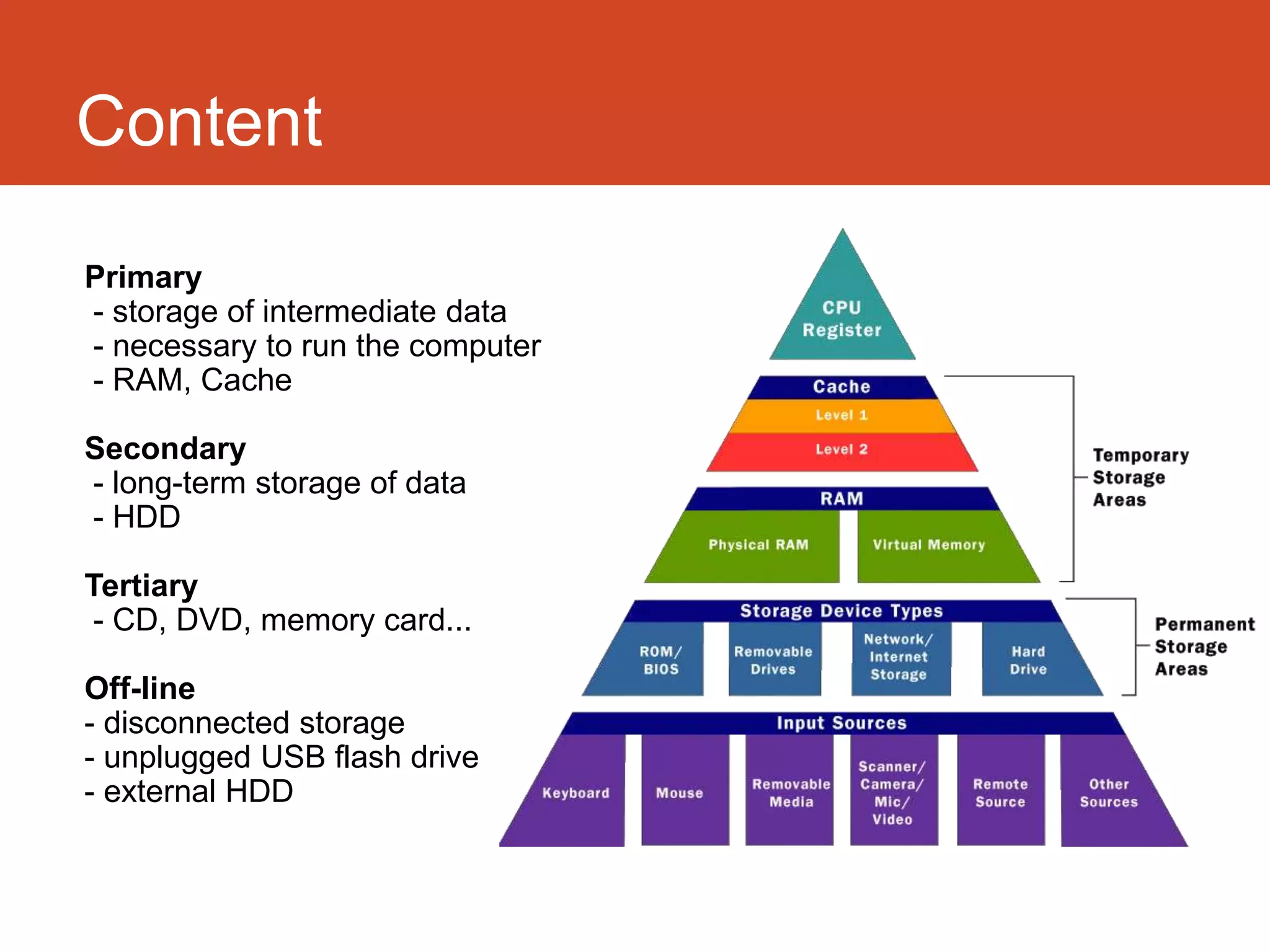
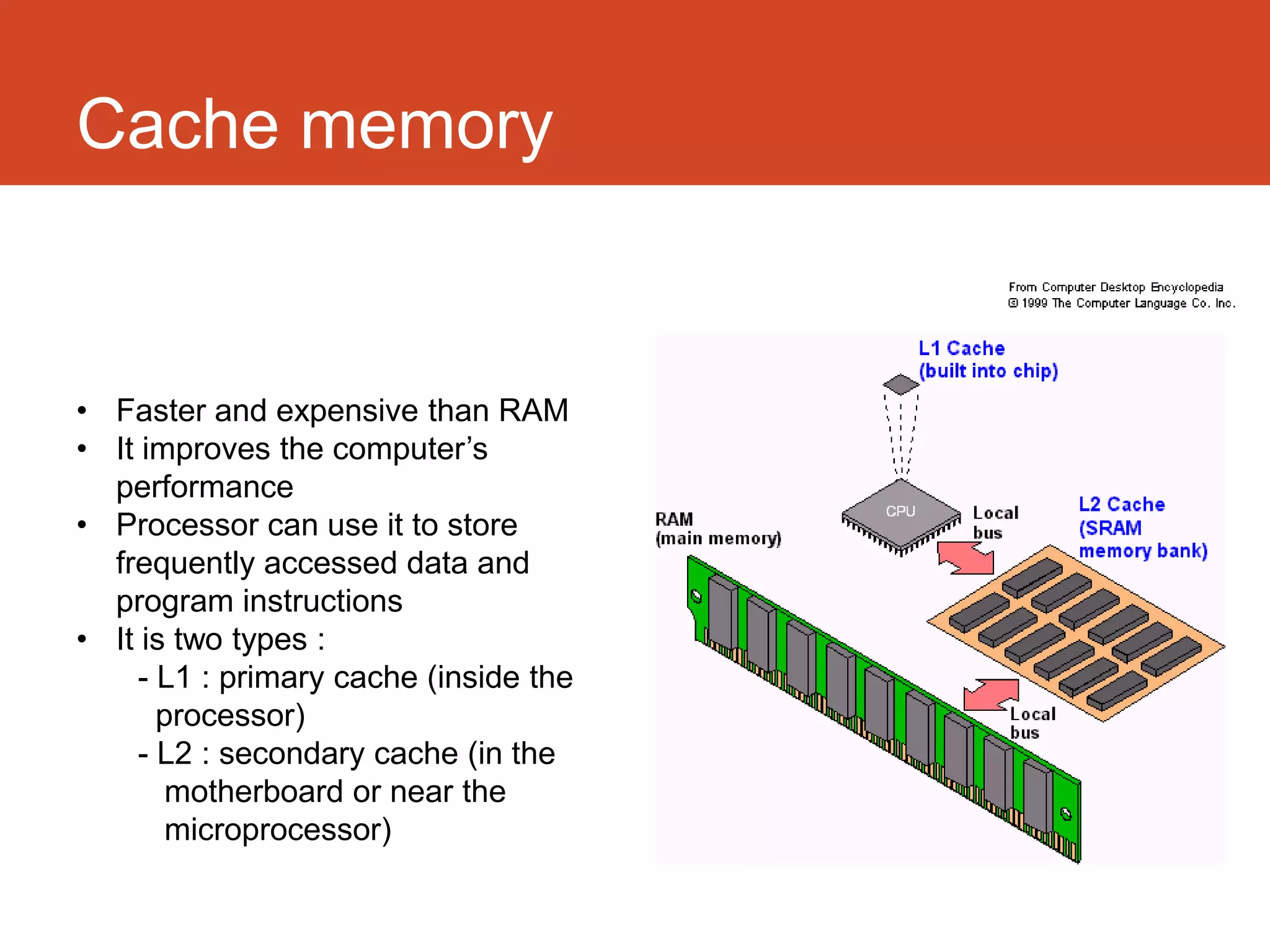
Storage provides capacity for files and information through devices like hard disks, while memory provides working space through RAM. Primary storage includes RAM and cache for running the computer, while secondary storage is long-term storage like hard disks. RAM is volatile memory used for running programs, coming in static RAM and dynamic RAM forms. ROM is read-only memory storing basic instructions. Cache memory improves performance by storing frequently used data and instructions. Optical storage includes CDs, DVDs, and Blu-rays, while magnetic storage encompasses floppy disks and hard disks. Flash memory offers portable options like USB drives and solid-state drives.