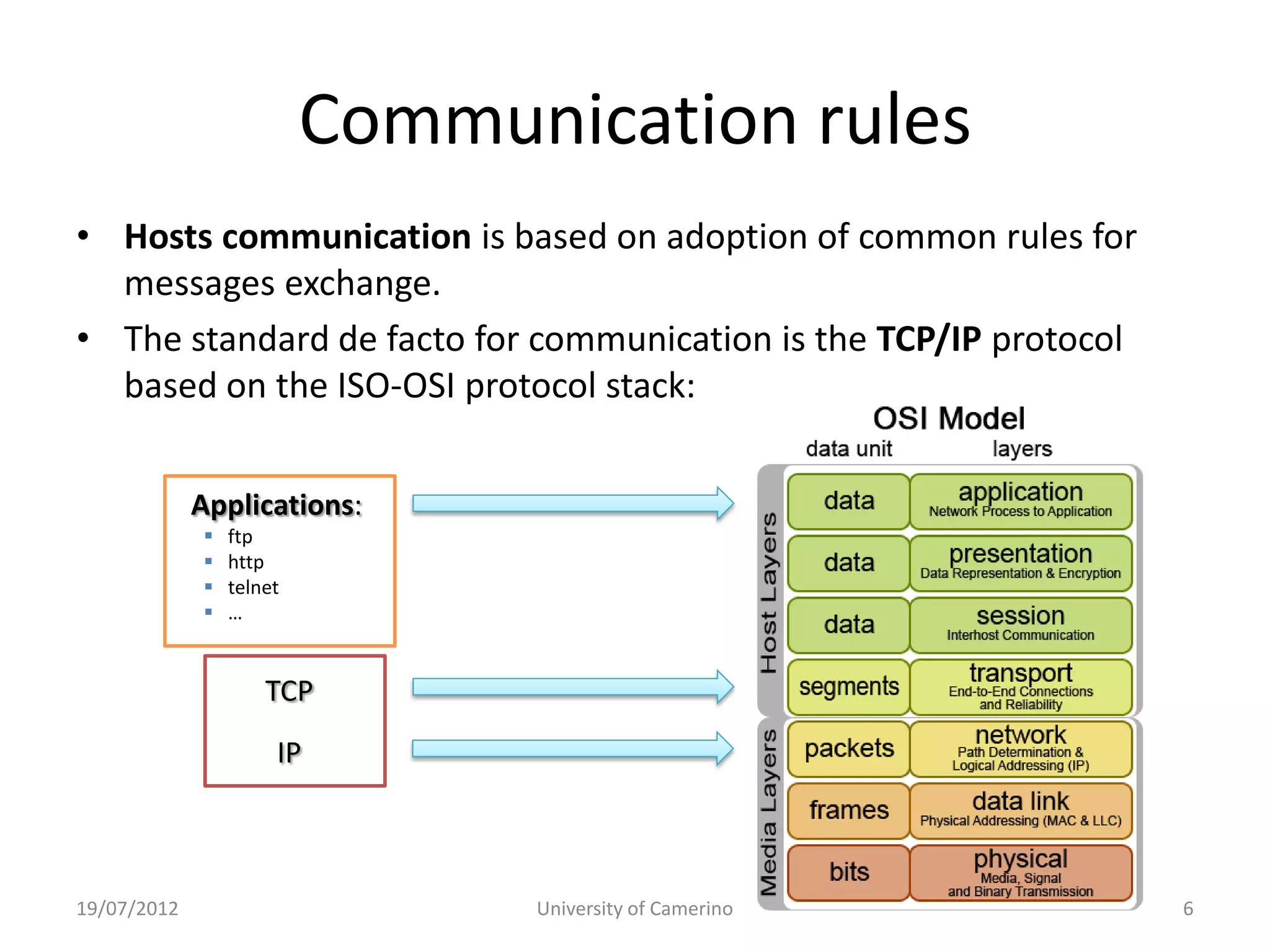
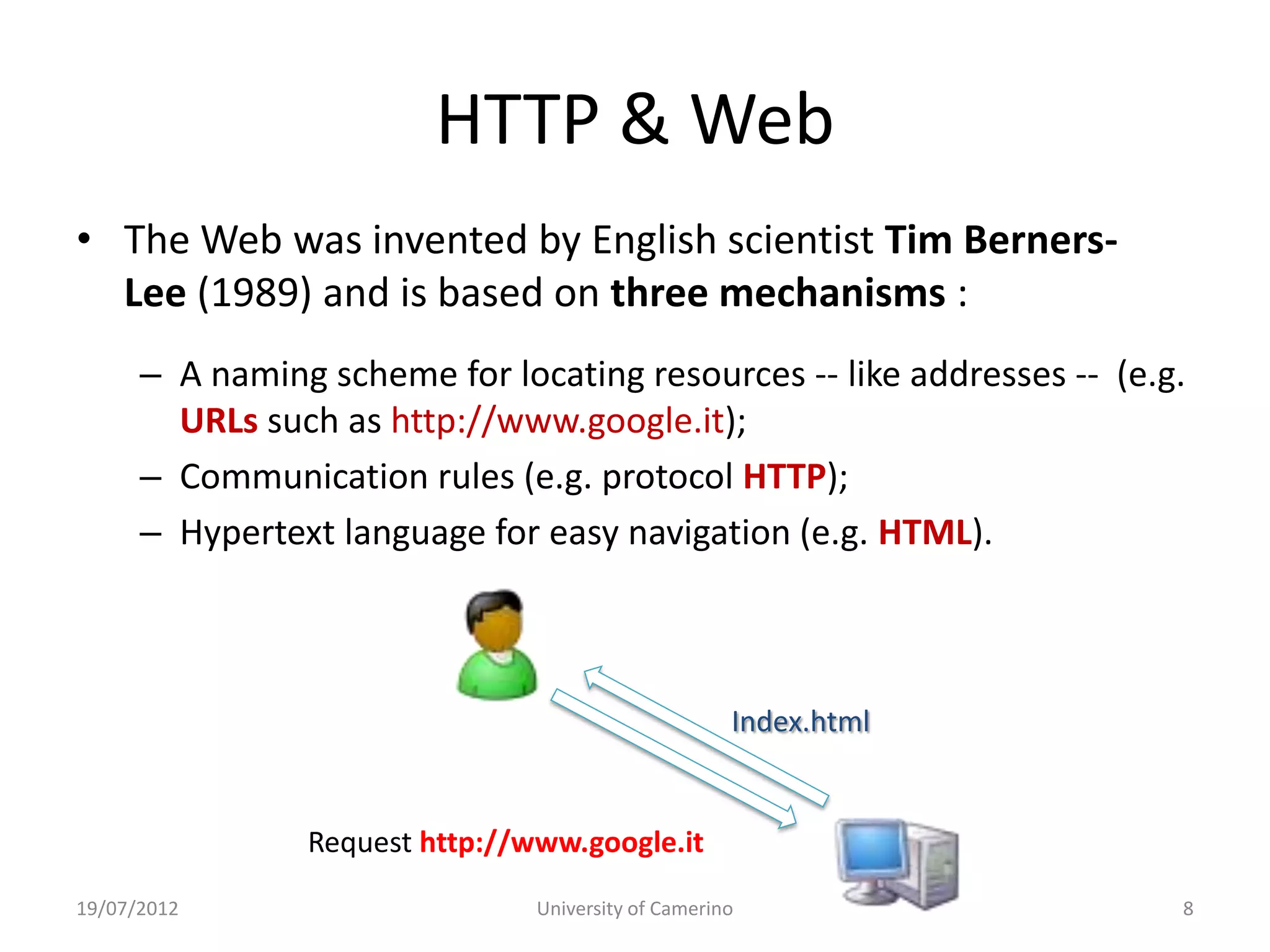
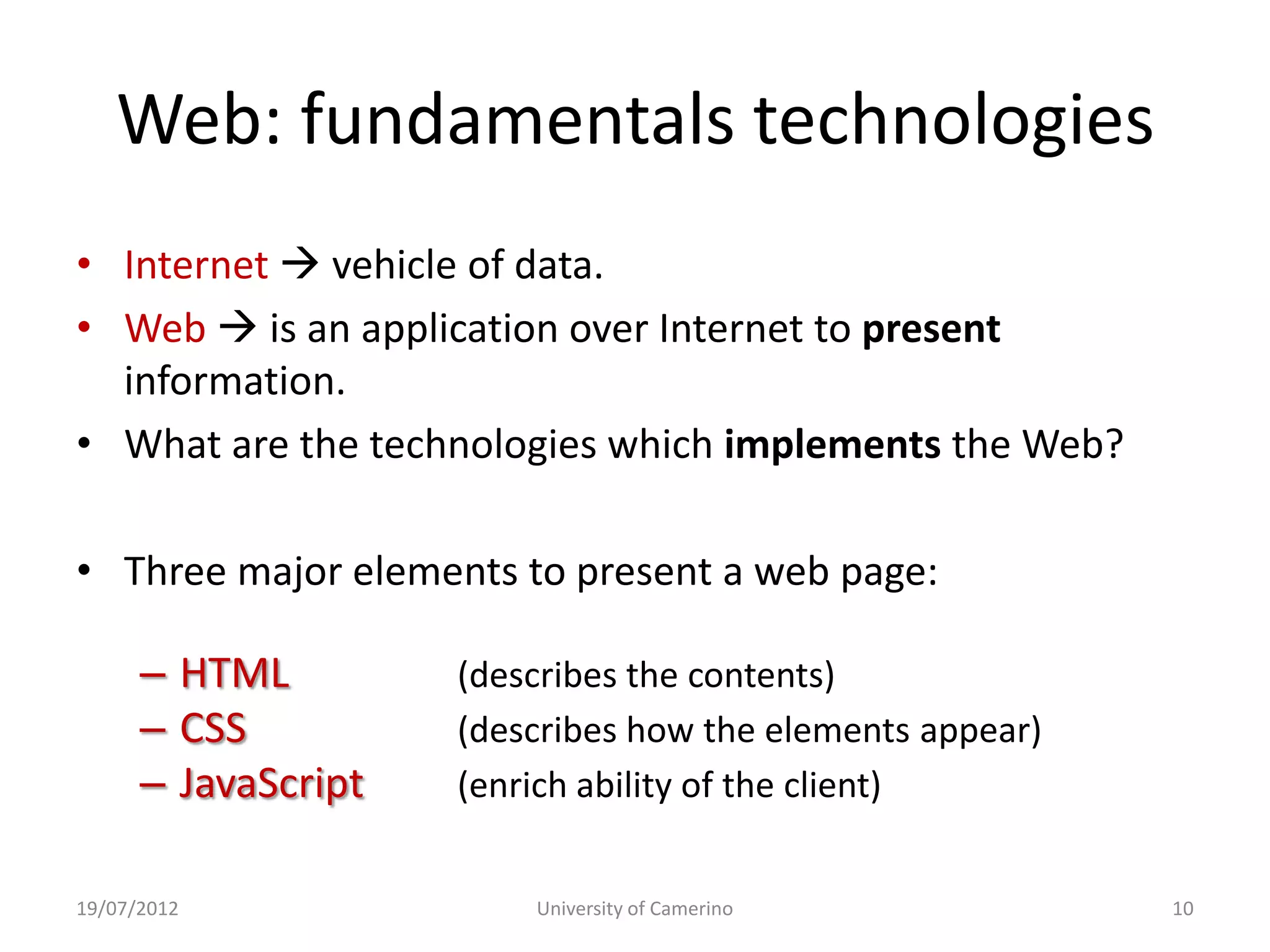
