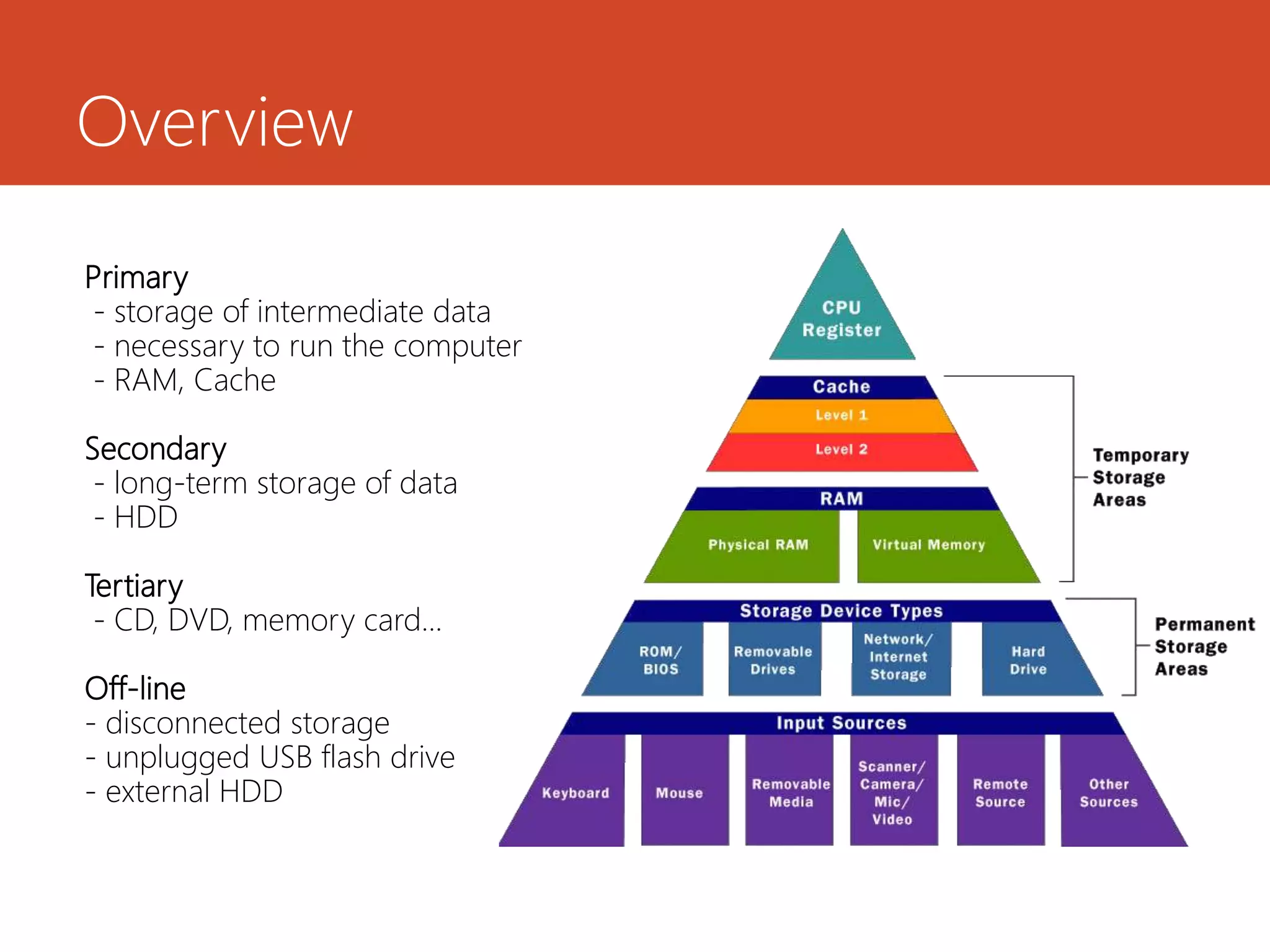
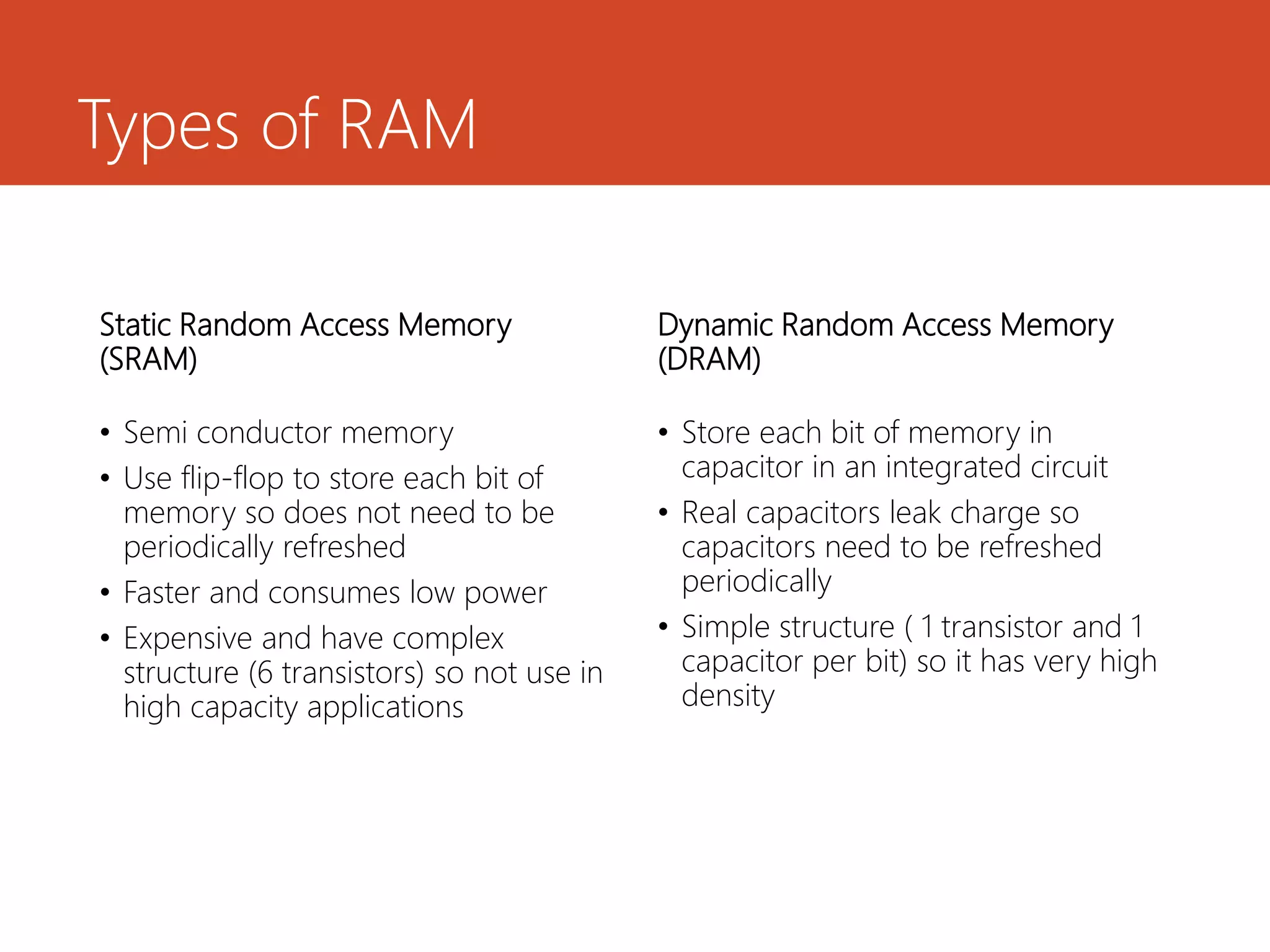
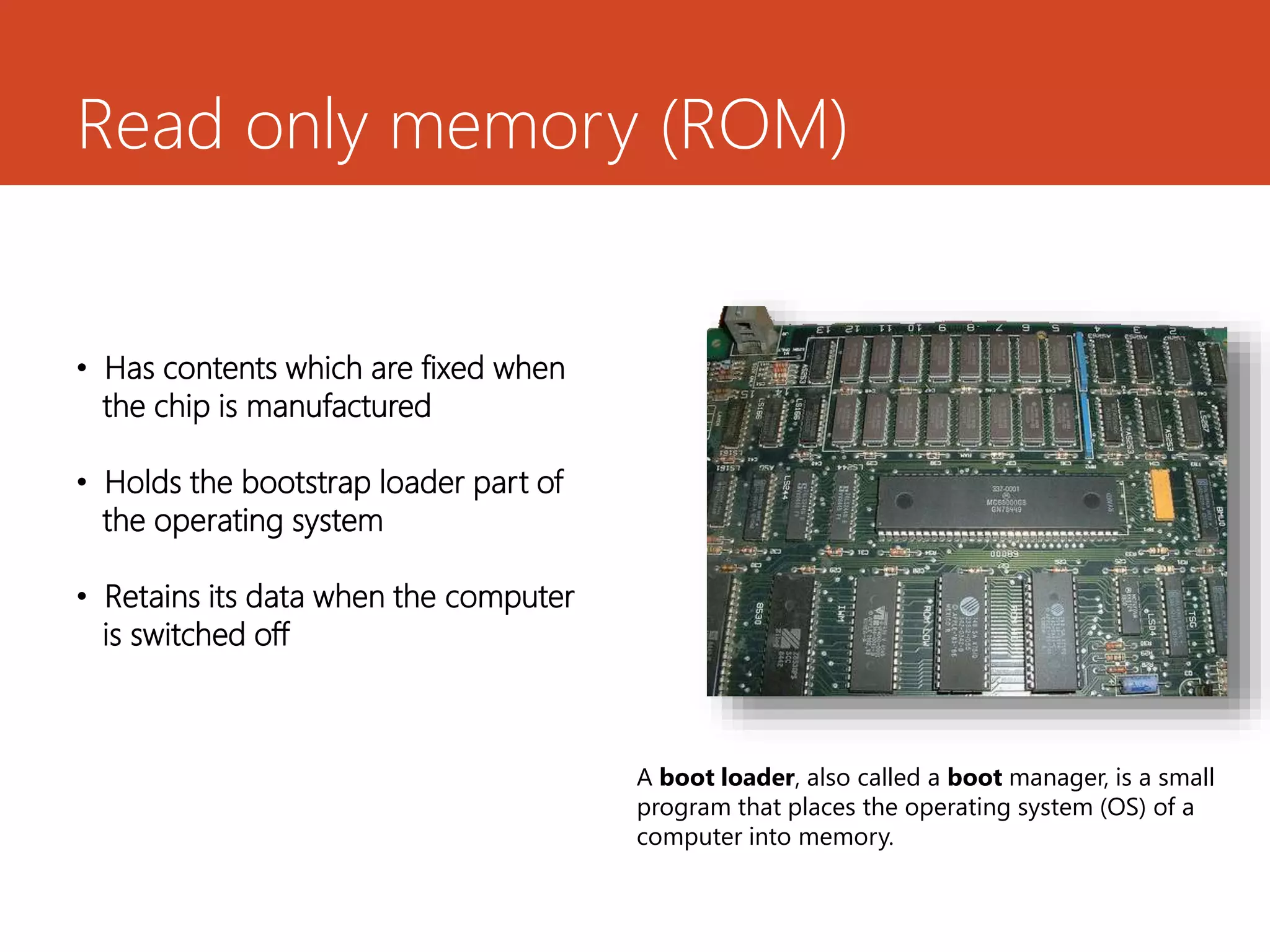
