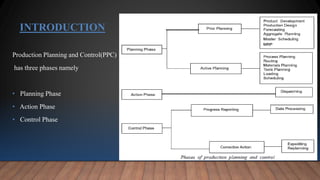
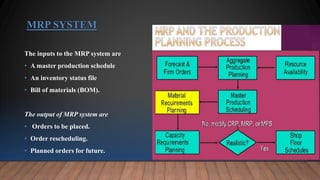
This document provides an overview of materials requirement planning (MRP). It discusses that MRP has three phases - planning, action, and control. MRP determines the quantity and timing for acquiring dependent demand items to satisfy production schedules. MRP is a production planning and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. The document then discusses the history, objectives, inputs/outputs, types of MRP users, and advantages and disadvantages of MRP.