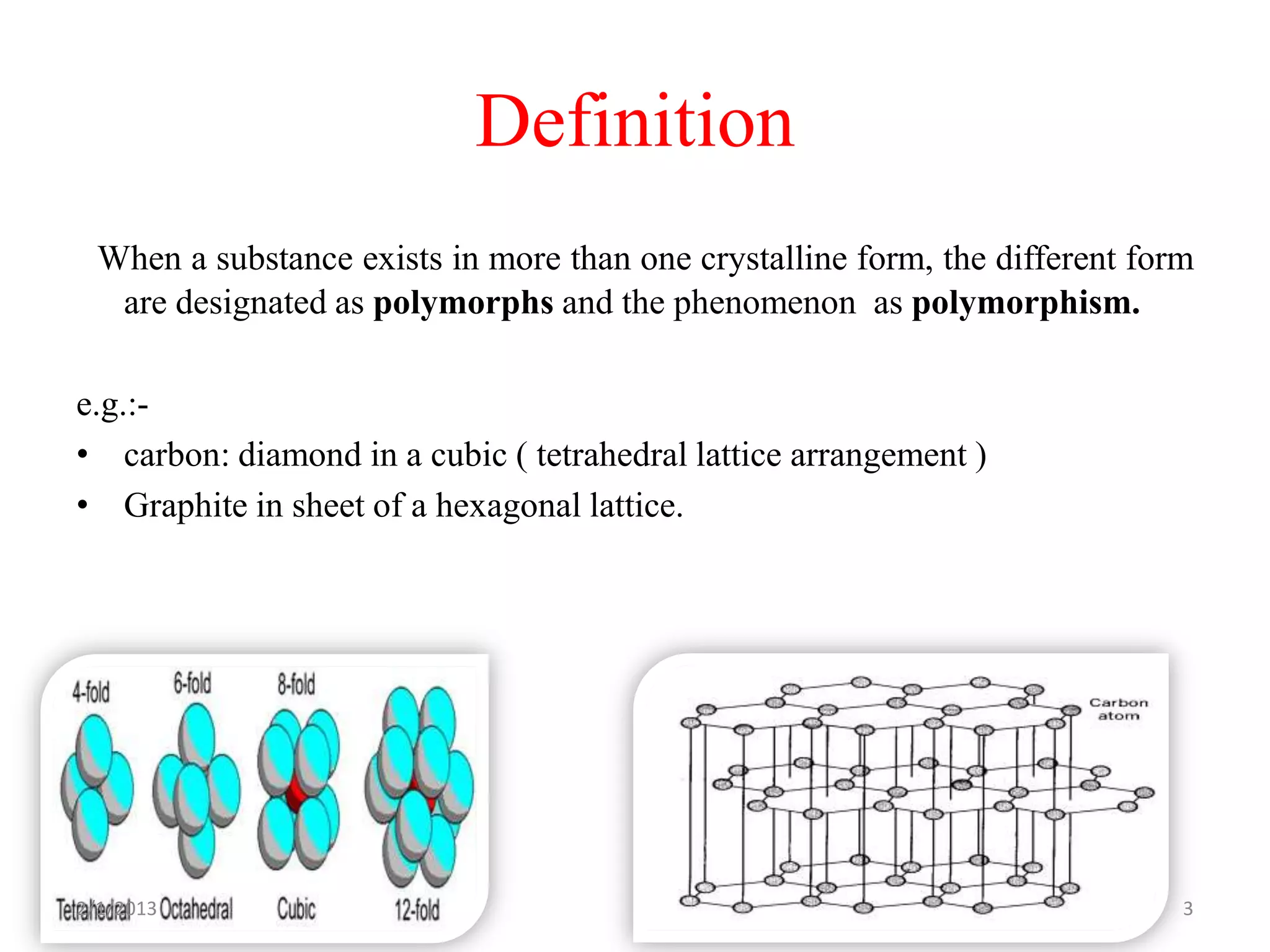
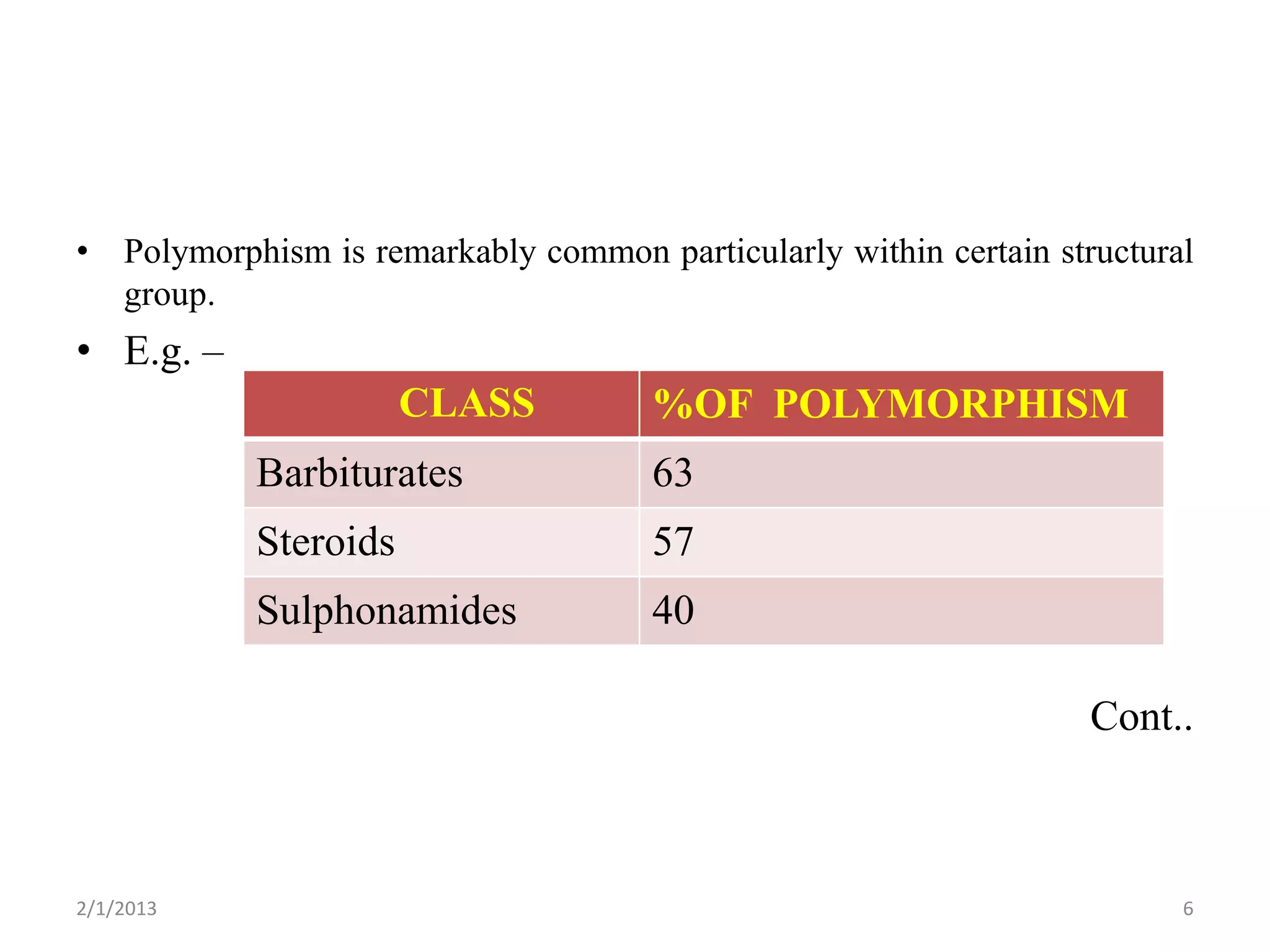
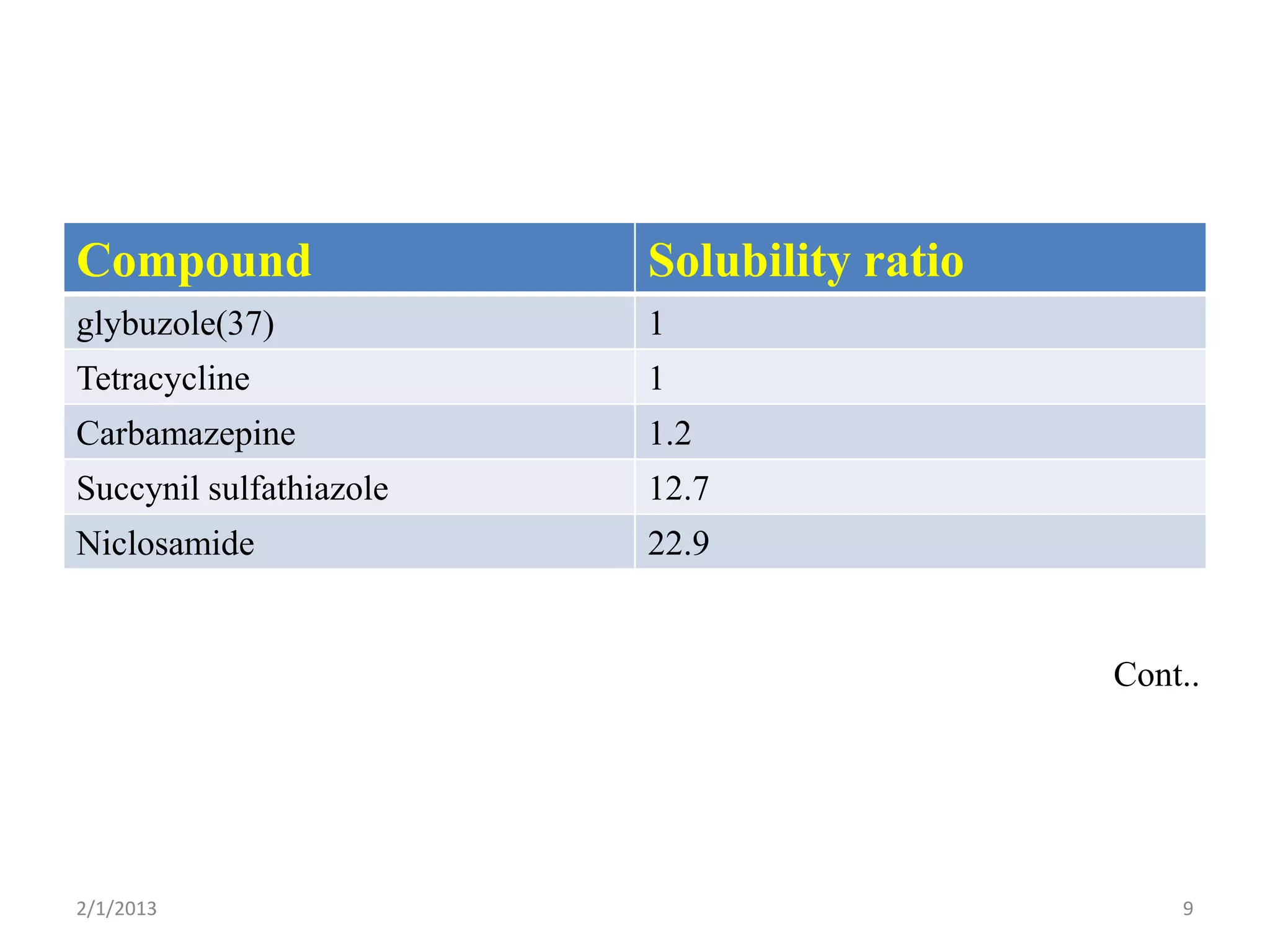
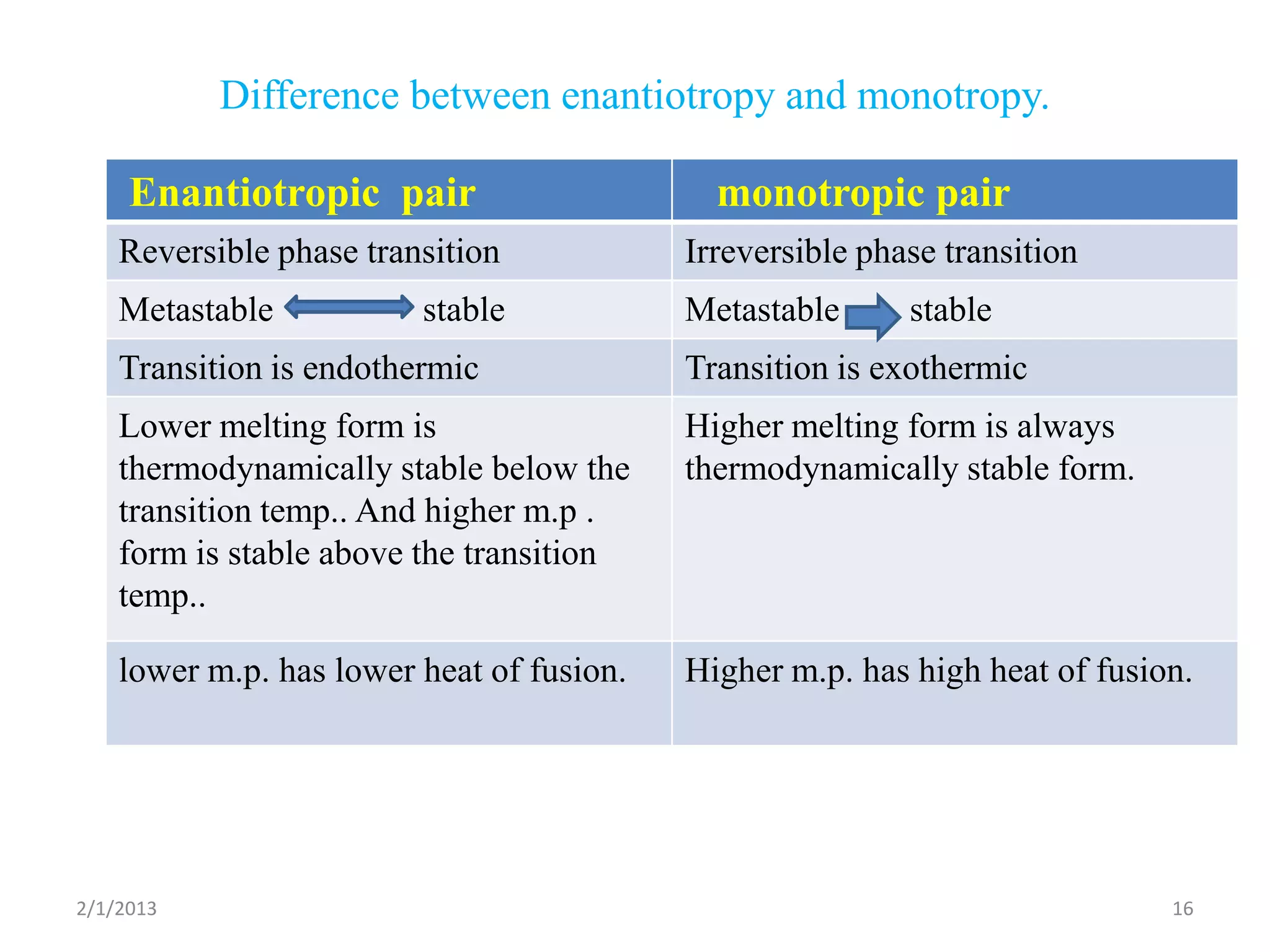