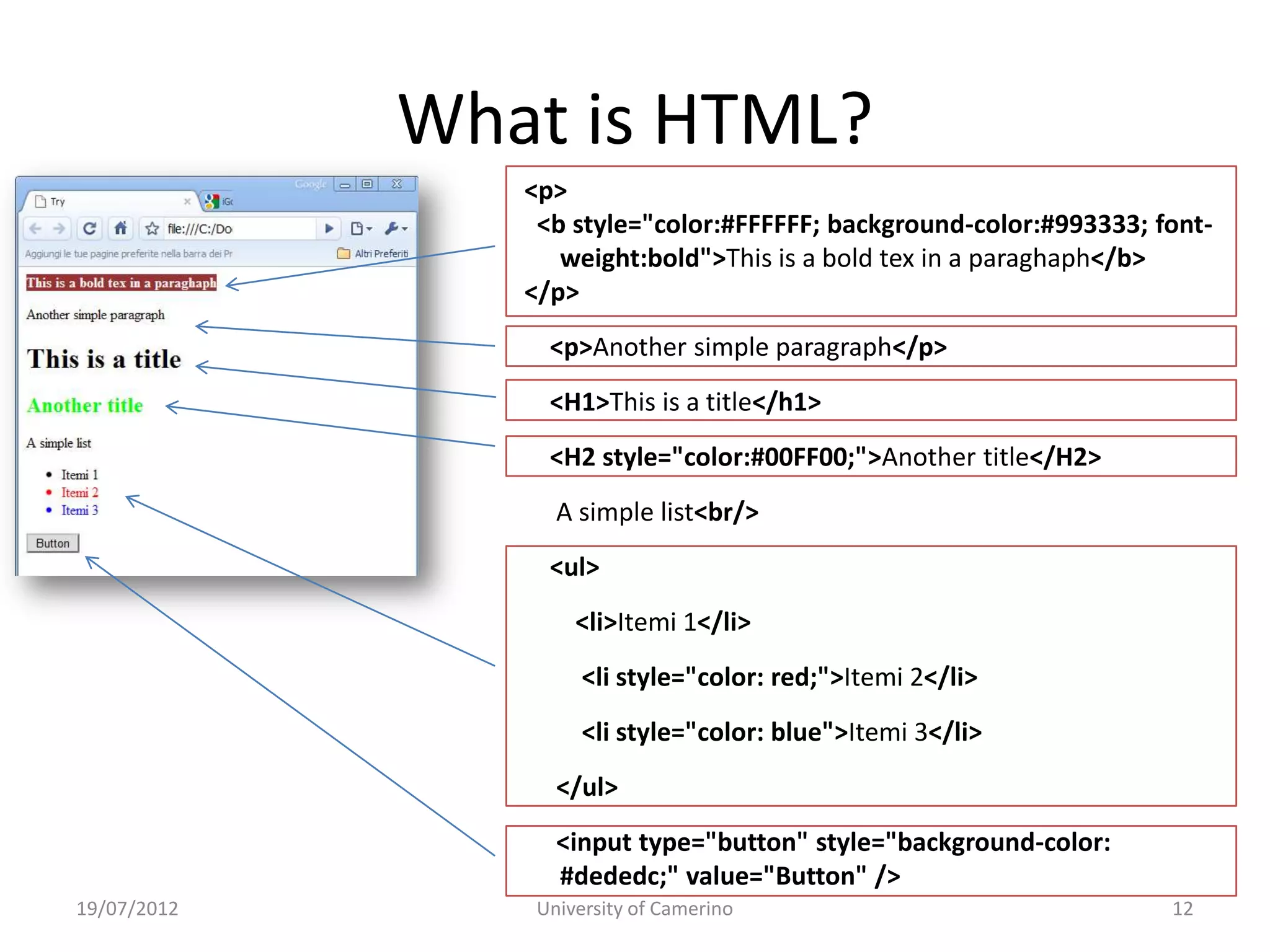
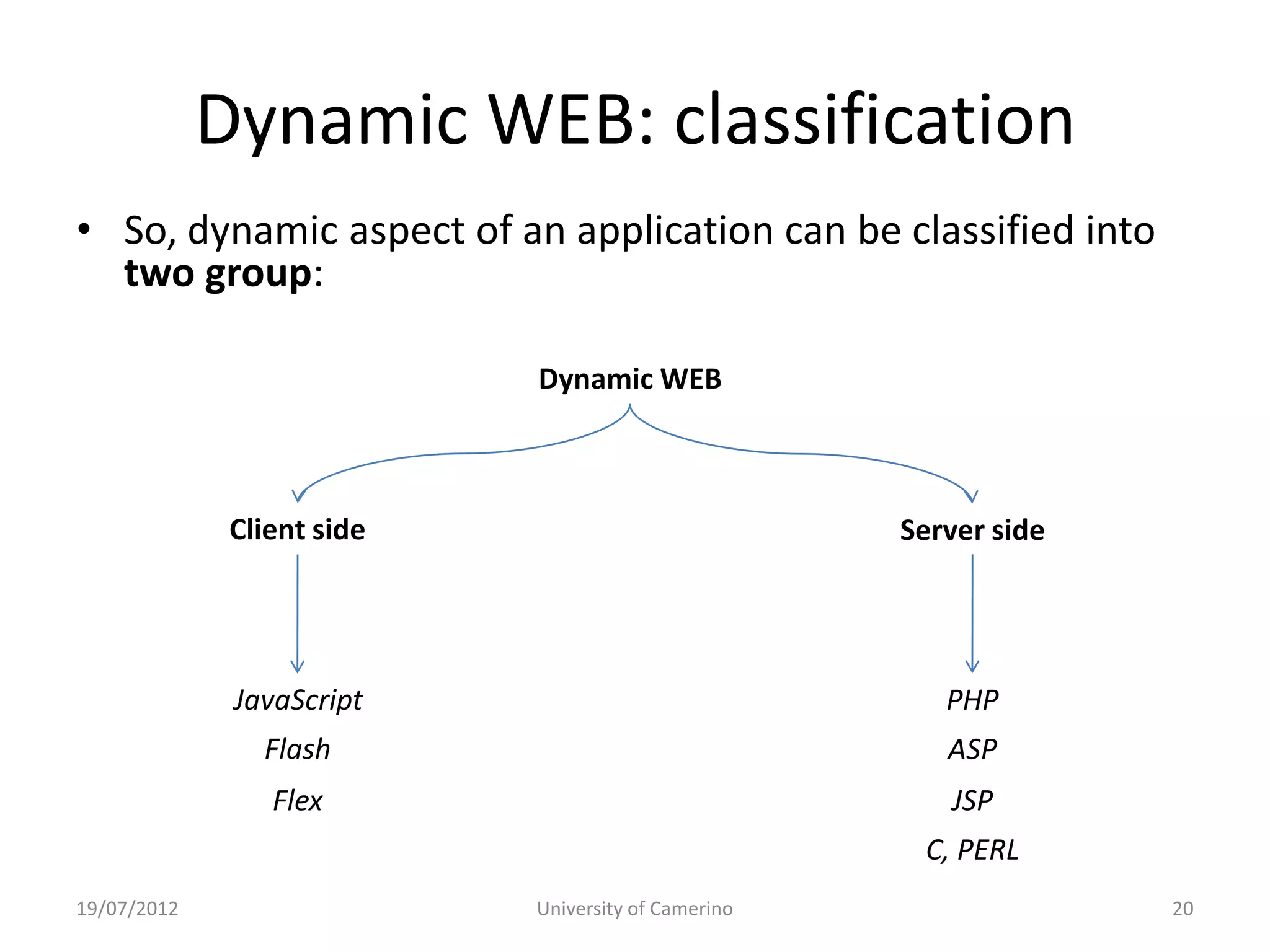
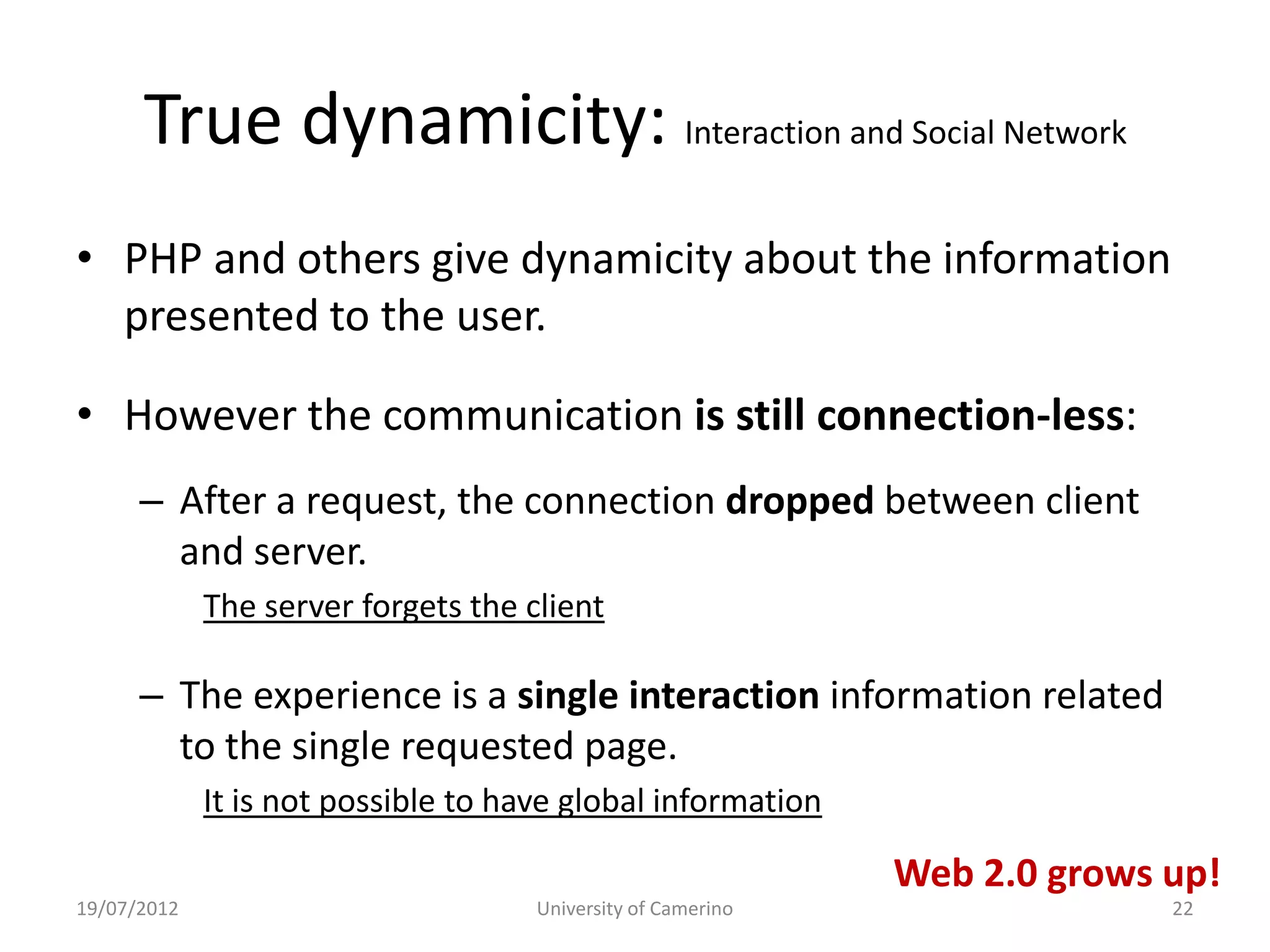
