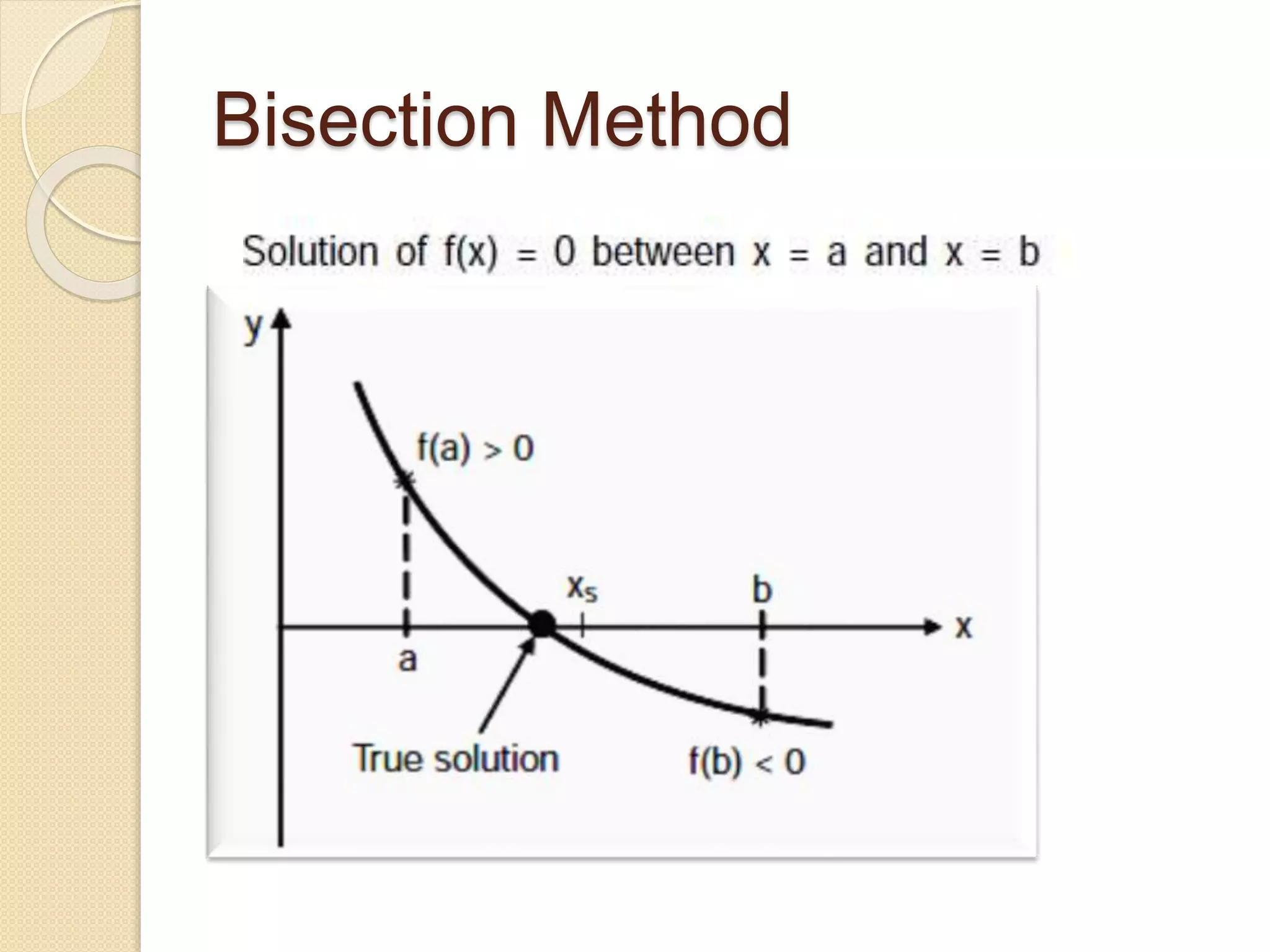
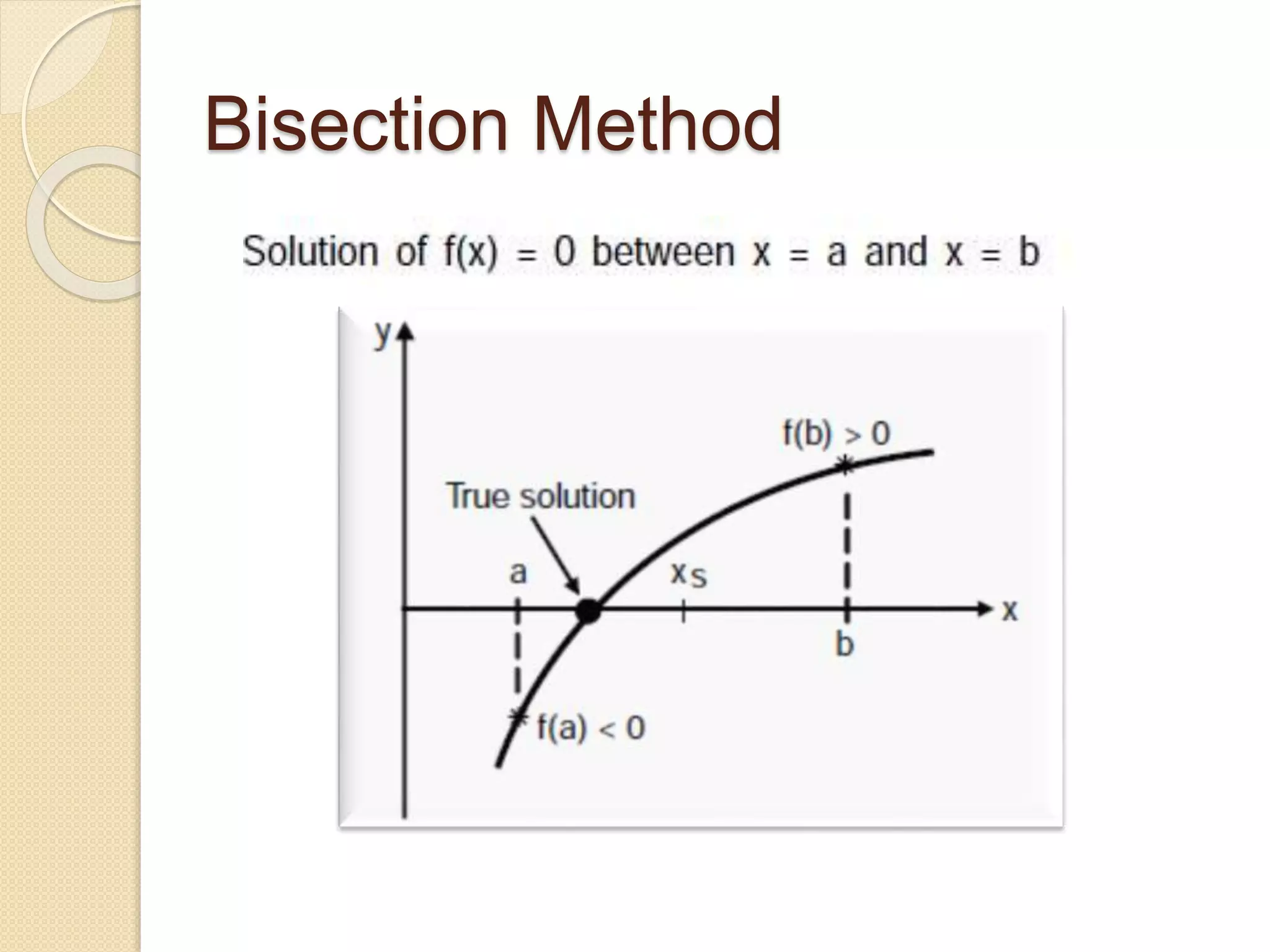
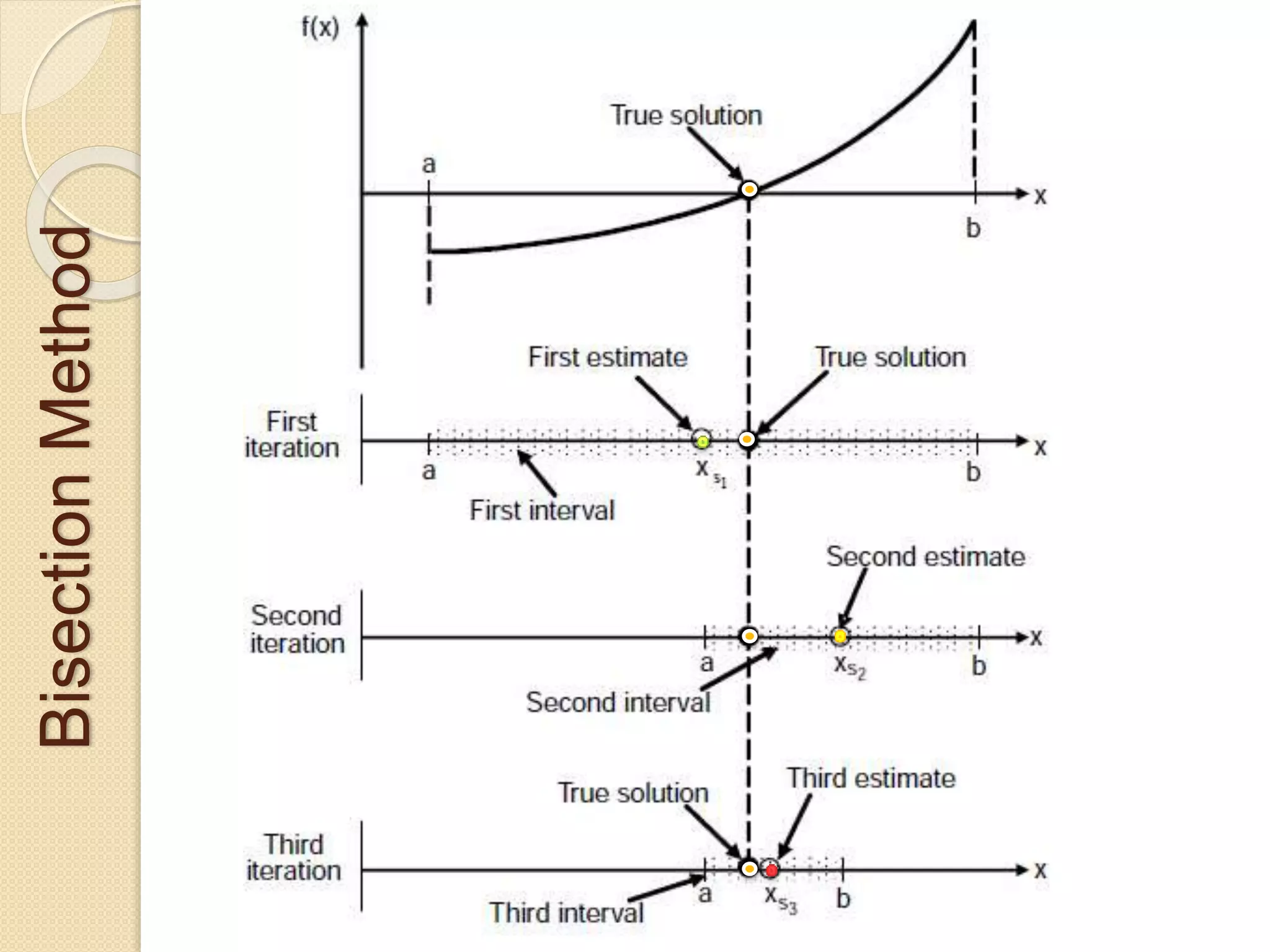
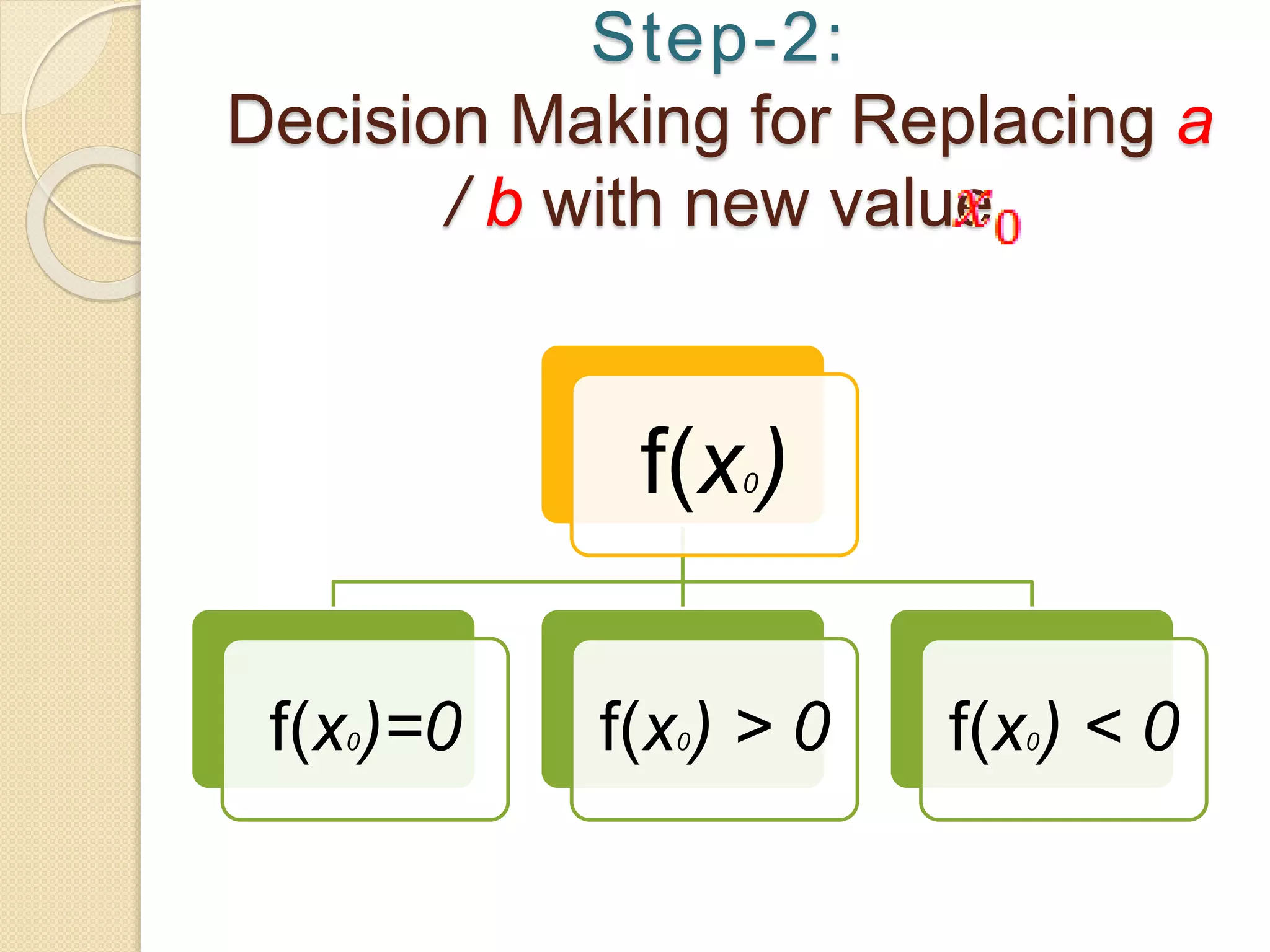
