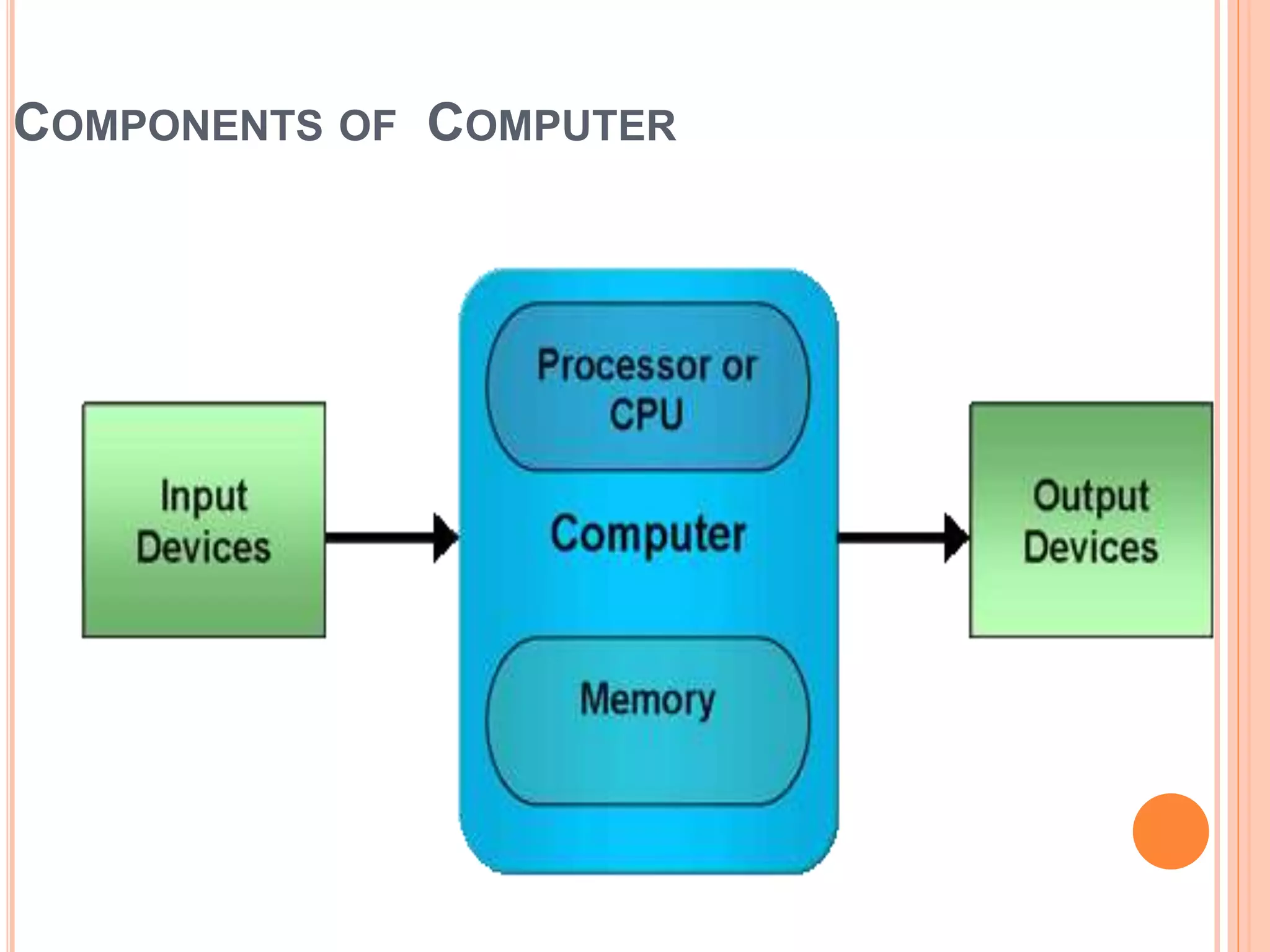
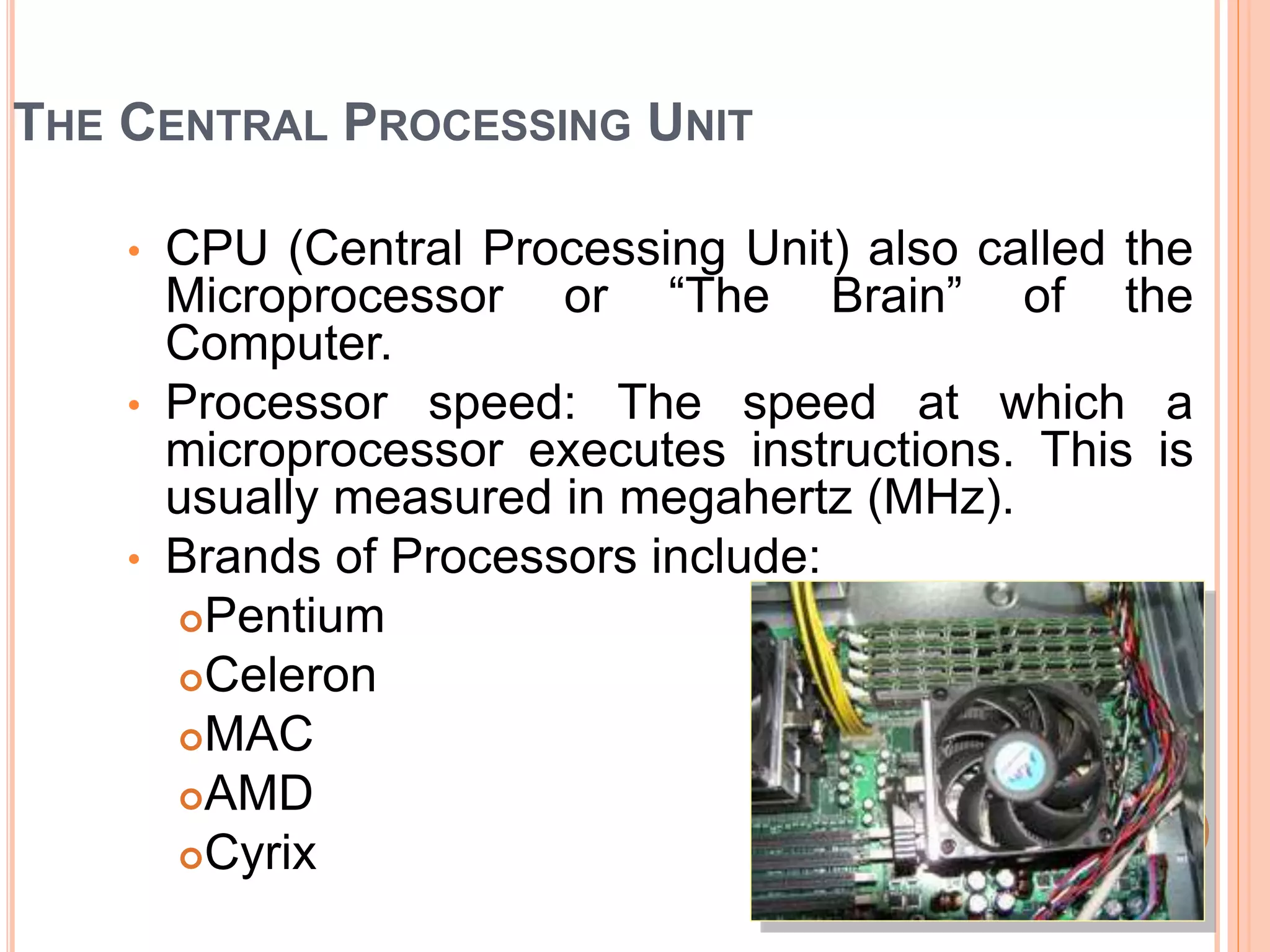
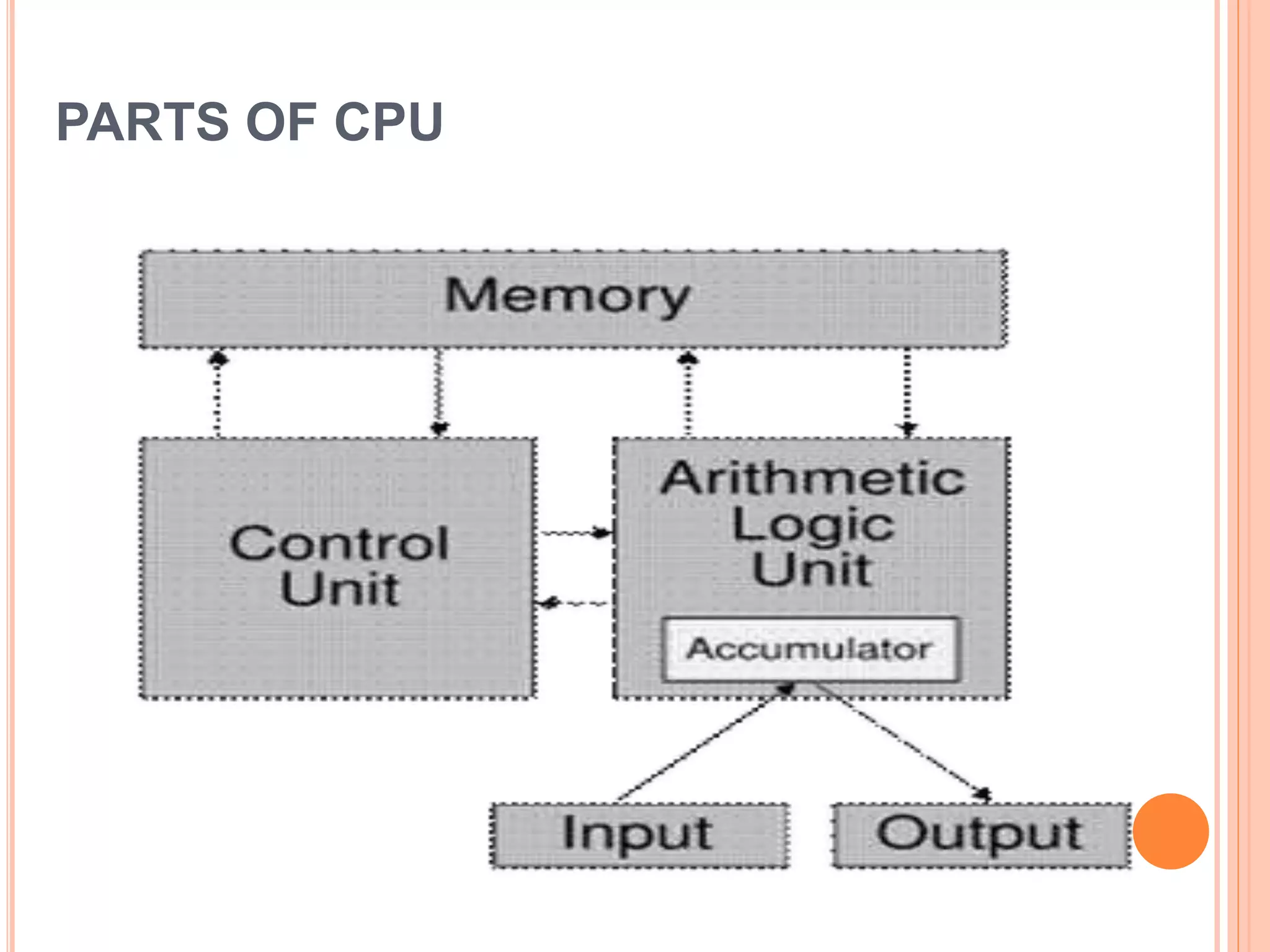
