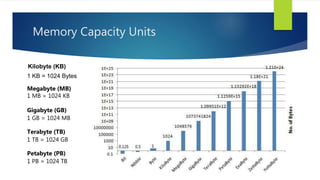
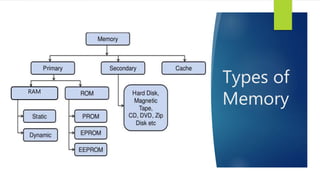
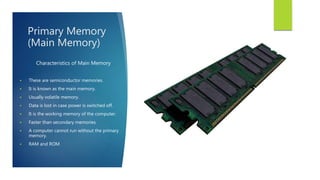
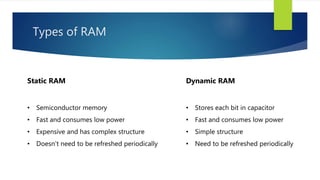
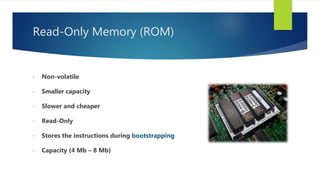
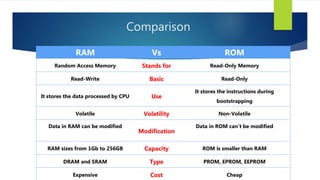
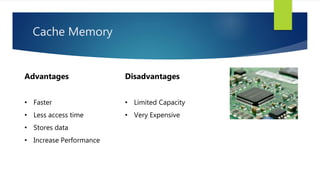
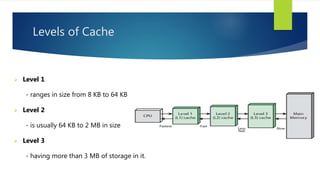
Memory is a core component of computers that allows CPUs to interact with programs and data. It was invented in the 19th century and has grown enormously in capacity over time. Memory comes in two main types - primary memory (RAM) which is volatile and holds active data and instructions, and secondary memory like hard disks which is non-volatile for long-term storage. RAM itself comes in variants like DRAM and SRAM that differ in how they store bits of data. ROM is read-only memory that stores instructions during startup. Caches provide even faster access than RAM but have limited capacity. Overall memory allows computers to function by temporarily or permanently holding the digital information they require.



![CPU and Memory contact
Memory consists of cells where the data is
stored i.e. numbers, instruction etc.
The CPU accesses each location in memory by
using a unique number, called a memory
address
Index [3] is 11
100
101
110
10
11
101
110
10
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Address => Data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memory-200605060027/85/Complete-Computer-Memory-Information-4-320.jpg)