This document discusses polymorphism as part of a preformulation study seminar. It defines polymorphism as the ability of a substance to exist in two or more crystalline forms that have different molecular arrangements. The key points covered include:
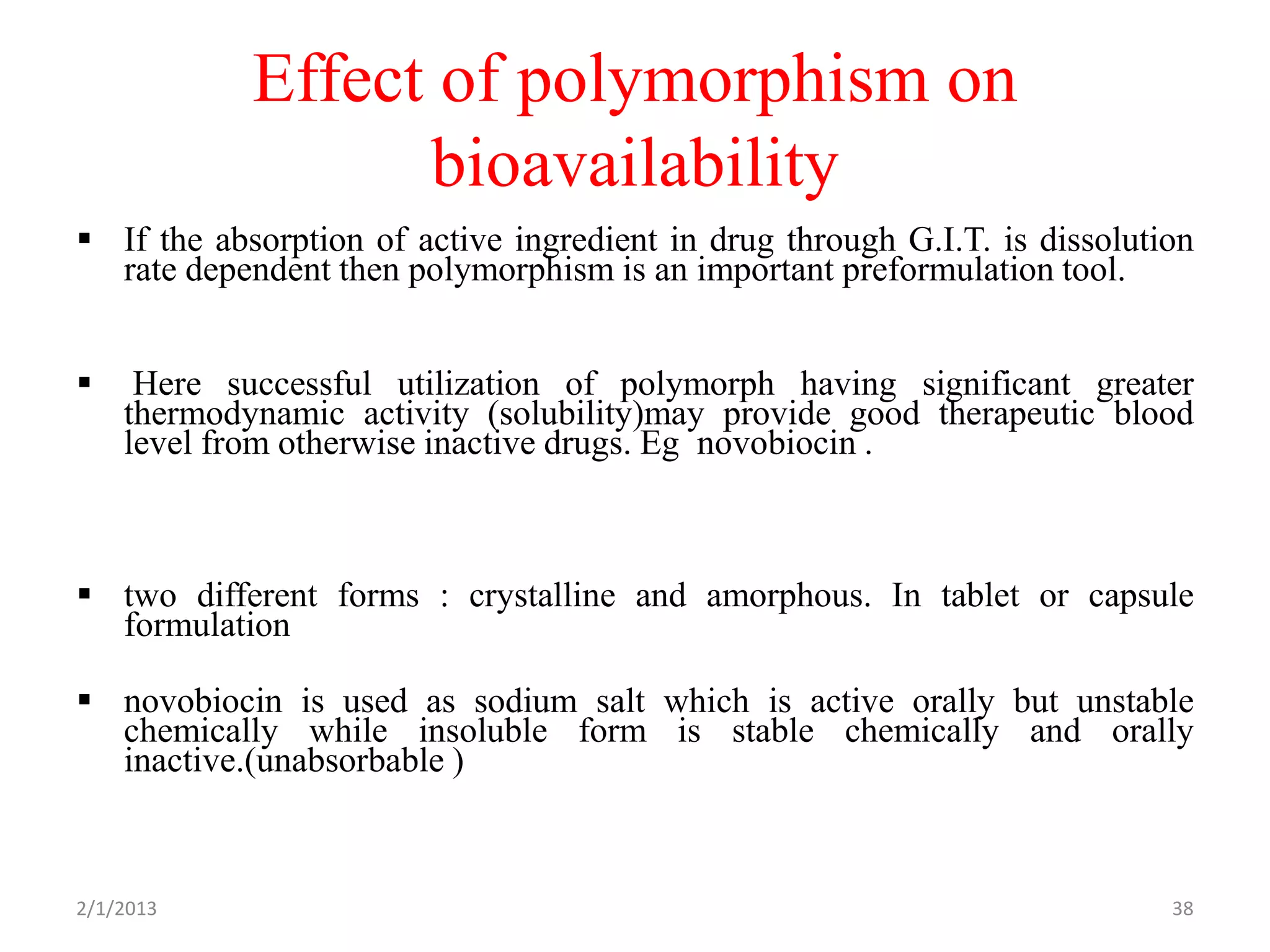
- The need to study polymorphism to select the most stable and soluble form for formulations. Metastable forms often have better bioavailability.
- Various methods to identify and characterize polymorphs such as X-ray diffraction, thermal analysis techniques like DSC and TGA, and microscopy.