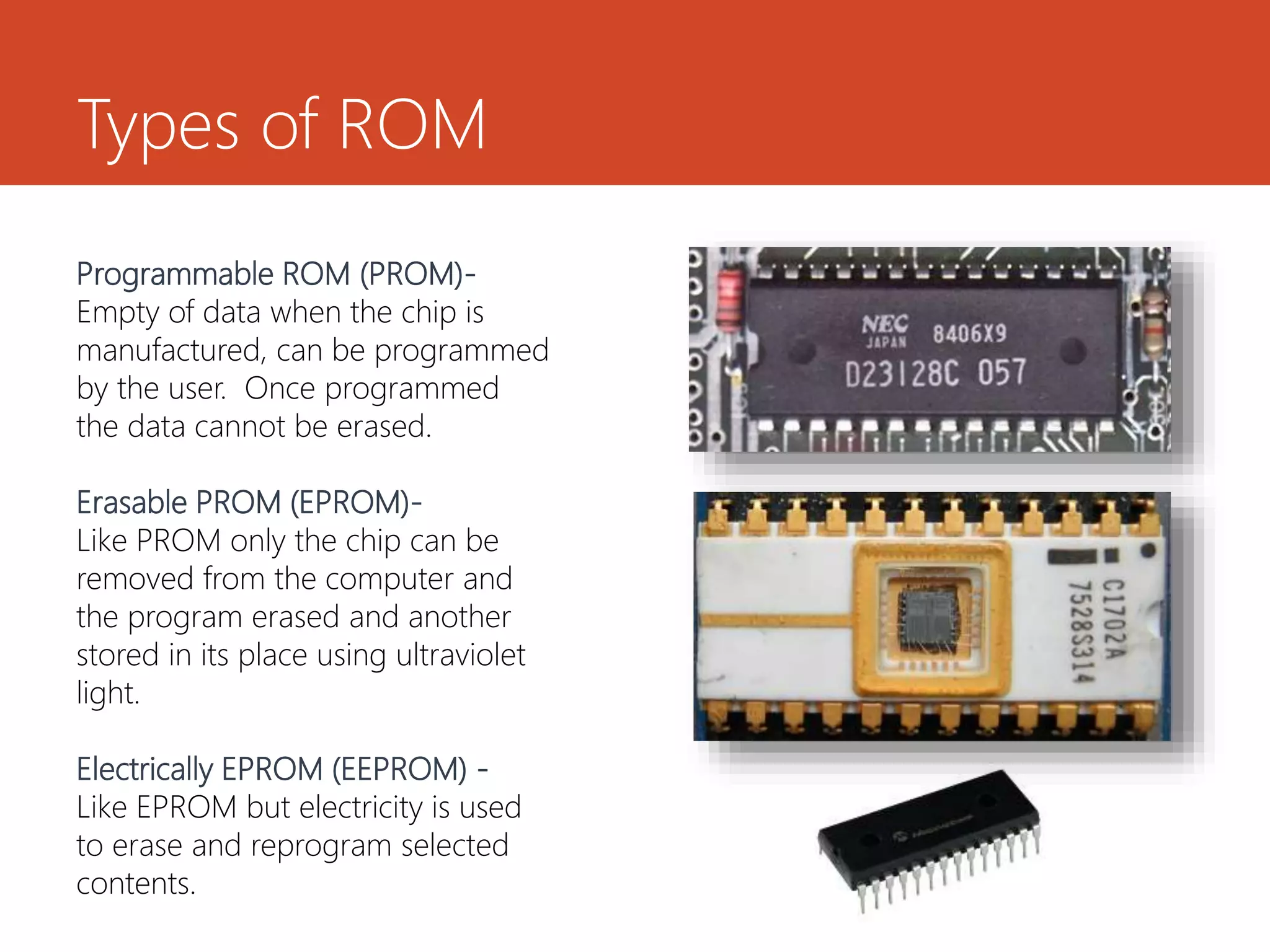
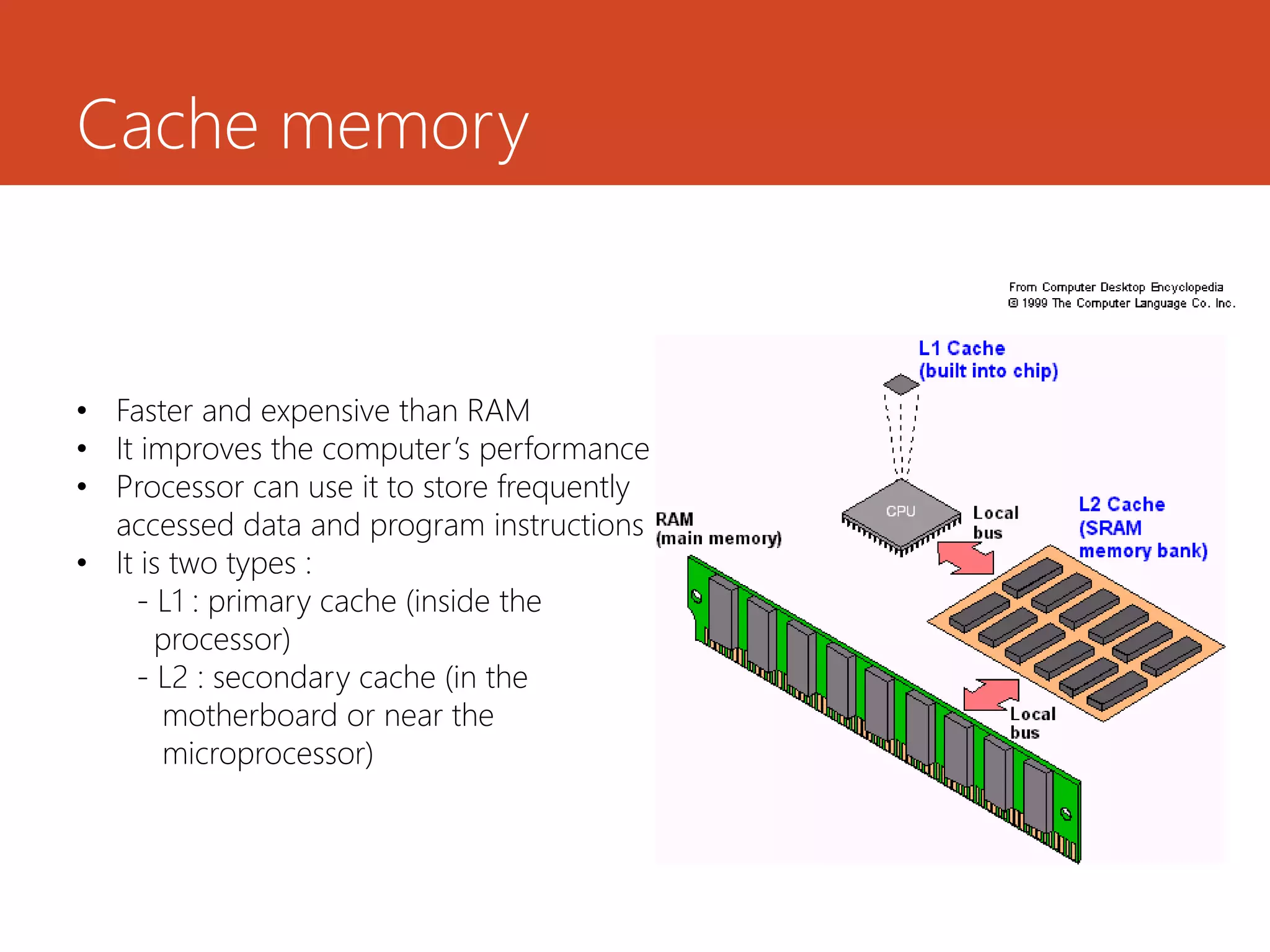
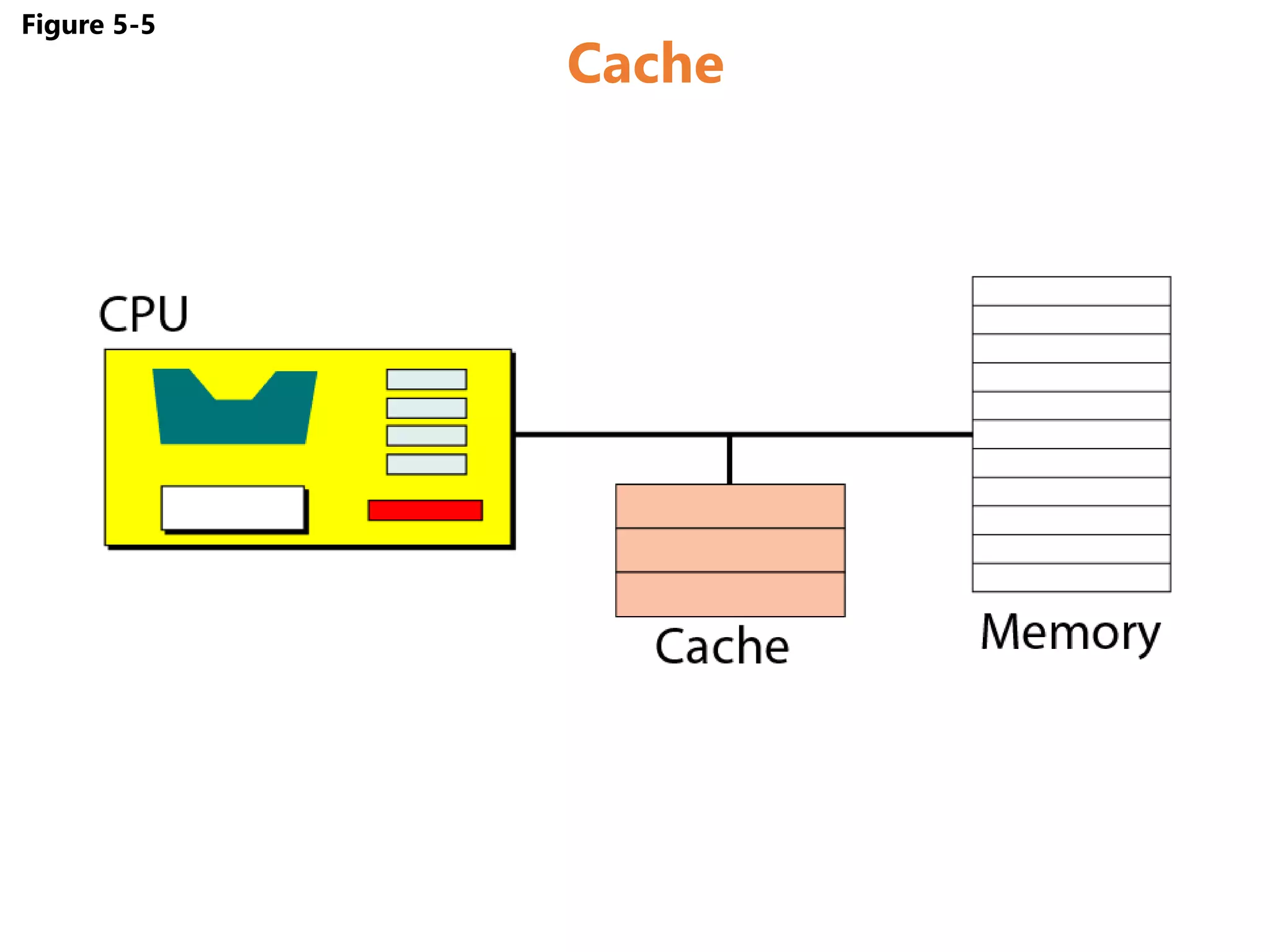
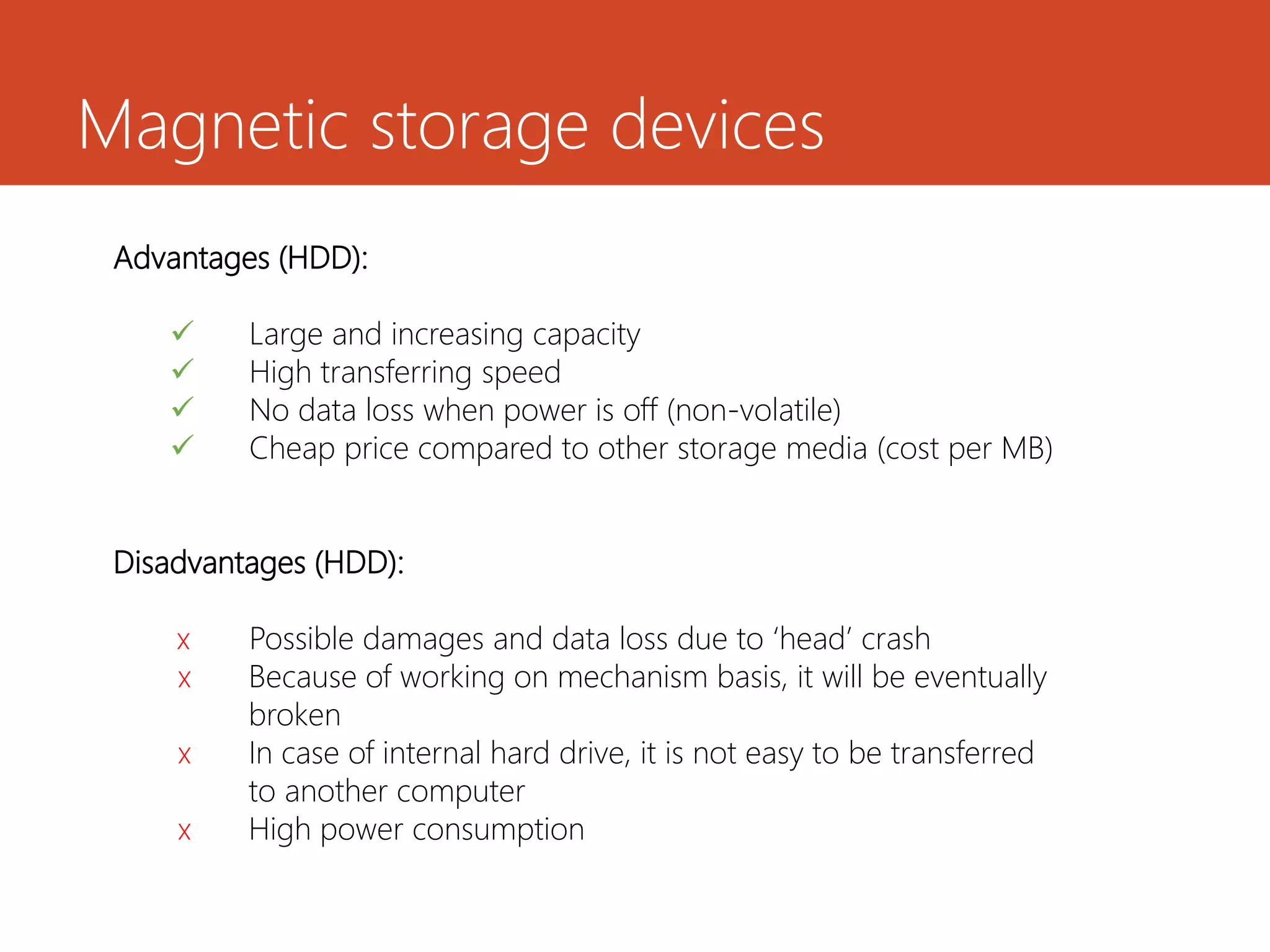