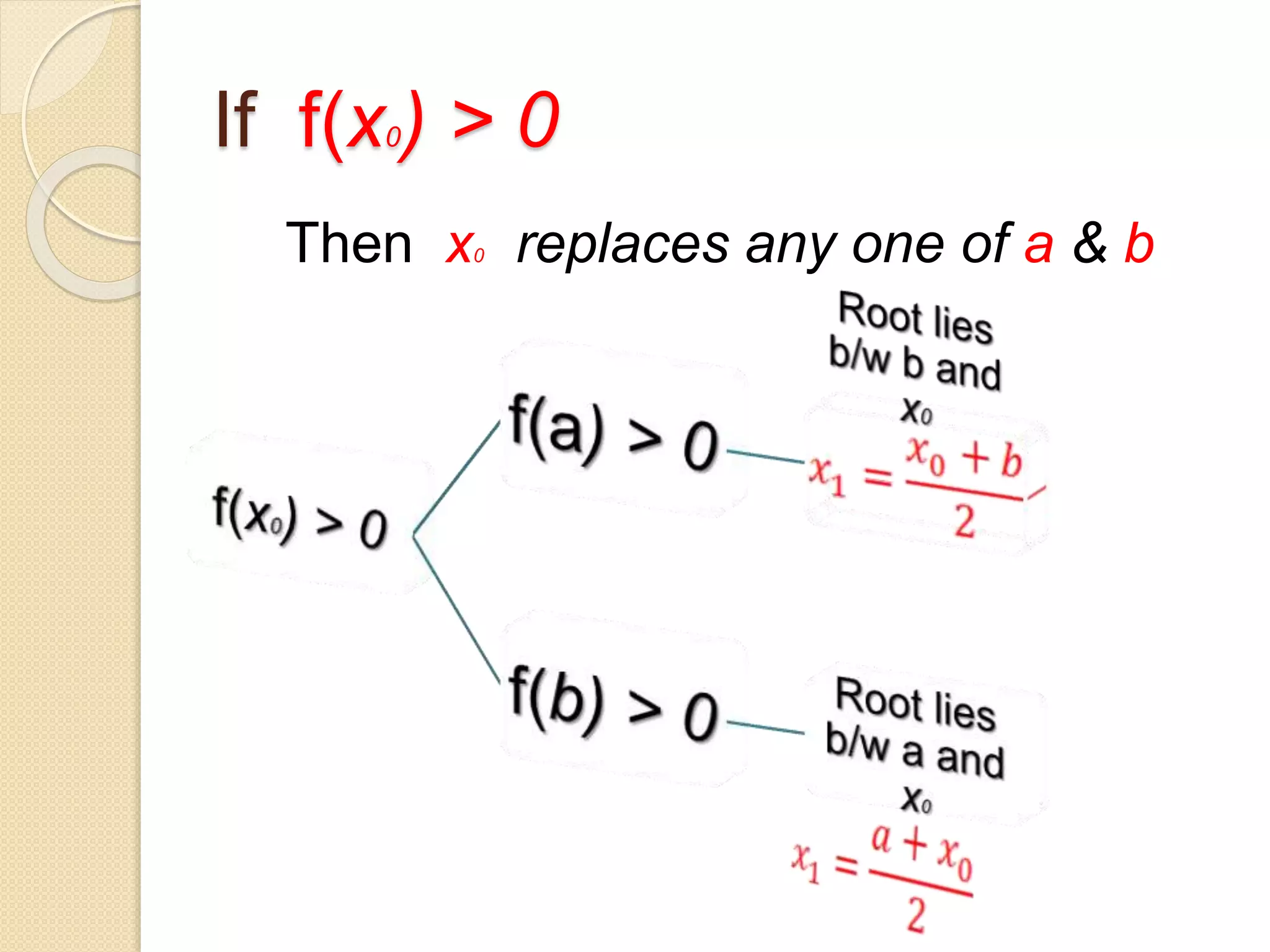
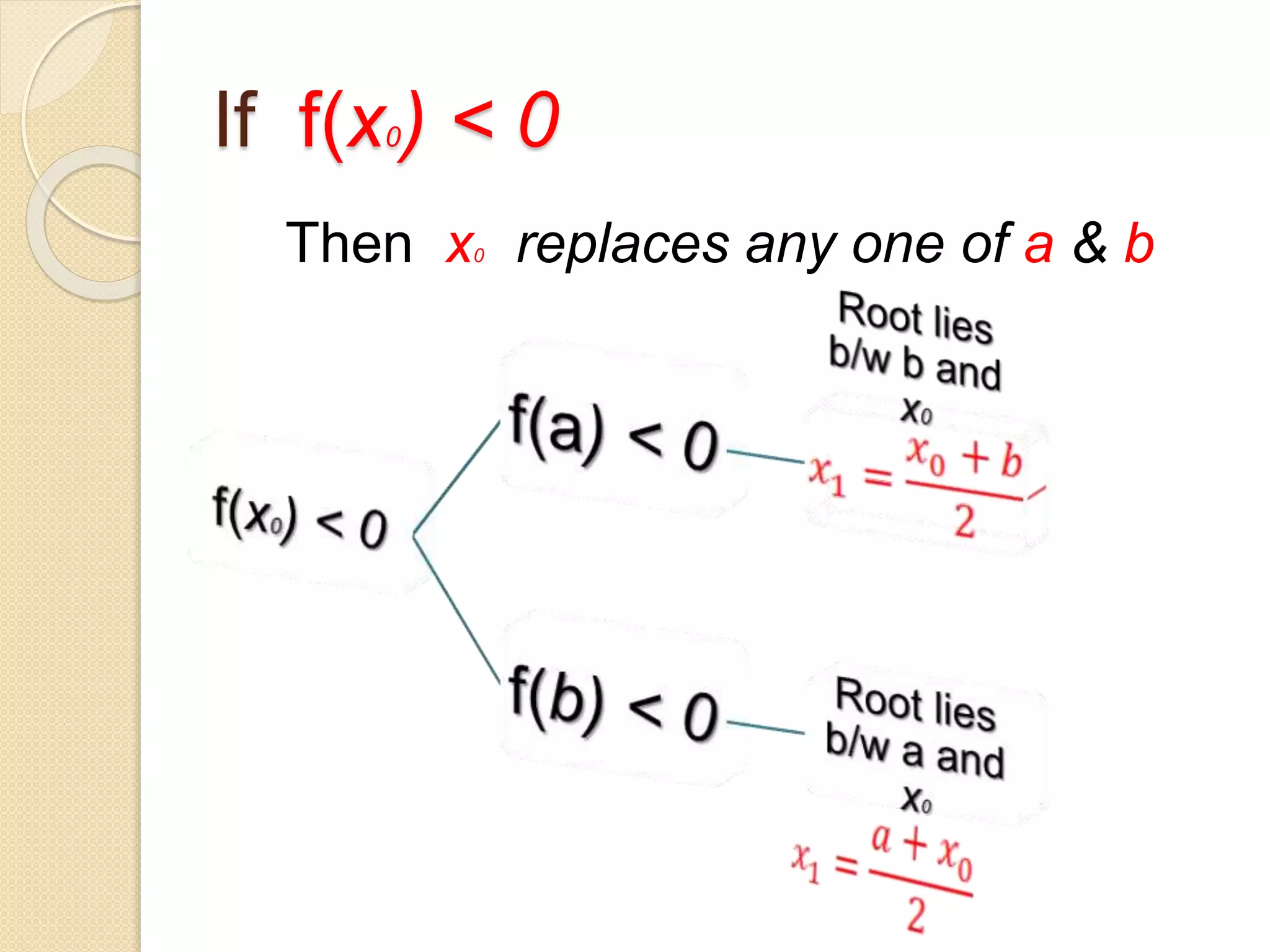
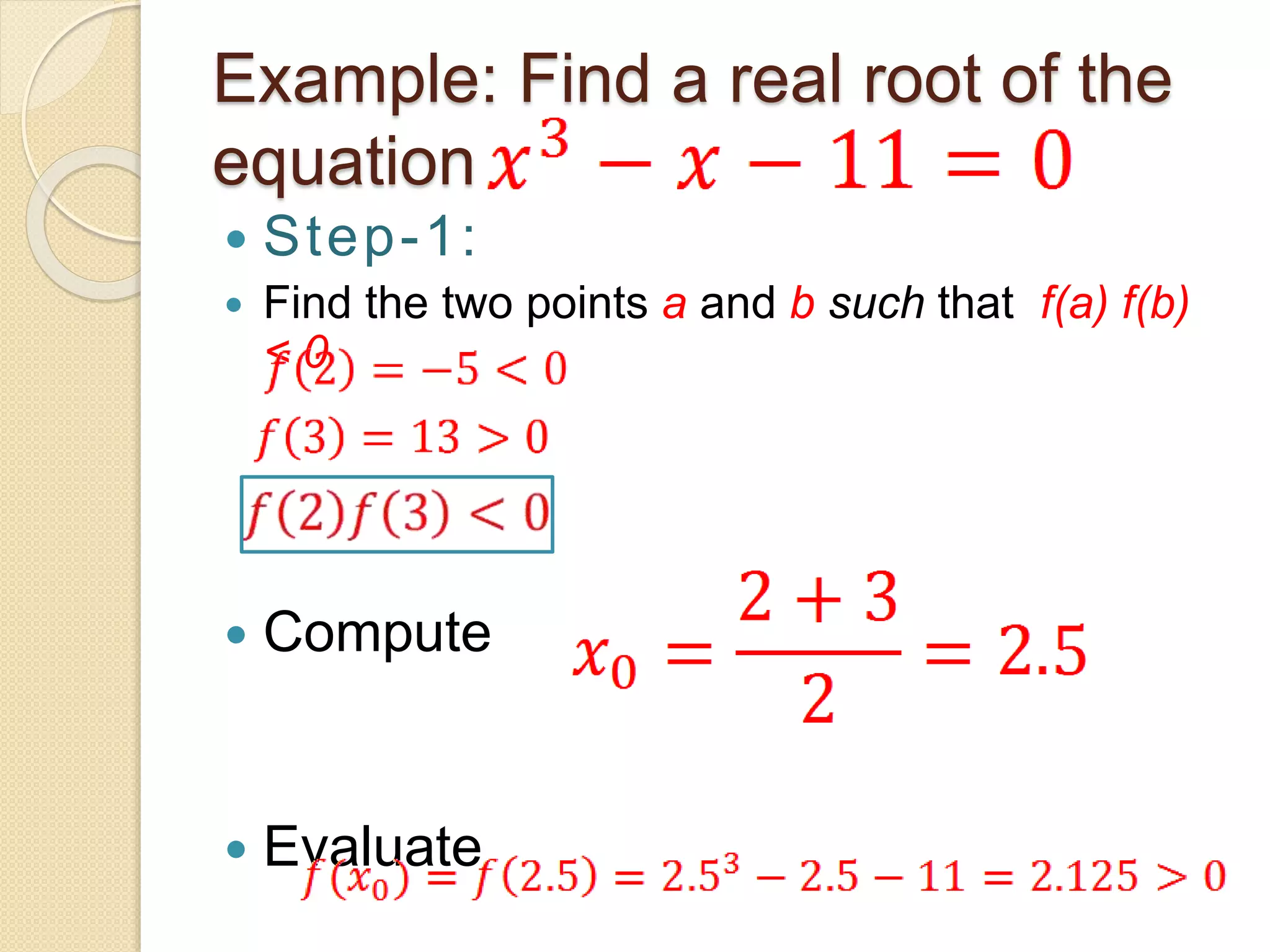