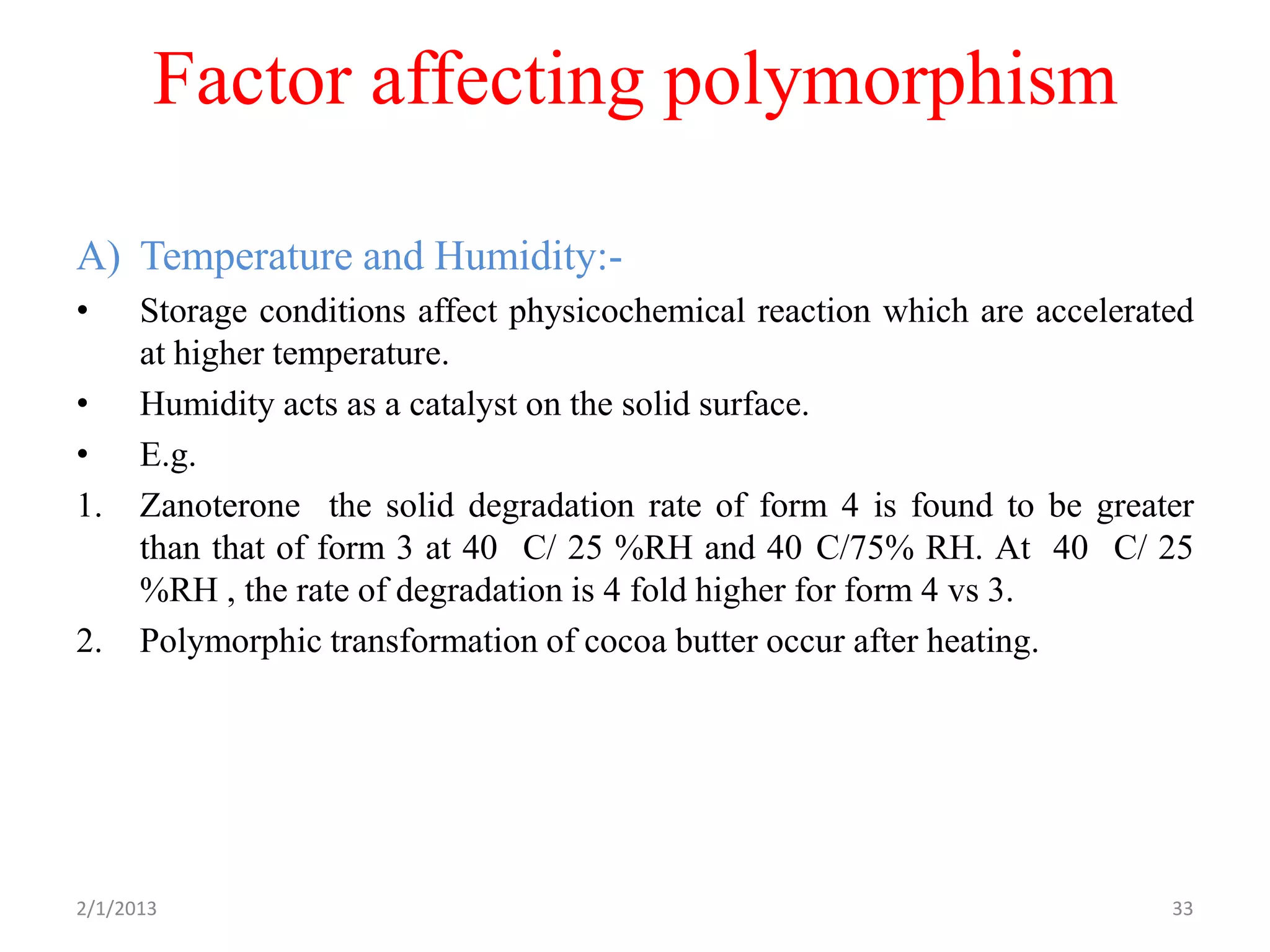
- Factors that can influence polymorphic transitions like temperature, humidity, solvents, grinding, and compression during tableting.