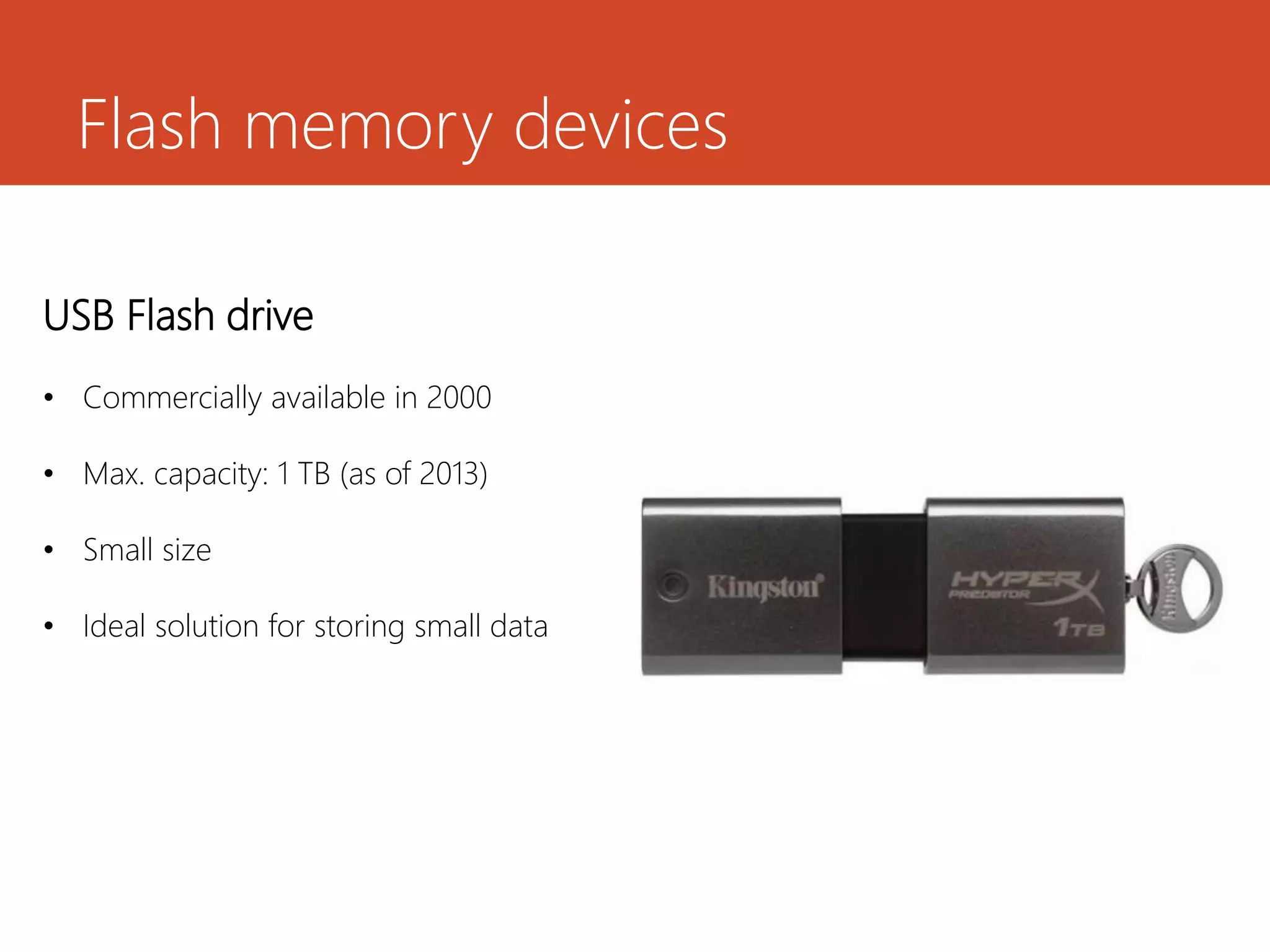
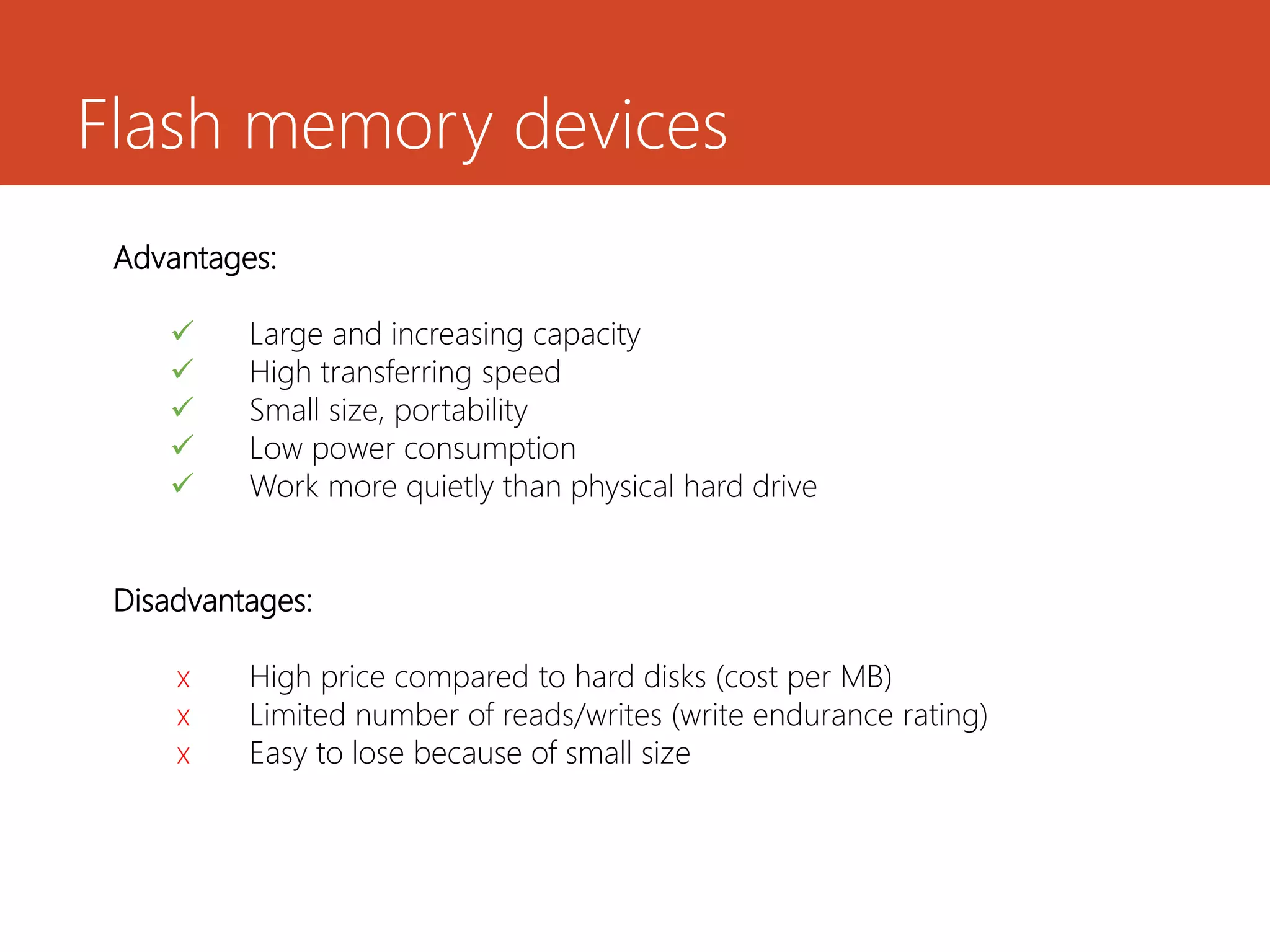
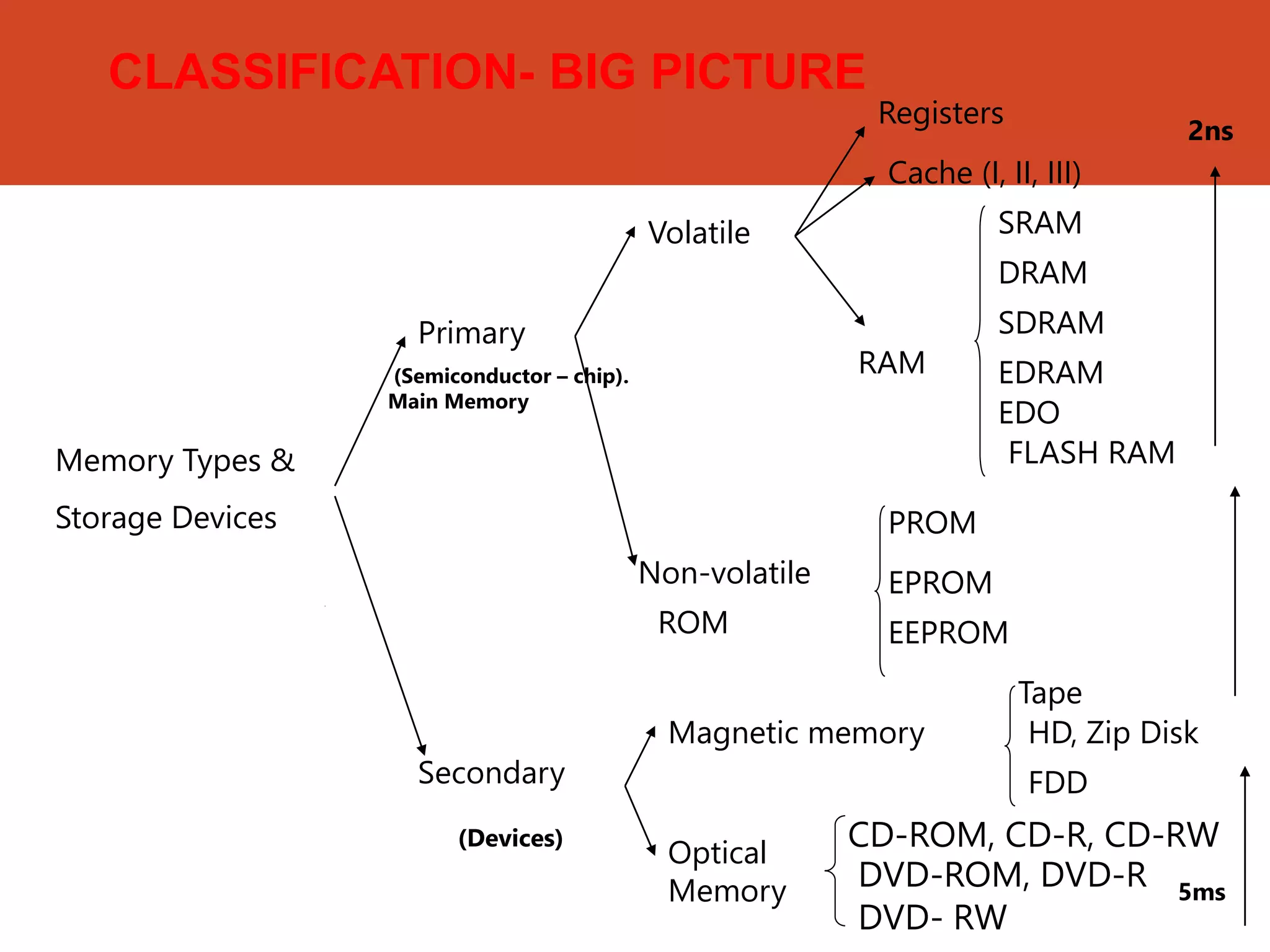
Memory and storage devices can be classified in different ways. Memory refers to temporary storage locations used by the computer's processor to perform operations, while storage refers to permanent locations used to retain data even when power is removed. There are three main types of memory: primary (RAM), secondary (cache), and tertiary (ROM). RAM is volatile and used for active programs and data, while ROM is non-volatile and holds the computer's startup instructions. Common storage devices include optical discs like CDs and DVDs, magnetic hard disks and tapes, and solid state flash memory used in USB drives and SSDs. Each have their own advantages like capacity, speed or portability.