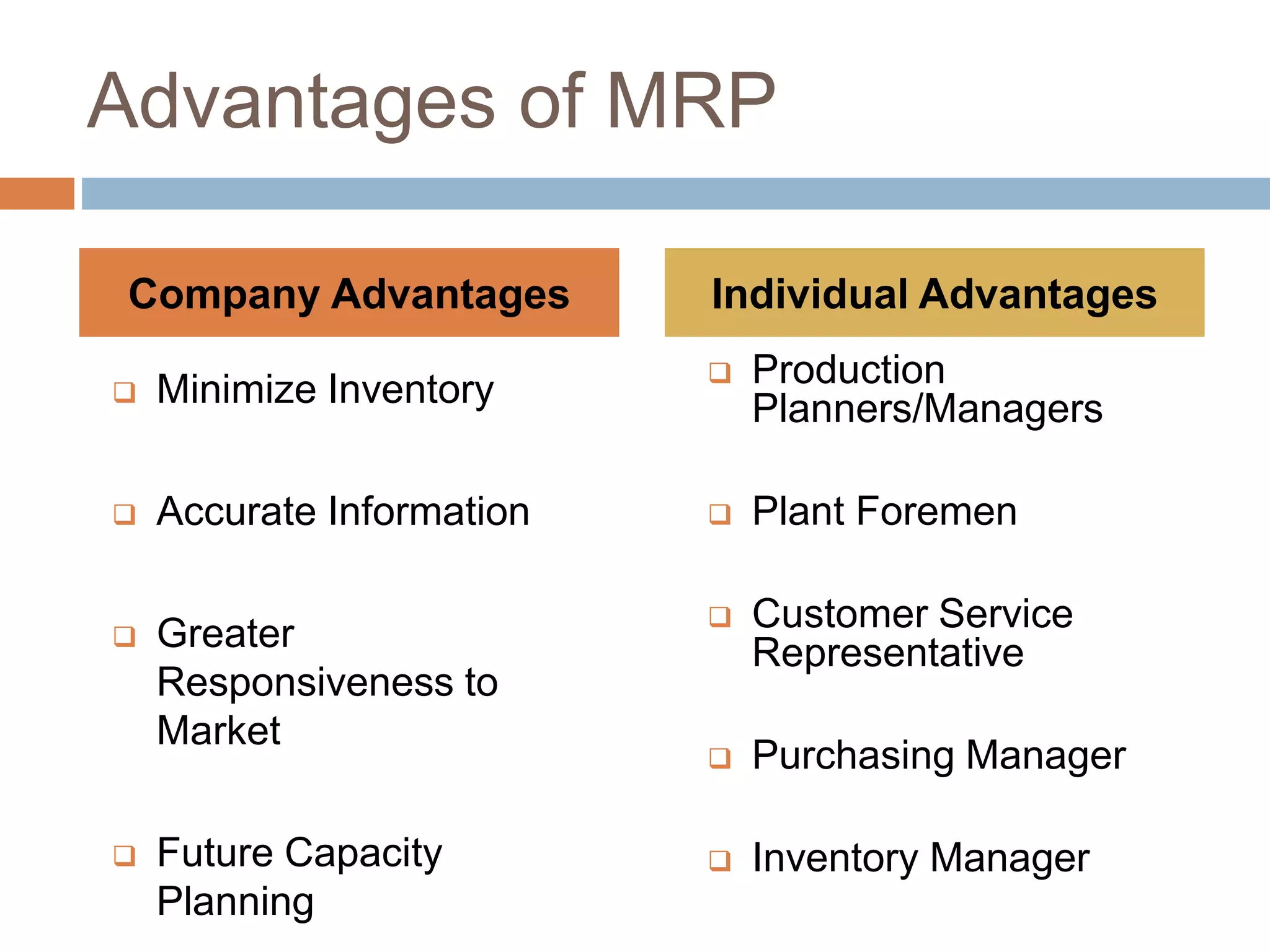
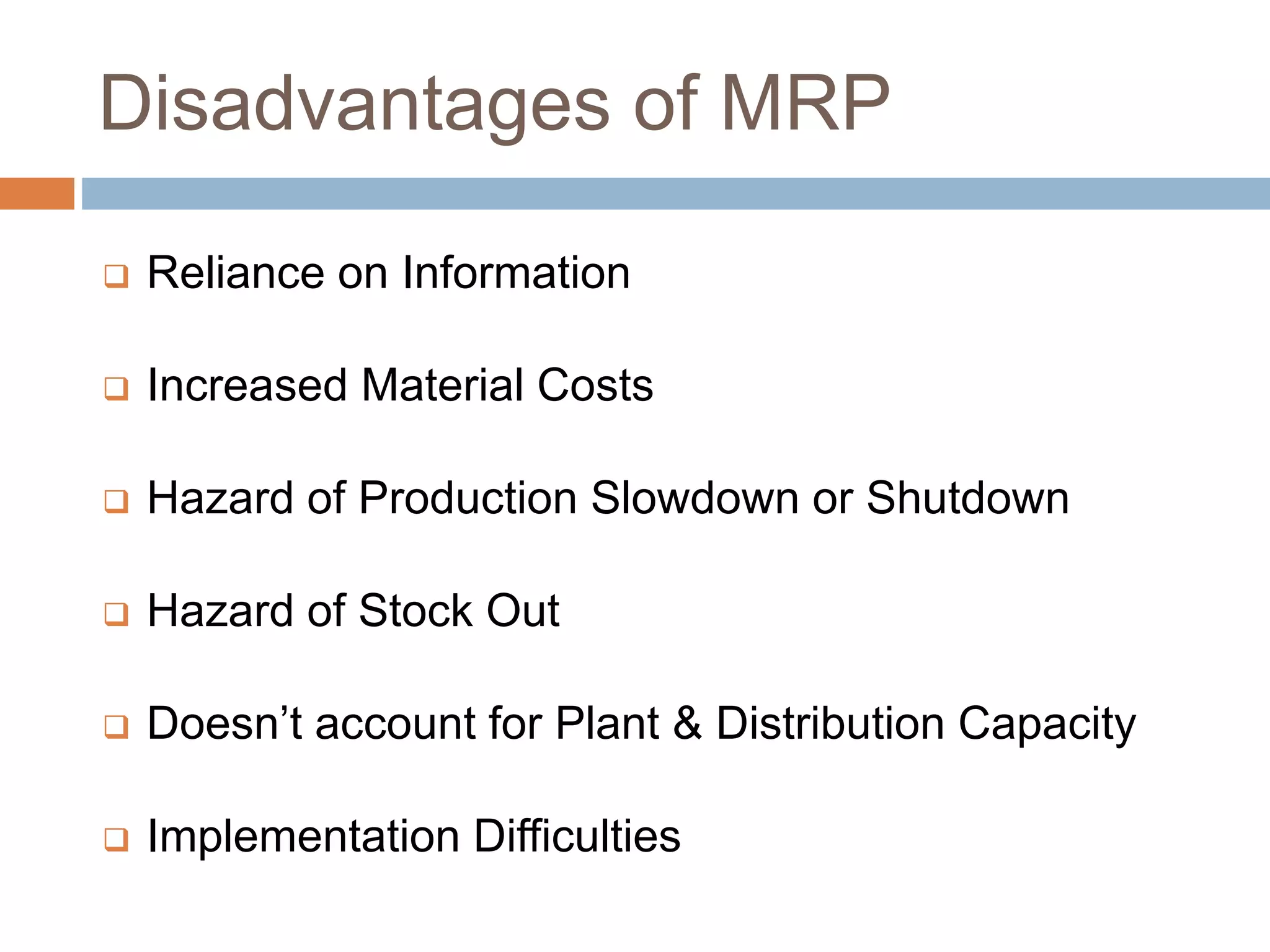
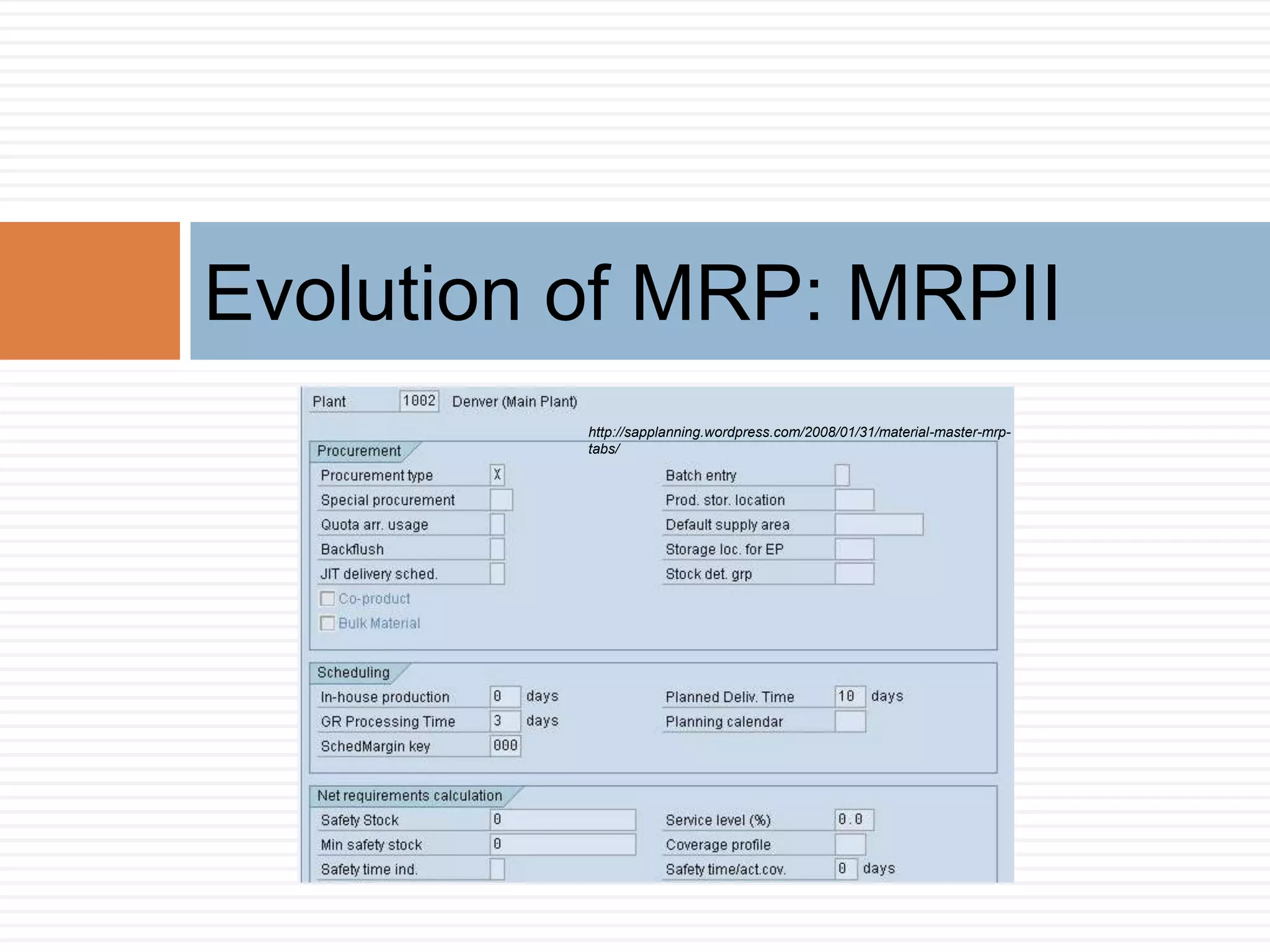