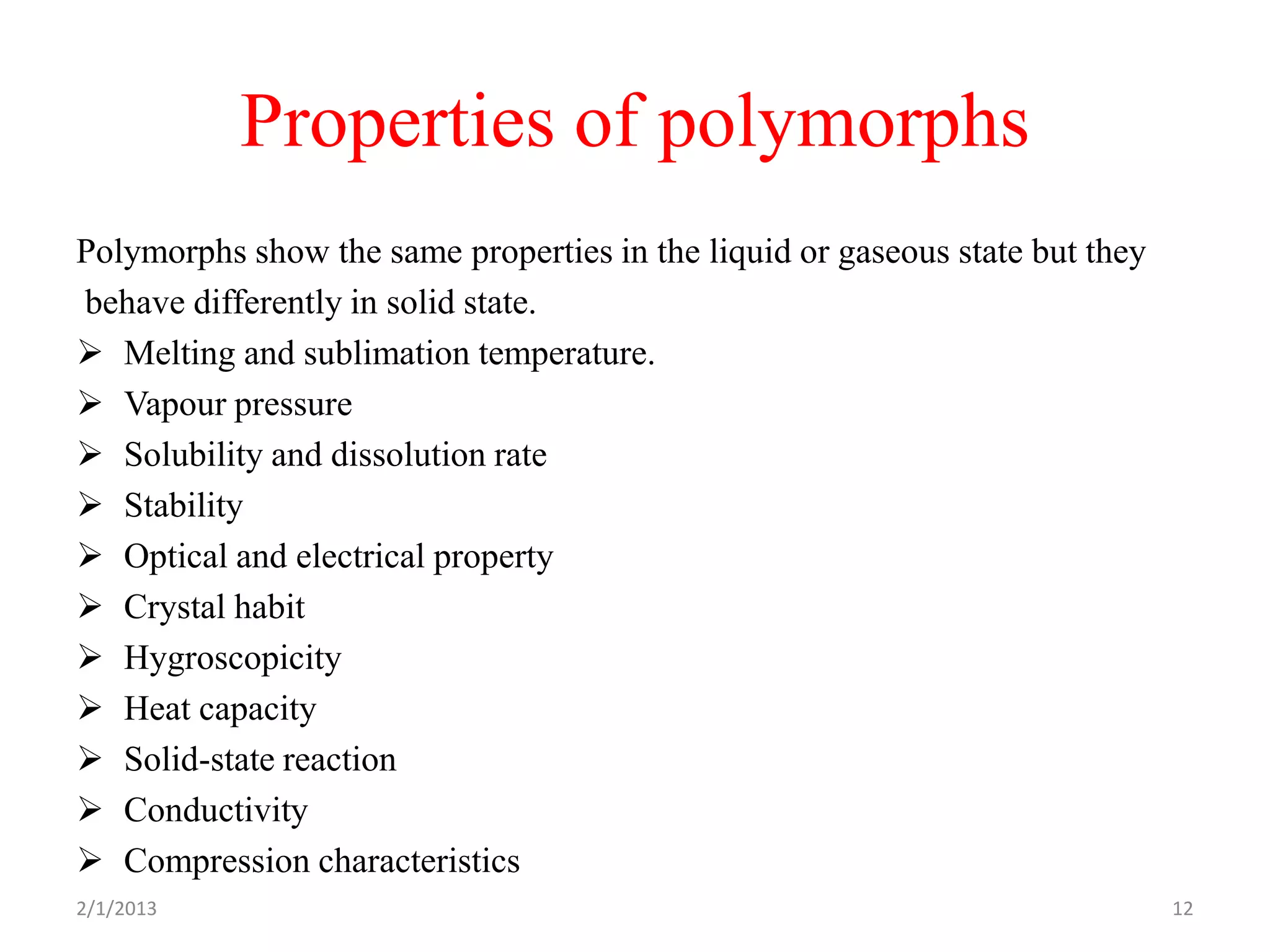
- The importance of understanding polymorphism for properties like