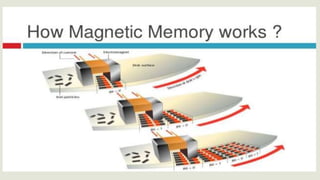
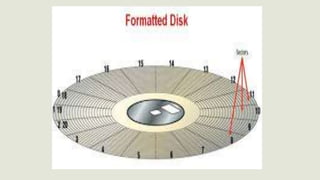
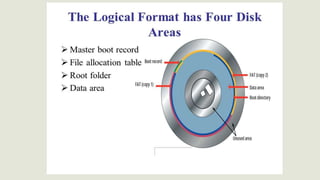
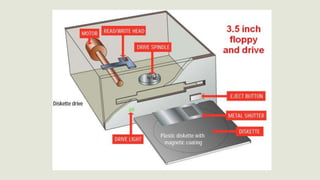
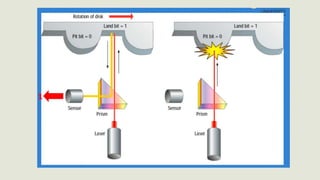
This document discusses different types of storage devices including optical storage devices. It provides a brief history of optical storage including the introduction of CDs in 1983, DVDs in 1996, and Blu-Ray in 2002. It describes how optical storage works by making marks on an optically readable medium that can be read back with a laser, and how data is stored in pits and lands. The document also outlines other storage devices like hard drives, solid state drives, flash memory, and magnetic storage devices.