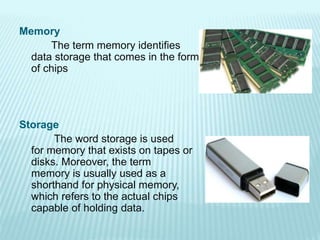
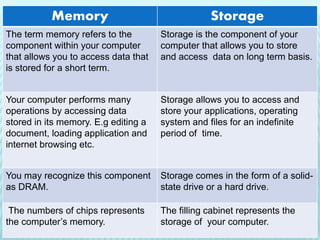
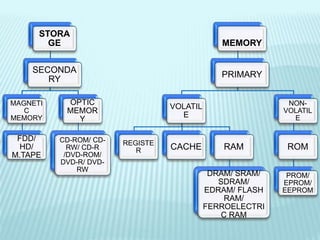
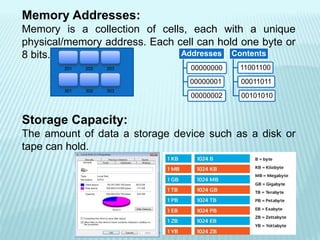
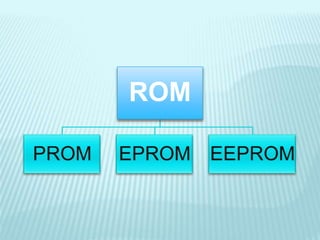
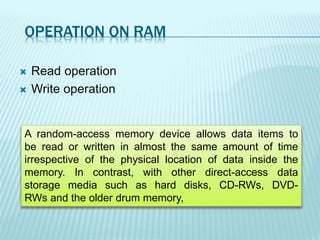
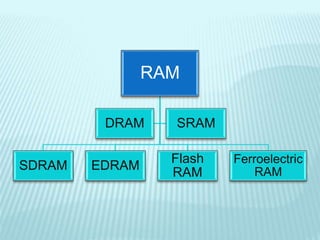
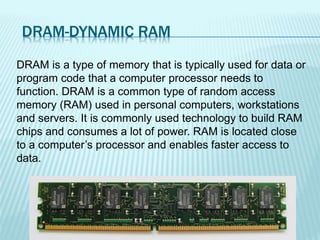
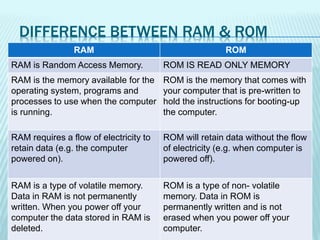
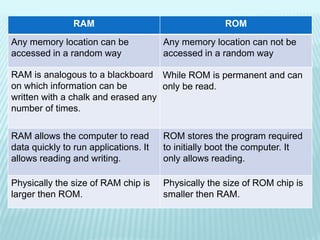
The document discusses the differences between computer memory and storage. It defines memory as temporary data storage that exists on chips, while storage refers to long-term data storage on tapes or disks. It describes primary memory (RAM) as volatile memory that allows quick access to data but must be constantly powered, while secondary storage (hard disks, optical disks) allows permanent long-term storage but is slower to access. The document provides examples of different types of memory chips (ROM, RAM) and storage devices (hard disks, optical disks).