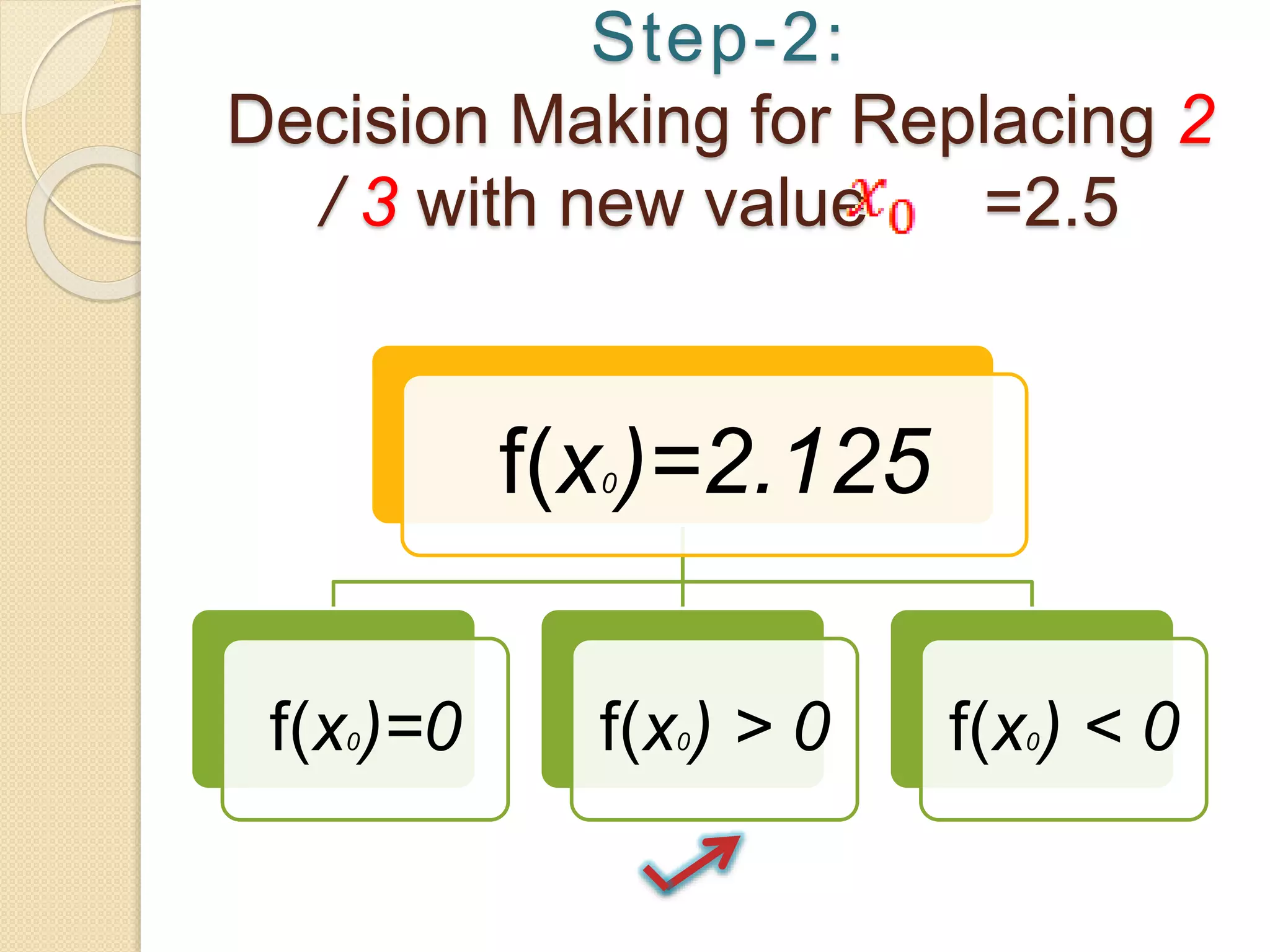
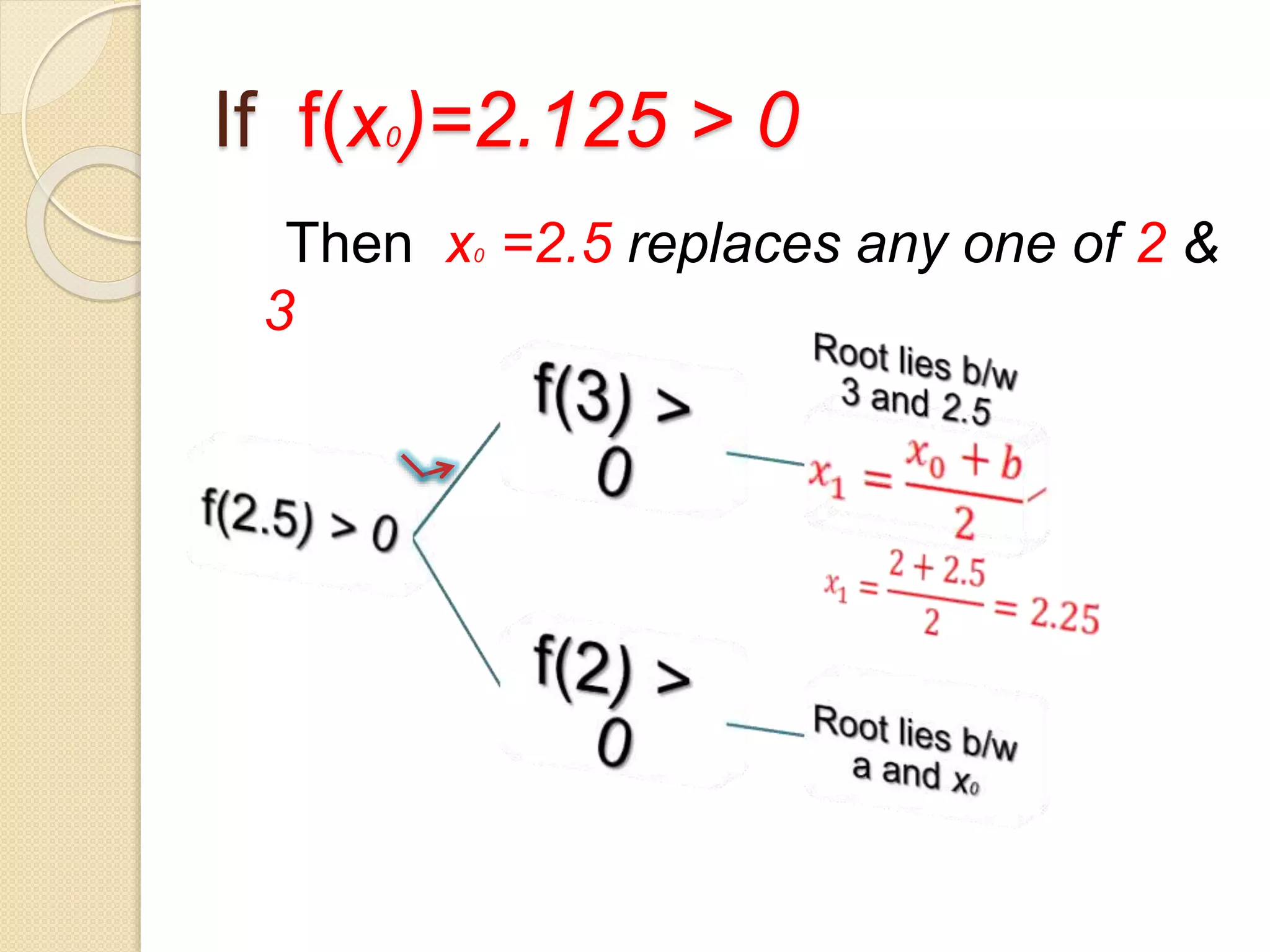
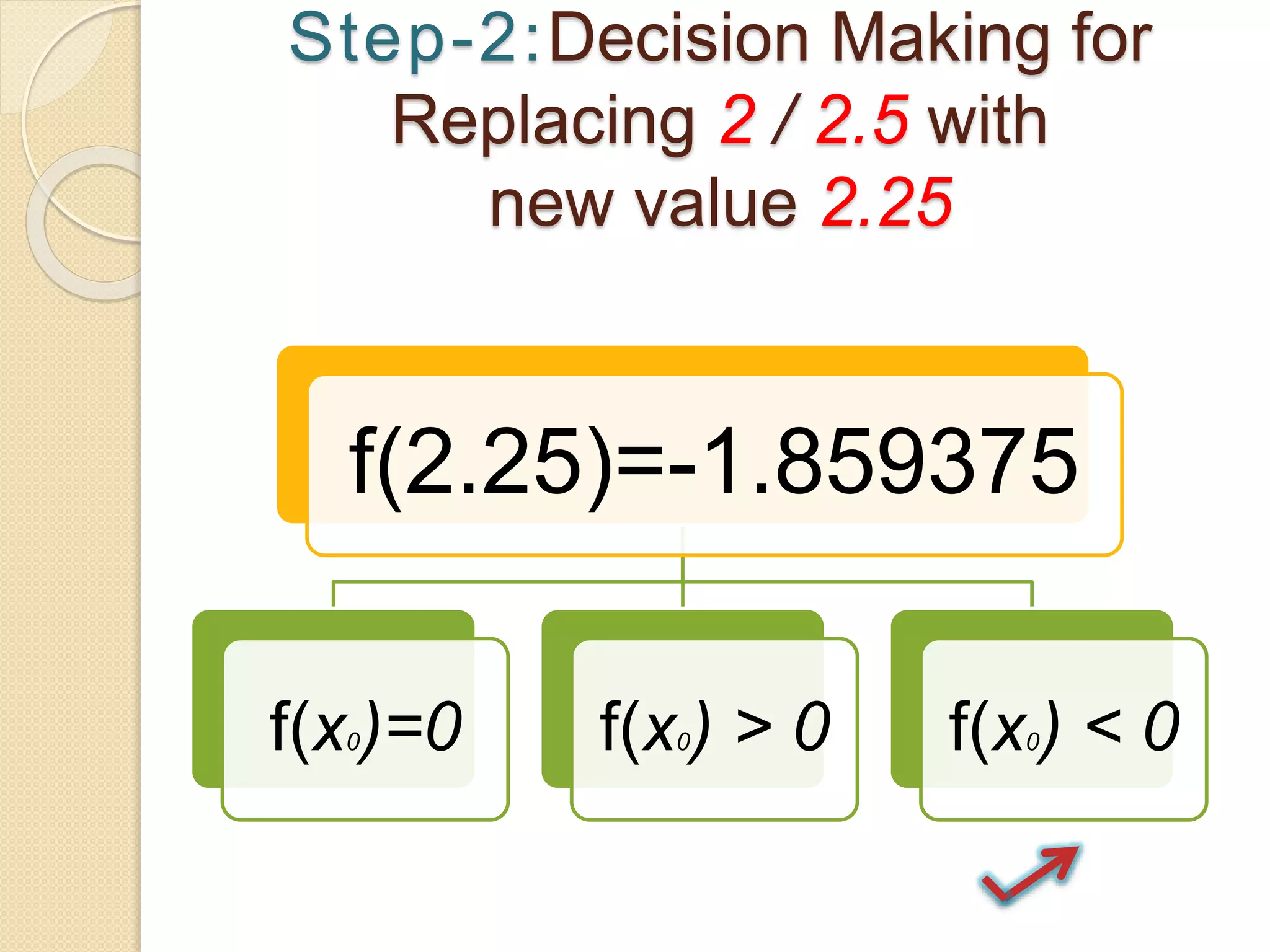
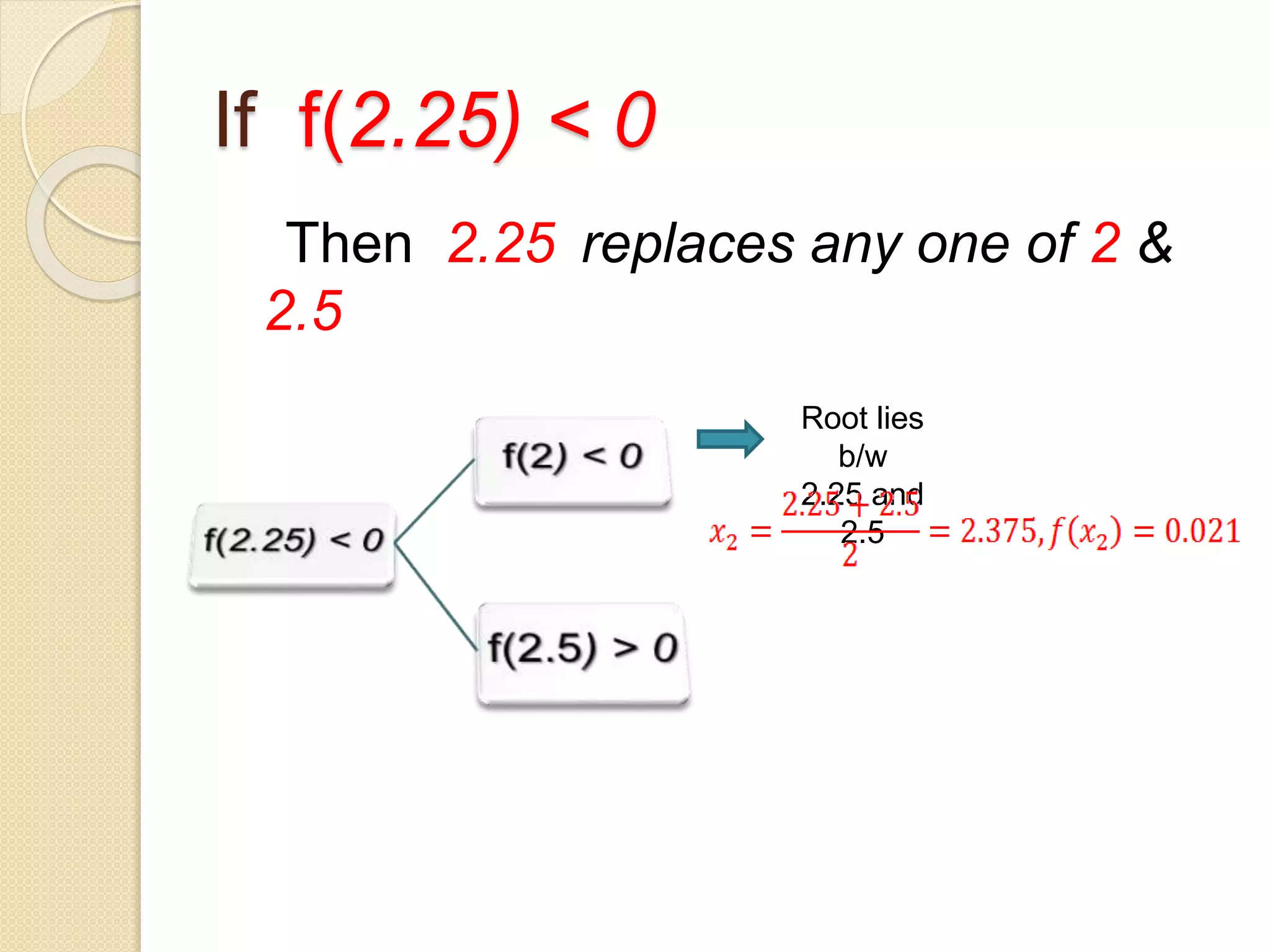