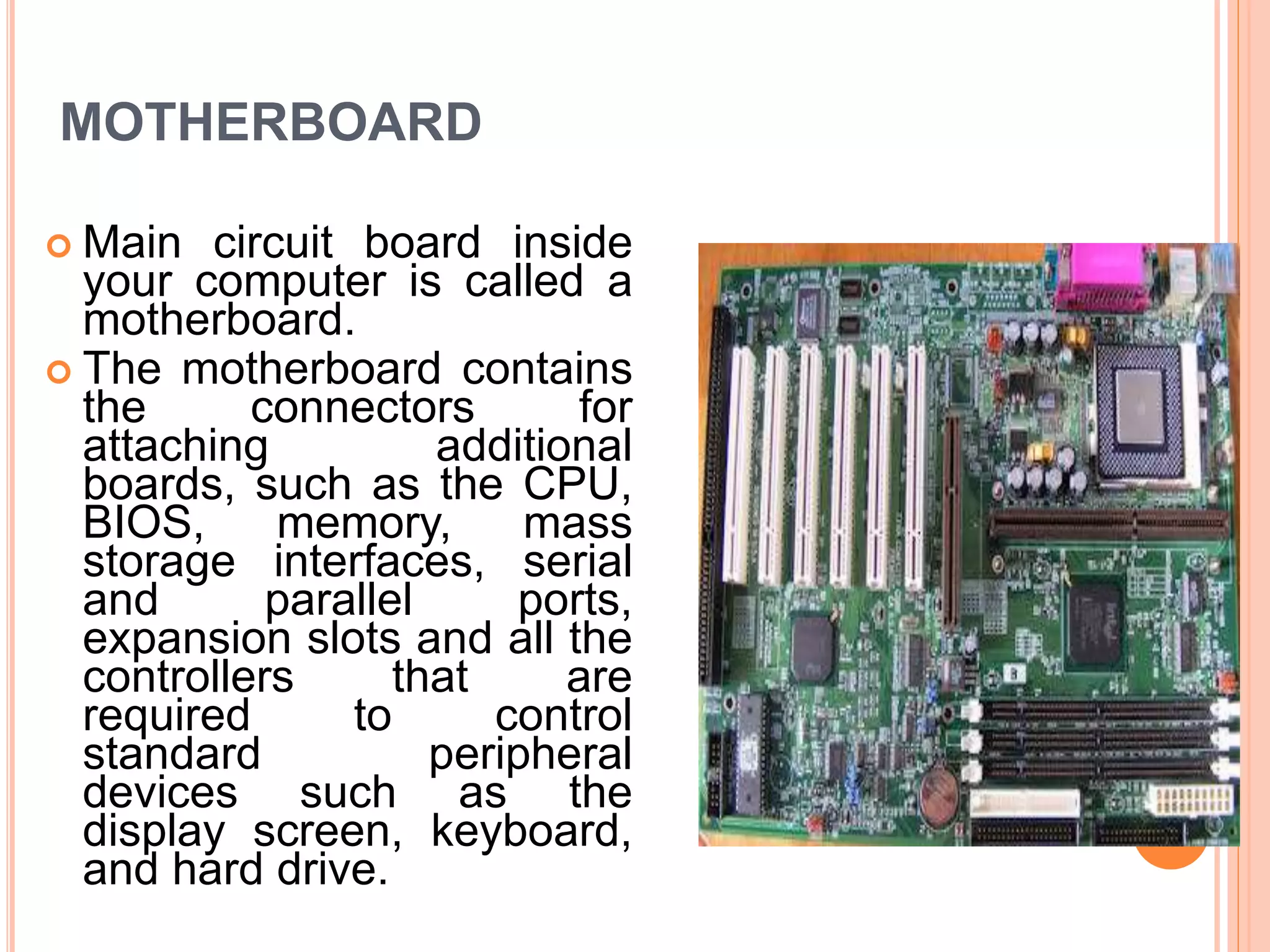
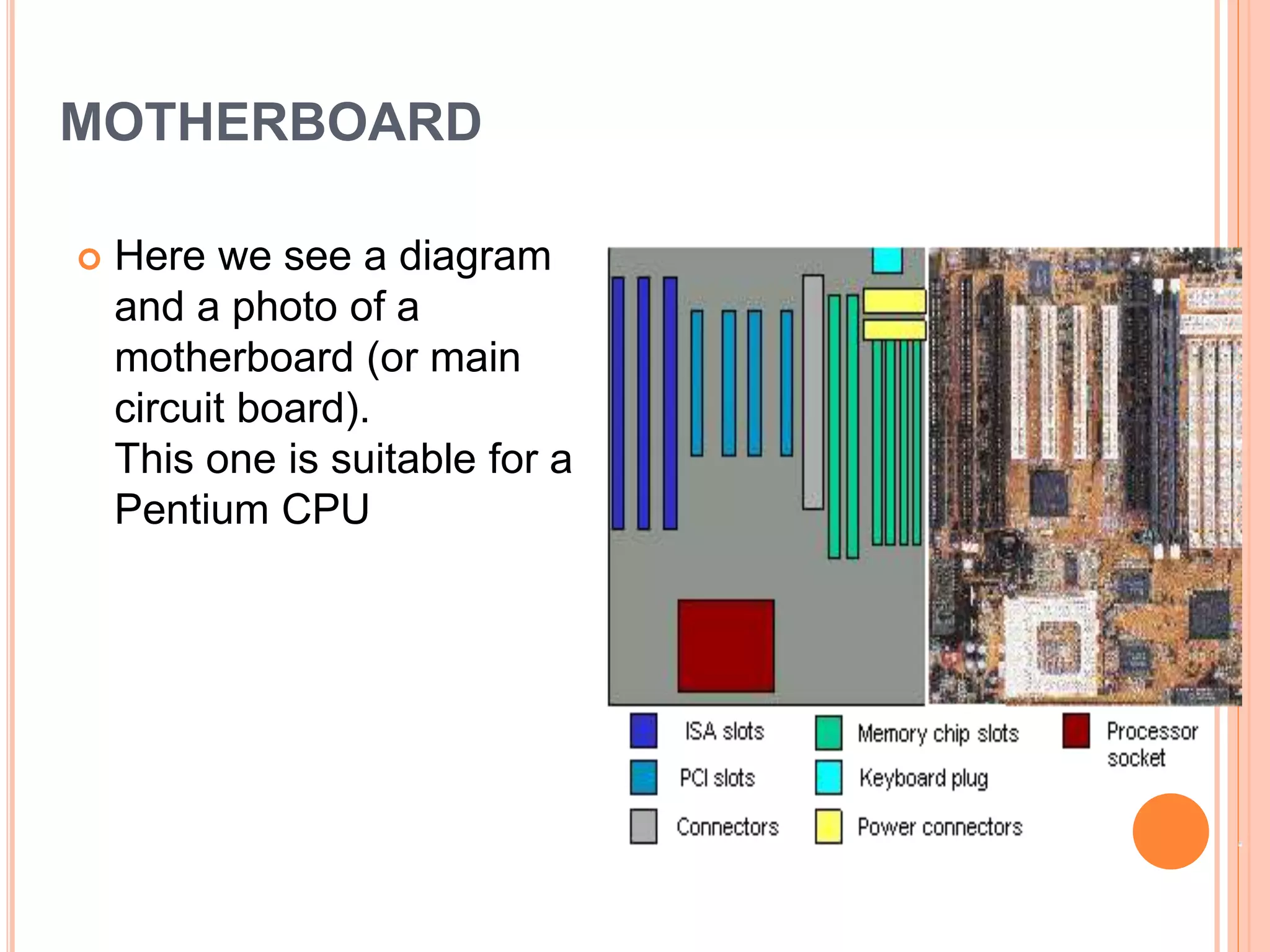
The document discusses the major components of a computer system, dividing them into hardware and software. It describes hardware components such as the central processing unit (CPU), motherboard, memory, input devices like keyboards and mice, and output devices like monitors and printers. It also discusses software types including system software like operating systems and application software. Memory, storage devices like hard drives, floppy drives, CD-ROM drives and DVD drives are also covered.