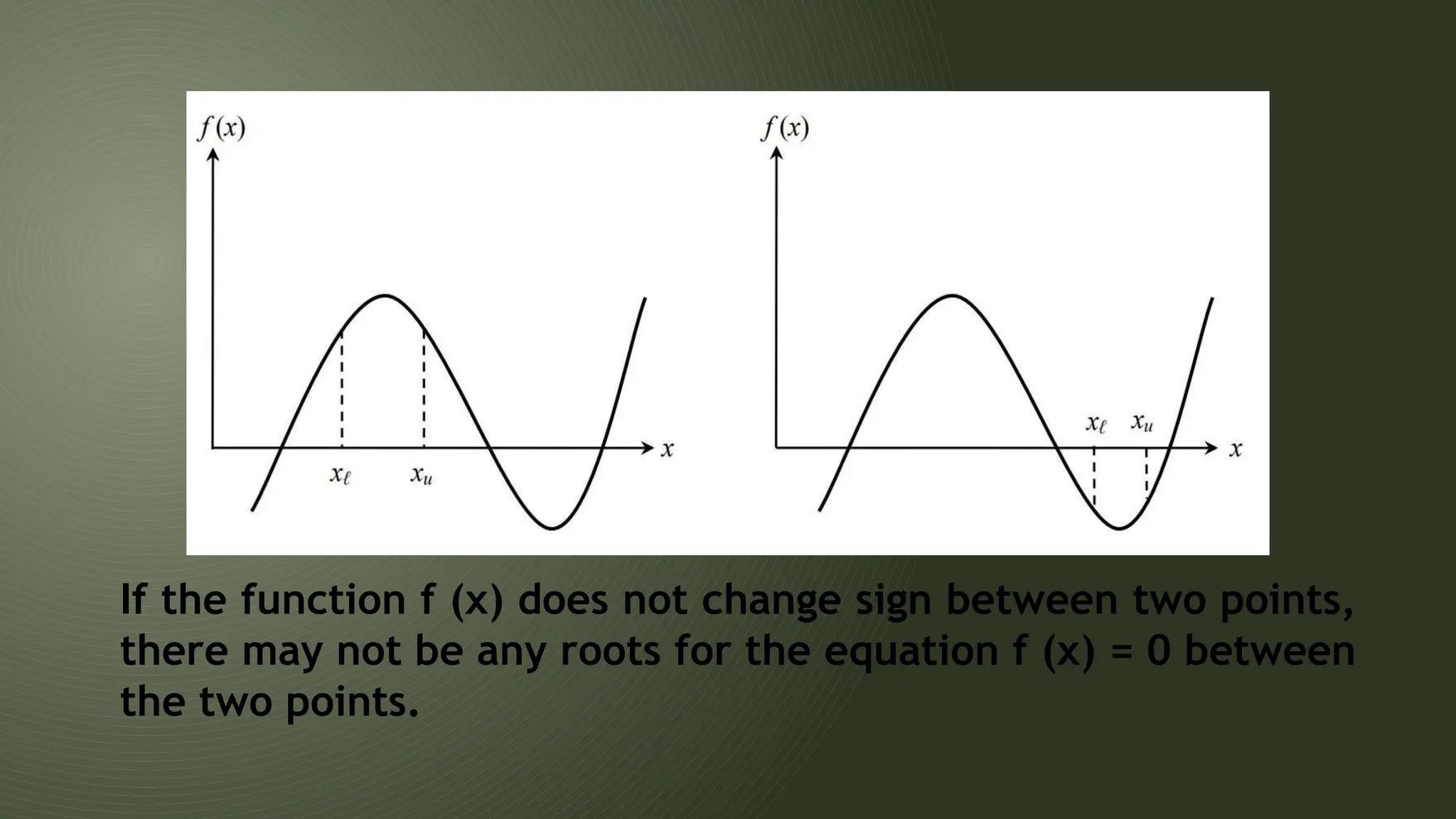
The bisection method is a straightforward root-finding technique that divides an interval and selects subintervals where a root may exist, providing slower but guaranteed convergence to a solution, given the function is continuous. The document details the method's procedure, including steps for selecting intervals, midpoint calculations, and iterative approximation, also noting its limitations such as slow convergence and inability to handle complex roots. Examples demonstrate application and comparison between analytical and programming results, highlighting its advantages and disadvantages.




![Procedure of Bisection Method
Step 1: Choose two approximations a and b
such that,
f(a)*f(b)<0
Step 2: Evaluate the midpoint c of [a,b]
given by,
c=(a+b)/2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bisectionaaa1-1-240830134357-c6ca0531/75/Presentation-on-the-bisection-method-pptx-6-2048.jpg)














![ x*exp(x)-1=0
Let f(x)=x*exp(x)-1
f(0)=0-1=-1
f(1) = 1.e-1=1.7182
So, the root lies in [0,1]
a = 0, b = 1
first iteration
x1 = (0 + 1)/2 = 0.5
f(x1)=f(0.5) = (0 .5)exp(0.5)-1= -0.175639
Here f(x1)*f(b)< 0
f(0.5)*f(1)< 0
So, x1 = a = 0.5
New interval [ 0.5,1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bisectionaaa1-1-240830134357-c6ca0531/75/Presentation-on-the-bisection-method-pptx-22-2048.jpg)
![Second iteration
x2 = (0.5+1)/2 = 0.75
f(x2)=f(0.75) = 0.5877
Here f(x2)*f(a)< 0
So, x2 = b = 0.75
New interval [ 0.5, 0.75]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bisectionaaa1-1-240830134357-c6ca0531/75/Presentation-on-the-bisection-method-pptx-23-2048.jpg)
![Similarly, x3=0.625 [0.5 , 0.625]
x4=0.5625 [0.5625, 0.625]
………………………………………
……………………………………
………………………………………
x12=0.56713855
here x12=0.56714 (to five decimal places)
so , the root of equation f(x) is 0.56714](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bisectionaaa1-1-240830134357-c6ca0531/75/Presentation-on-the-bisection-method-pptx-24-2048.jpg)
![ x**3-5*x+3=0
Let f(x) = x**3- 5x + 3
f(0)=0-5(0)+3= +3
f(1) = 1 - 5 + 3 = -1
So, the root lies in [0,1]
a = 0, b = 1
first iteration
x1 = (0 + 1)/2 = 0.5
f(x1)=f(0.5) = (0 .5)**3 - 5(0.5) + 3 = 0.625
Here f(x1)*f(b)< 0
f(0.5)*f(1) <0,
So, x1 = a = 0.5
New interval [ 0.5,1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bisectionaaa1-1-240830134357-c6ca0531/75/Presentation-on-the-bisection-method-pptx-25-2048.jpg)
![ Second iteration
x2 = (0.5+1)/2 = 0.75
f(x2)=f(0.75) = (0.75)**3 - 5(0.75) + 3 = -0.328125
Here f(x2)*f(a)< 0
f(0.75)*fa) <0,
So, x2 = b = 0.75
New interval [ 0.5, 0.75]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bisectionaaa1-1-240830134357-c6ca0531/75/Presentation-on-the-bisection-method-pptx-26-2048.jpg)
![Similarly, x3=0.625 [0,625, 0.75]
x4=0.6875 [0.625, 0.6875]
………………………………………
……………………………………
………………………………………
x20=0.65662075
x21=0.65662025
Here x20 ~ x21 (to six decimal places)
So, the root of equation f(x) is 0.656620](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bisectionaaa1-1-240830134357-c6ca0531/75/Presentation-on-the-bisection-method-pptx-27-2048.jpg)