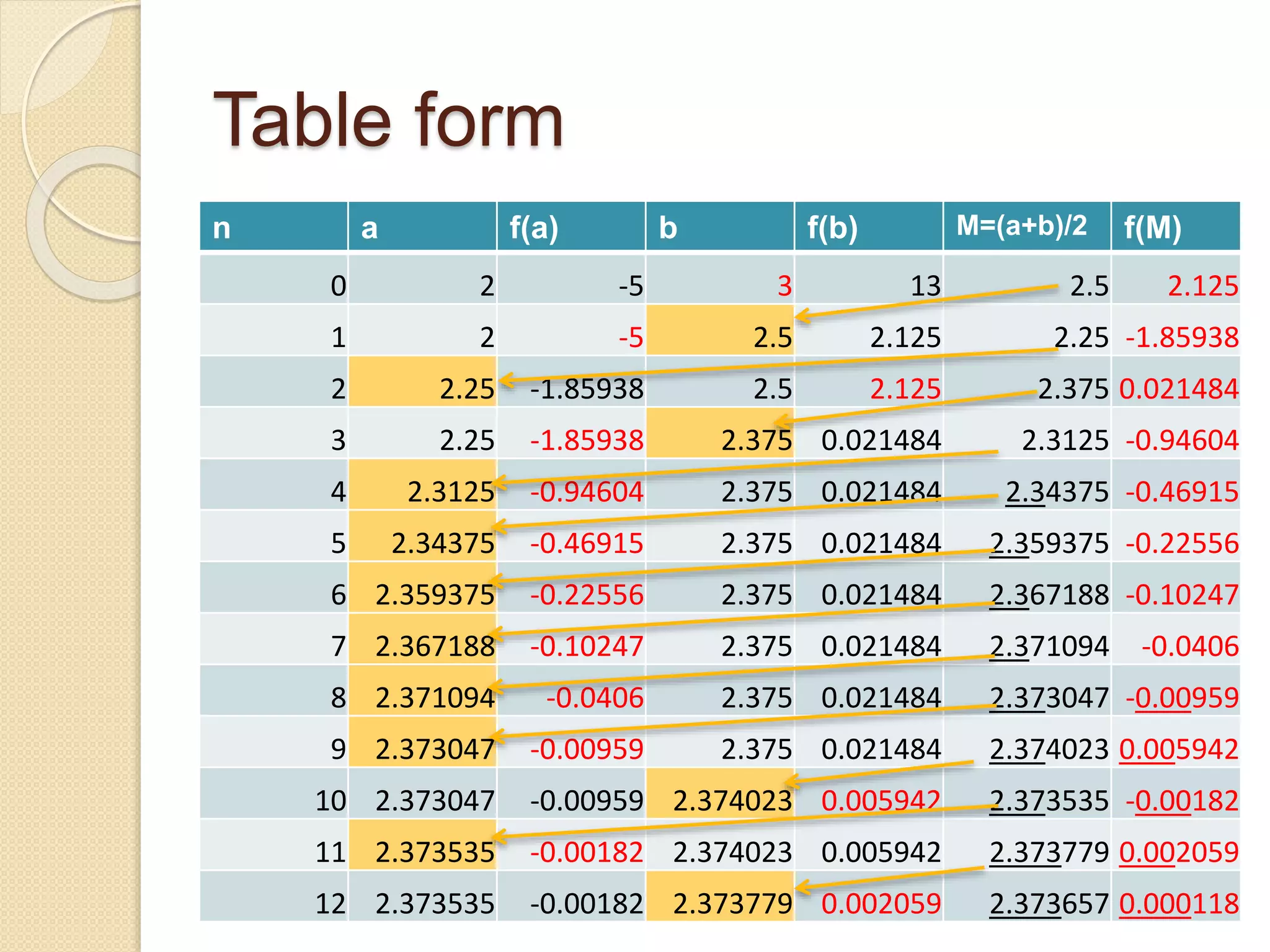
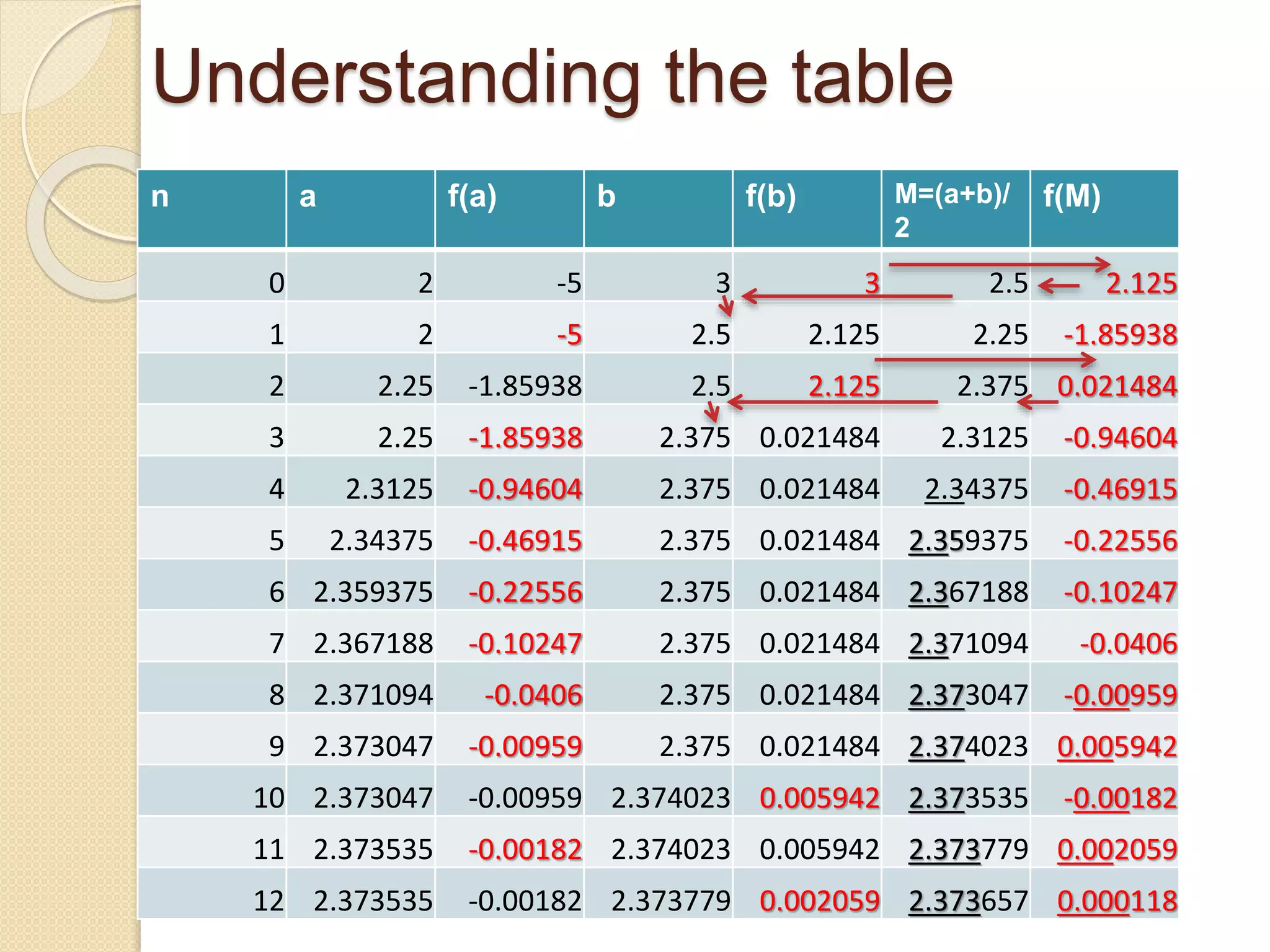
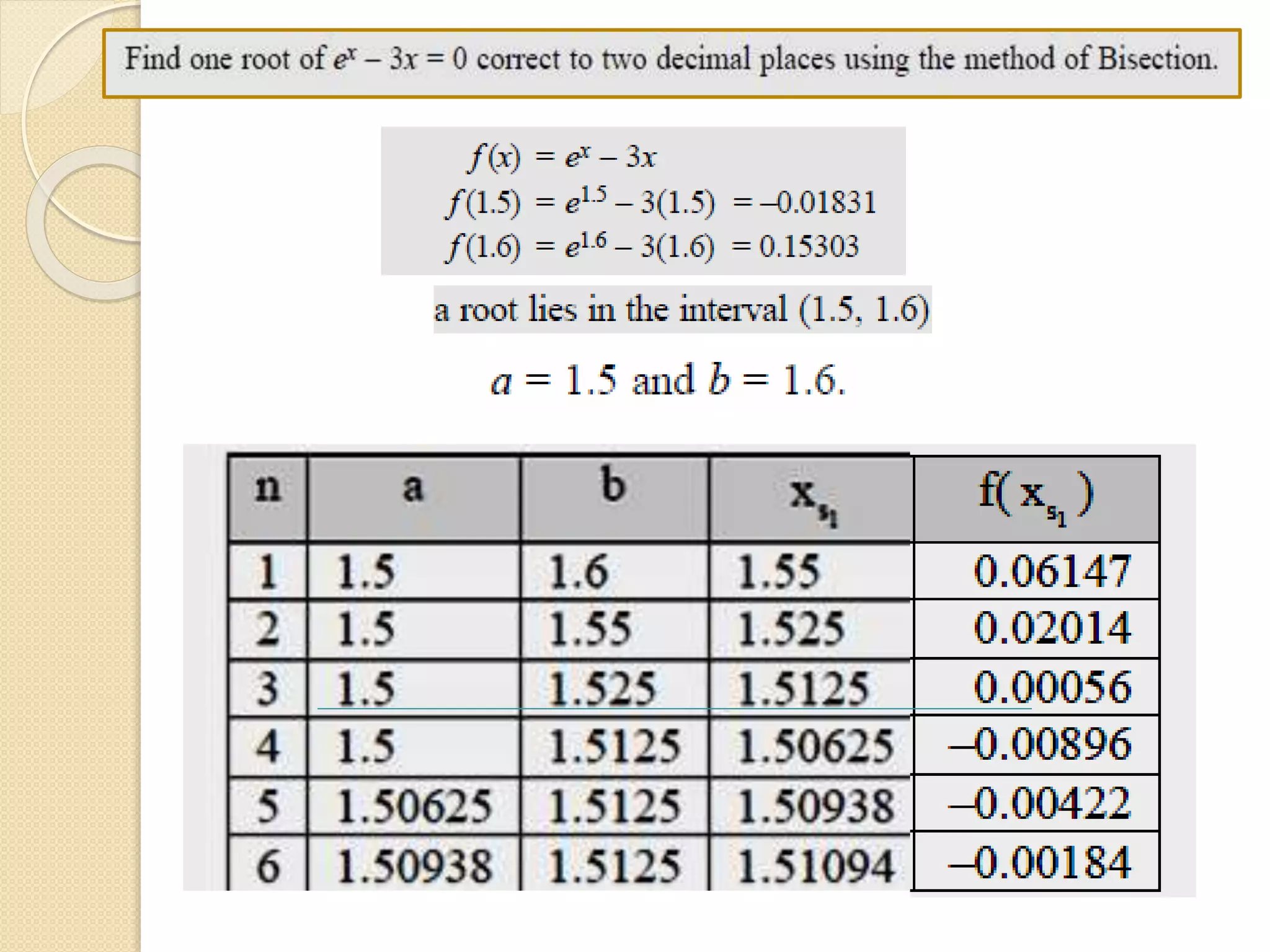
The document discusses the bisection method for finding real roots of equations. It provides the step-by-step algorithm for applying the bisection method. The key steps are: (1) find two values a and b where the function has opposite signs, (2) compute the midpoint x0 between a and b and evaluate the function there, (3) replace either a or b with x0 depending on whether f(x0) is positive or negative, and (4) repeat until the desired accuracy is reached. The document includes an example of applying the bisection method to find the root of the equation f(x) = x^3 - 2x - 5 between 2 and 3.