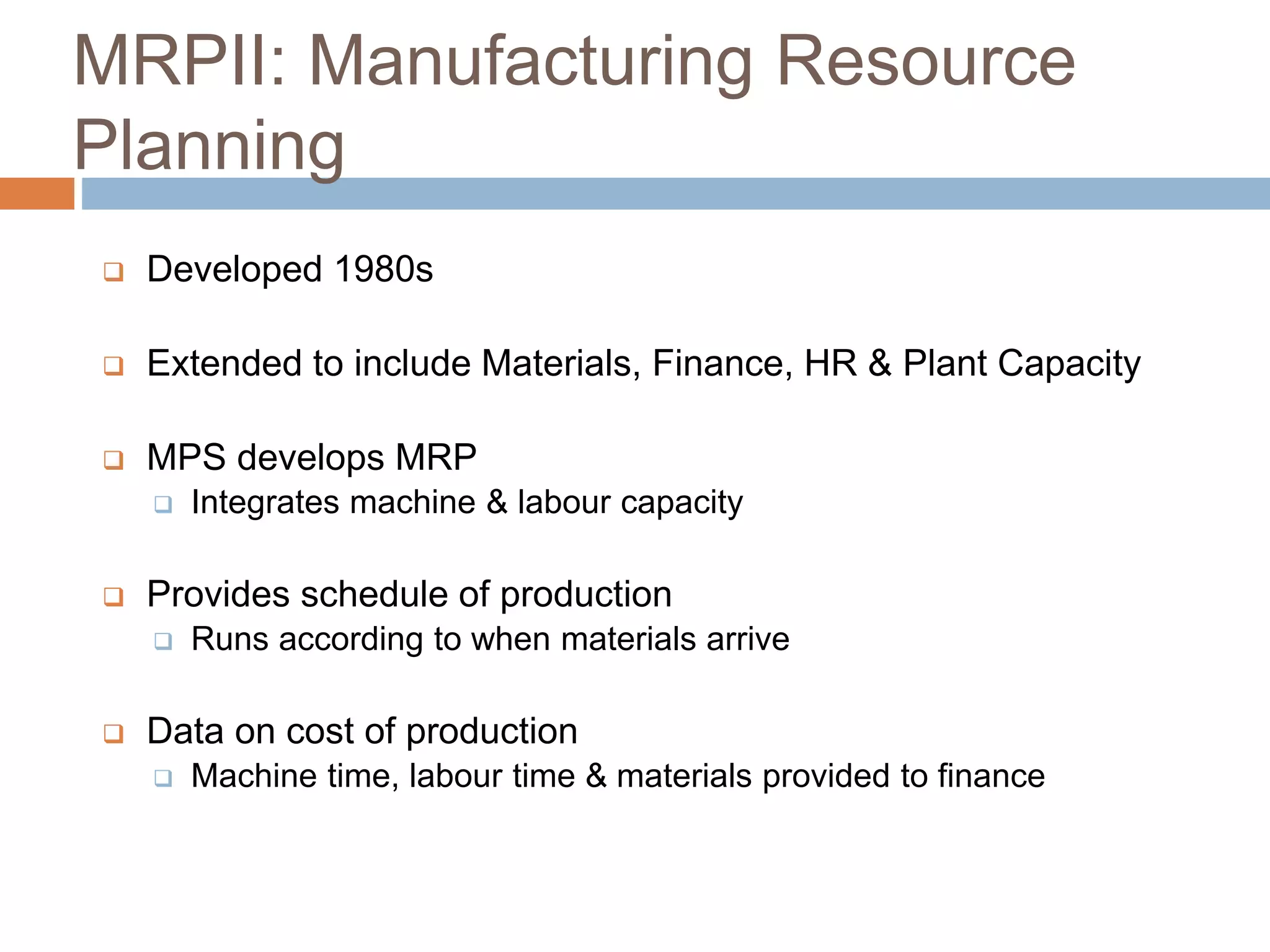
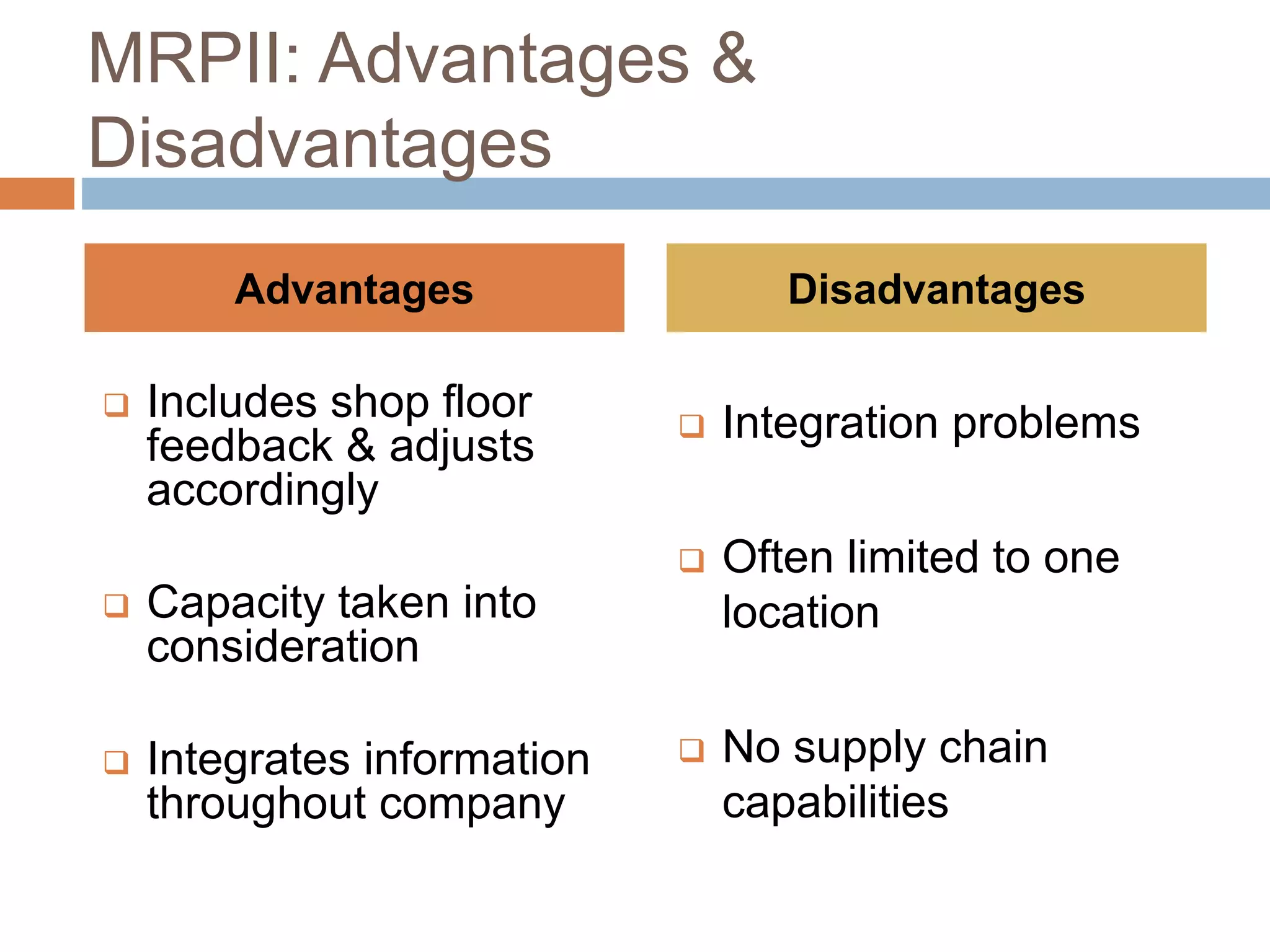
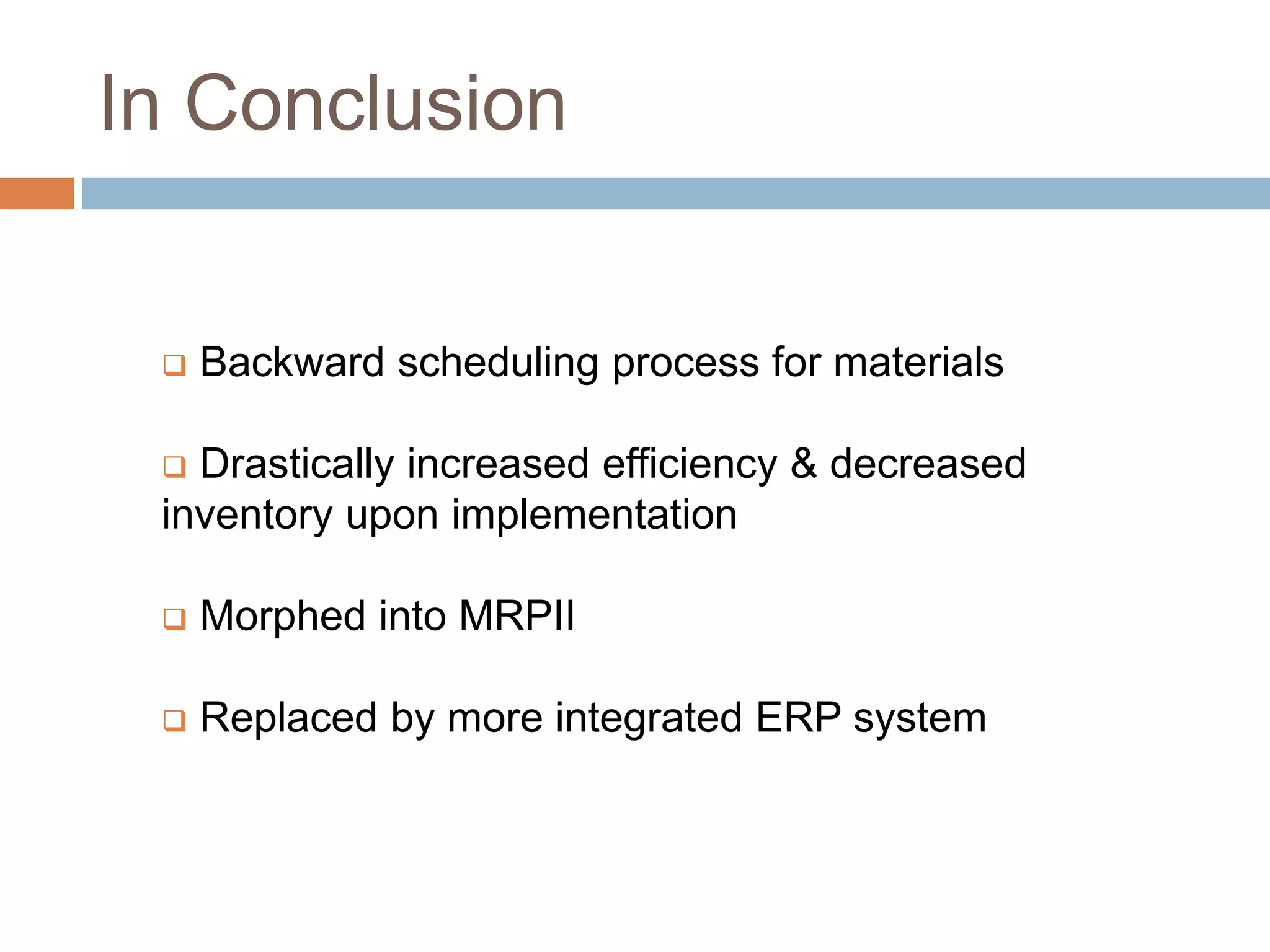
MRP is a system used in manufacturing to plan production schedules and material requirements. It takes inputs like the master production schedule and bill of materials to calculate net requirements through a process of exploding, netting, and offsetting. This helps control inventory levels and supports forecasted demand. MRP evolved into MRPII, which further integrates capacity planning, production scheduling, and other functions. While MRP improved efficiency, it also has disadvantages like reliance on accurate information and limited capacity planning.