The bisection method is a step-by-step way to find where a function crosses zero (its "root"). It works by narrowing down a range where the root must be, cutting that range in half each time until it's precise enough.
How It Works:
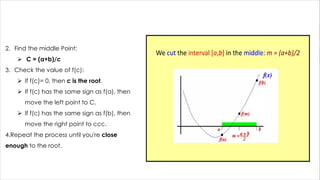
Pick two starting points where the function has opposite signs (one positive, one negative).
Find the midpoint between them and check its value.
Replace either the left or right point with this midpoint, keeping the sign change.
Repeat this halving process until the range is as small as you need.
Key Points:
Always works for continuous functions that change sign.
Simple and reliable, but not the fastest method.
Doesn't need complex calculations, just basic evaluations.
Example: Used in engineering and science to solve equations when exact solutions are hard to find.
A go-to method when you need a dependable way to find roots!

![Introduction
1. What is the Bisection Method?
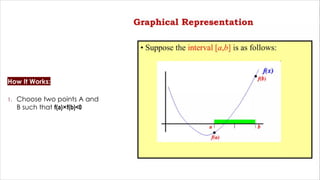
• It is a numerical method used to find the root of a mathematical function.
• A root is the value of x that makes the function f(x)=0.
• The method works by repeatedly dividing an interval in half and checking where the root lies.
• The Bisection Method works only if the function is continuous (no breaks or jumps).
Ø It needs two starting points: [A] and [B], where:
• f(a) is negative, and
• f(b) is positive
• This means the root lies between [A] and [B].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bisectionmethod-250524204823-cce28462/85/The-Bisection-Method-A-Simple-Reliable-Root-Finding-Algorithm-2-320.jpg)