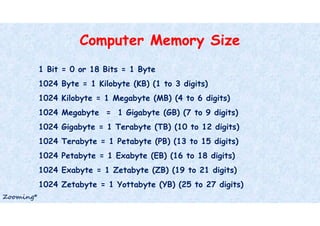
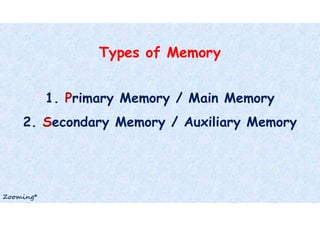
Computer memory stores data and instructions either temporarily or permanently. It comes in various types and sizes, from bits to yottabytes. Primary memory, also called main memory, is internal and integral to the CPU, providing the main working space. It is volatile and temporary. Secondary memory is external and permanent backup storage, including floppy disks, hard disks, optical disks, USB drives, and memory cards.