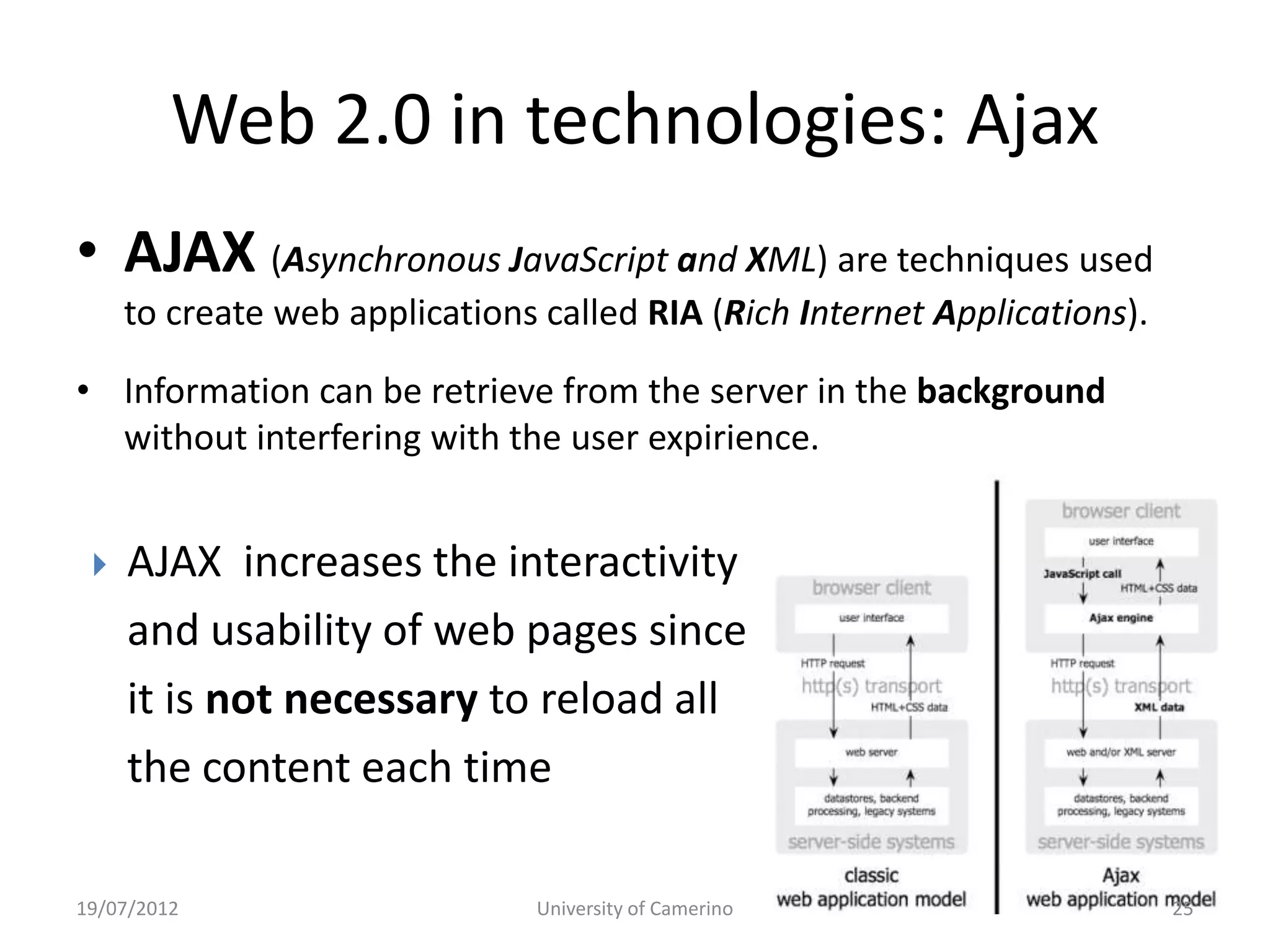
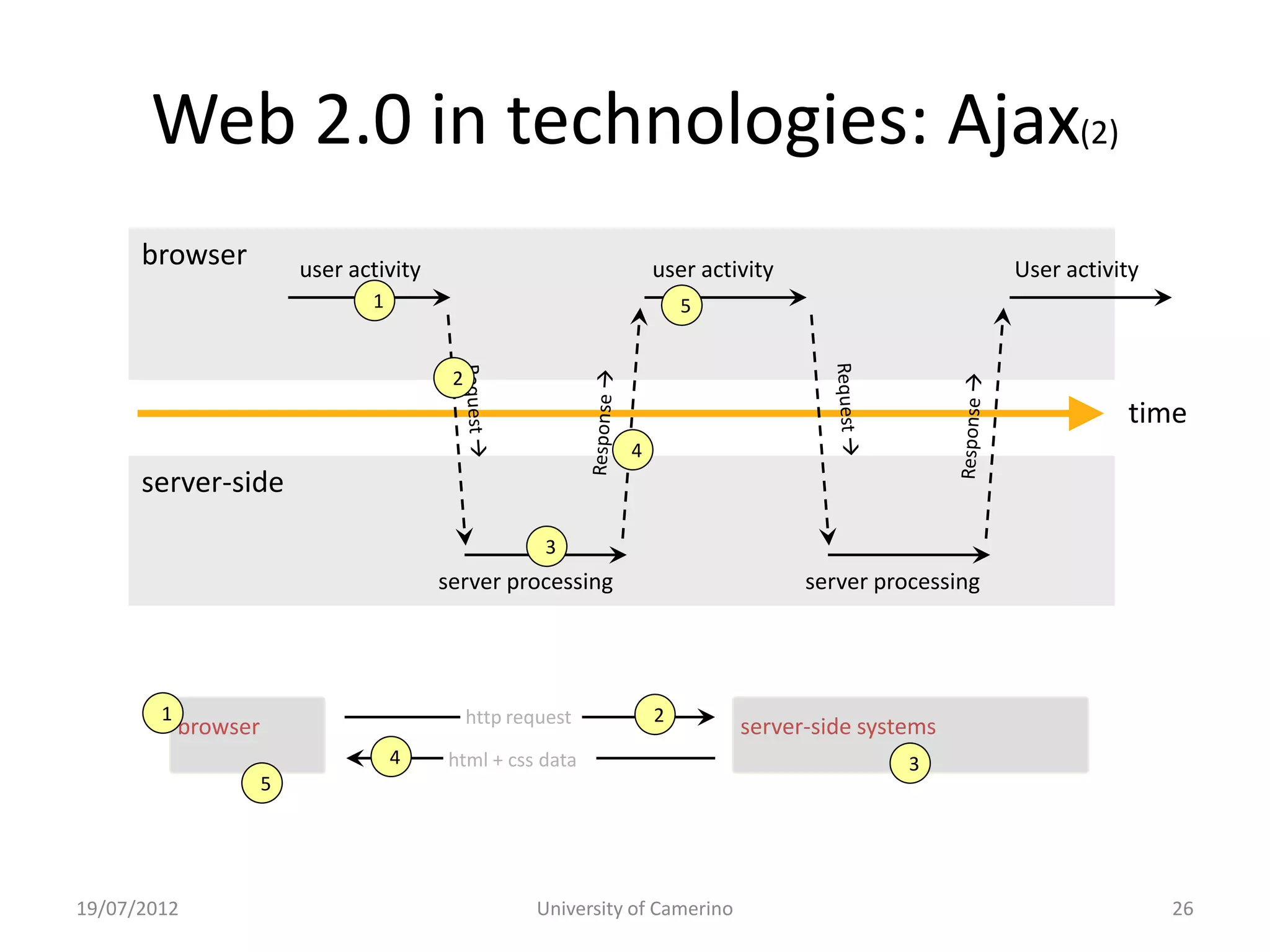
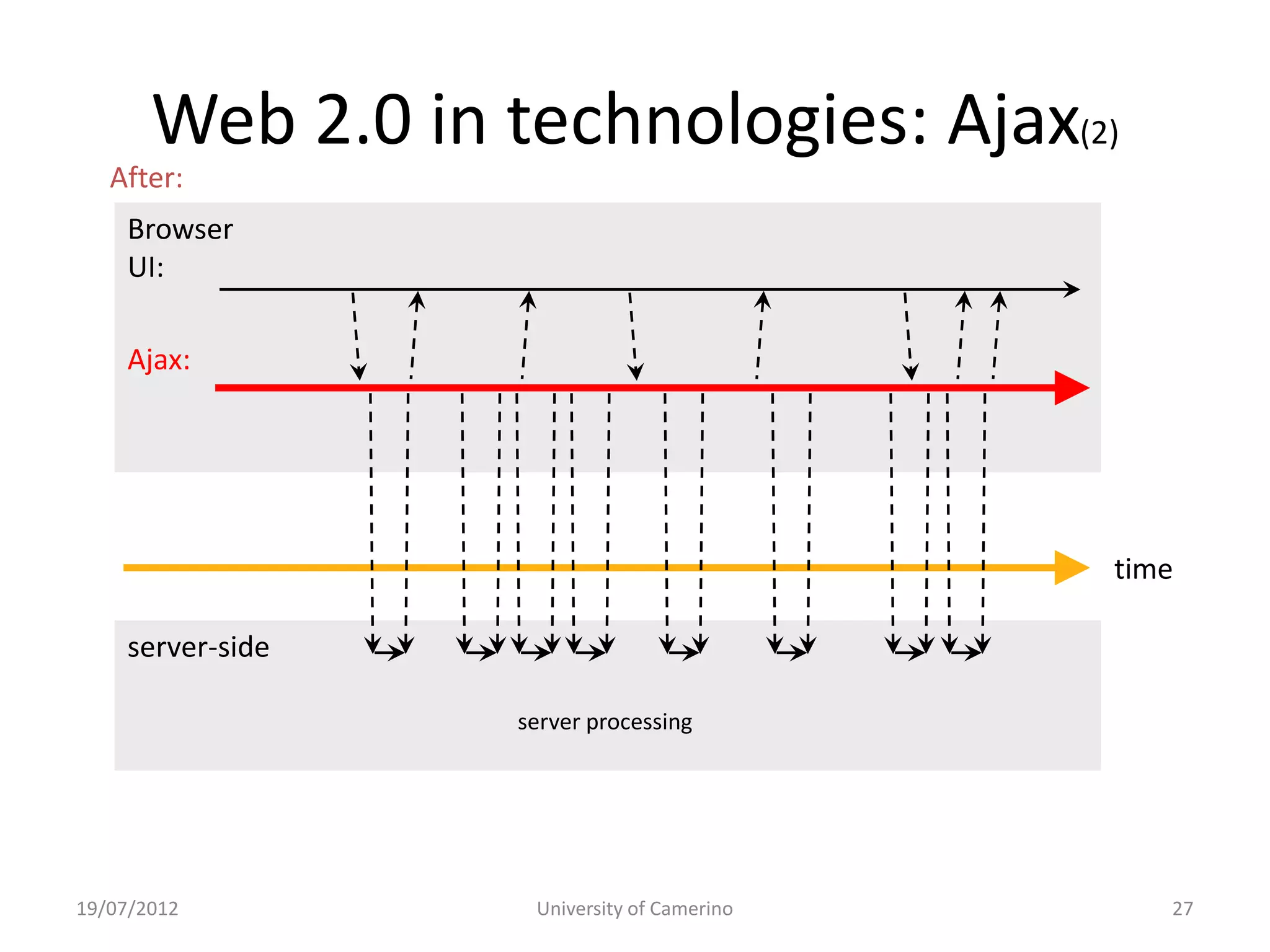
This document provides an introduction to fundamental concepts and technologies related to the Internet and World Wide Web. It discusses the differences between the Internet, which is a global system of interconnected computer networks, and the Web, which is a service that allows accessing multimedia documents over the Internet. The document then provides a brief history of the development of the Internet and Web. It explains basic Internet communication protocols and standards like TCP/IP and HTTP. It also describes HTML, CSS, and JavaScript which are key technologies for building static and dynamic Web pages.