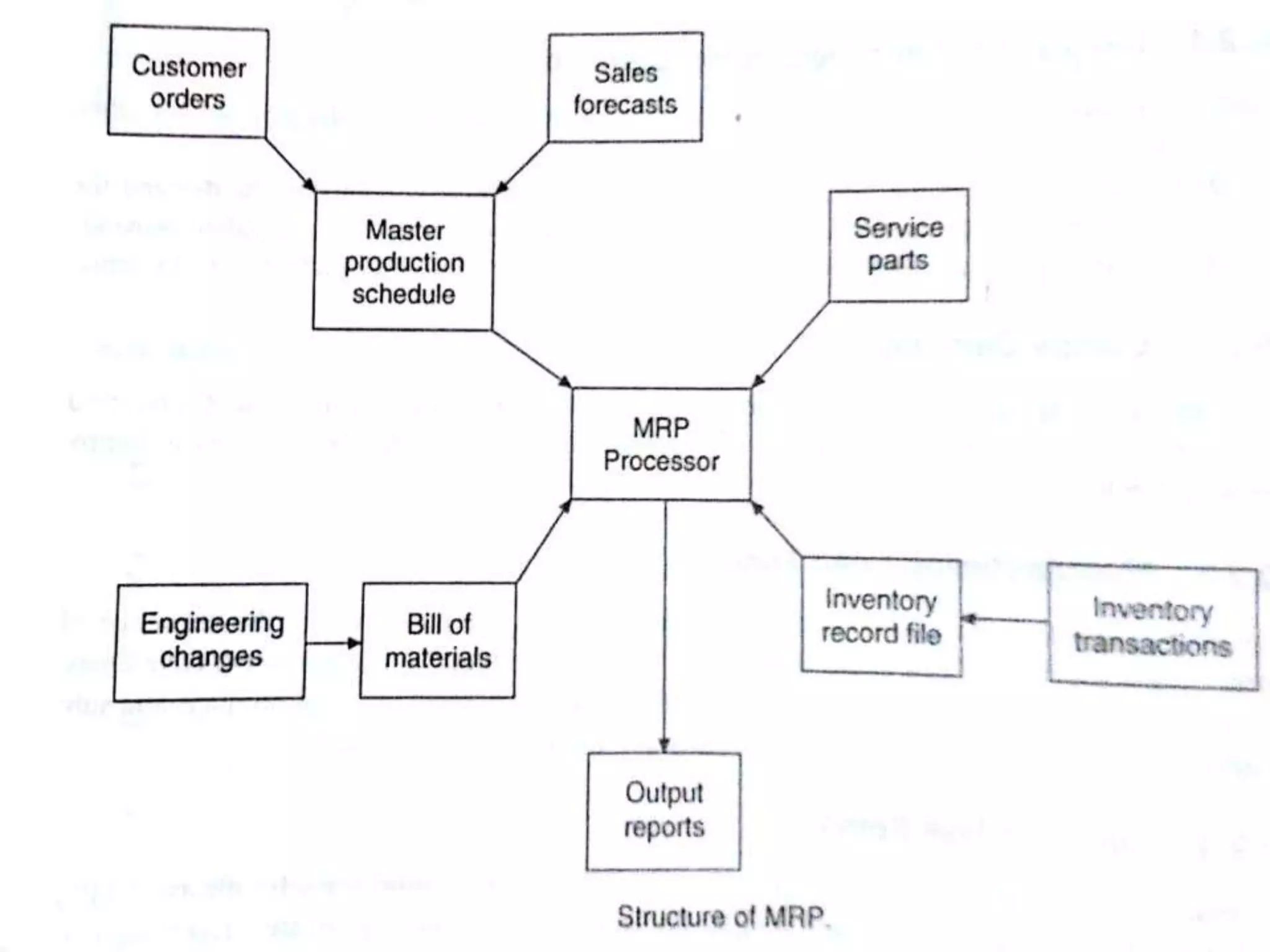
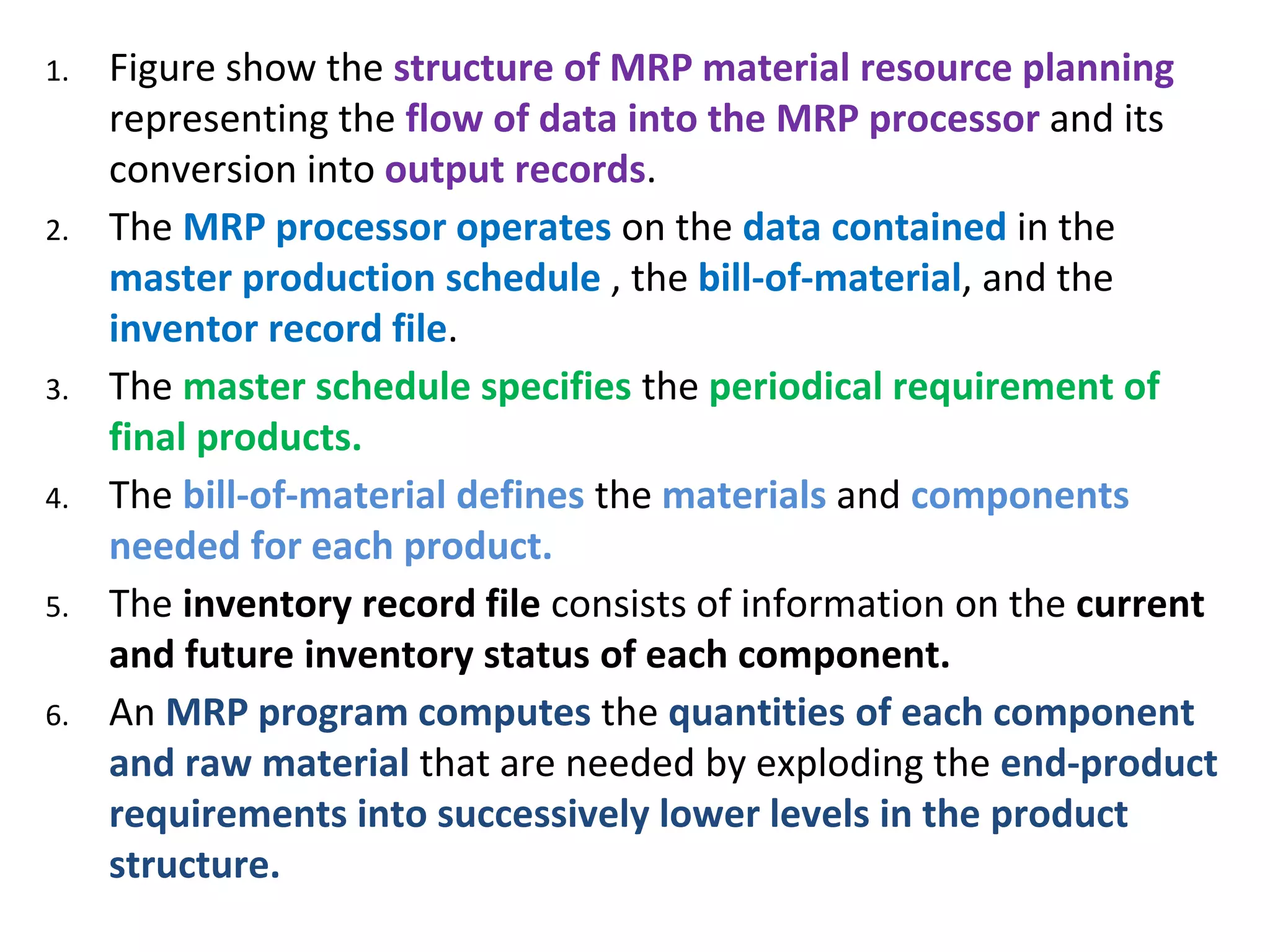
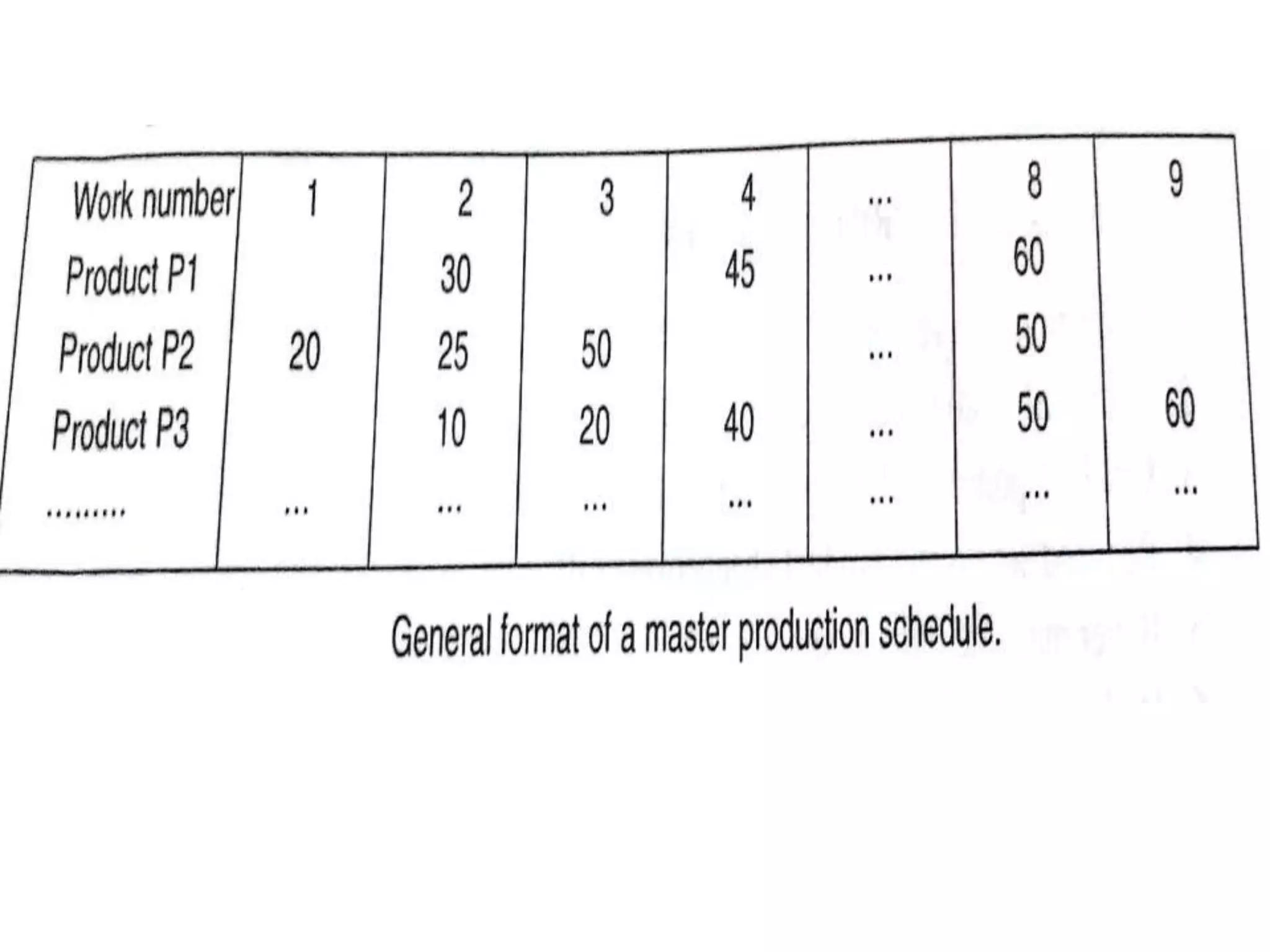
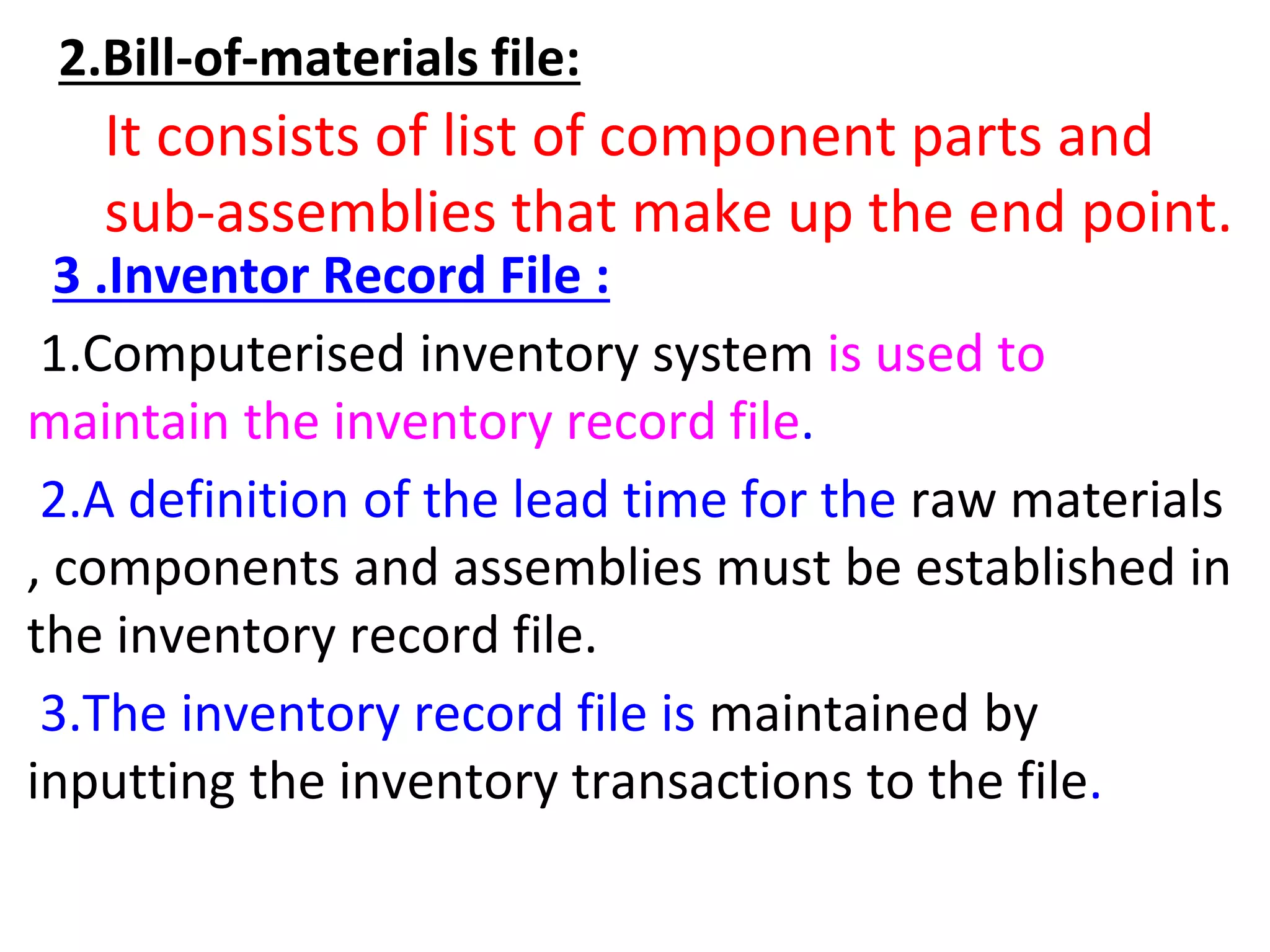
This document provides an overview of computer-aided manufacturing resource planning, including material resource planning (MRP), manufacturing resource planning (MRP II), capacity resource planning (CRP), and enterprise resource planning (ERP). It describes MRP as a computational technique that converts a master schedule for end products into a detailed schedule for raw materials and components. It also outlines the key concepts and inputs used in MRP, including independent/dependent demand, lumpy demand, manufacturing lead times, and common use items. The document then provides brief descriptions of MRP II, CRP, and ERP systems.