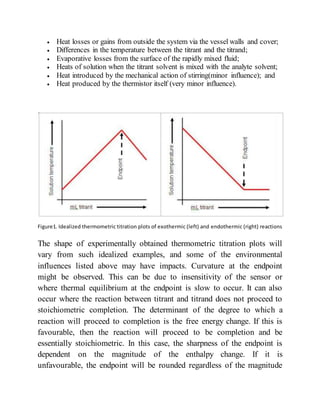
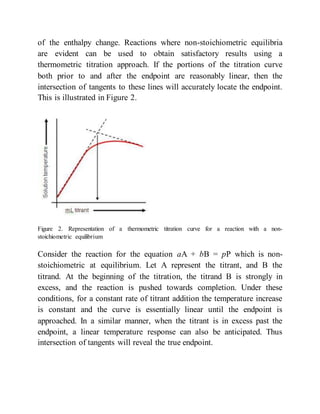
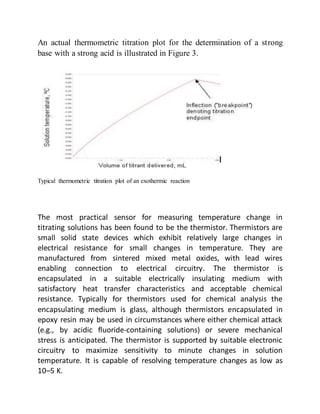
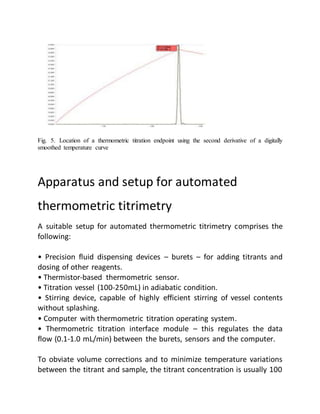
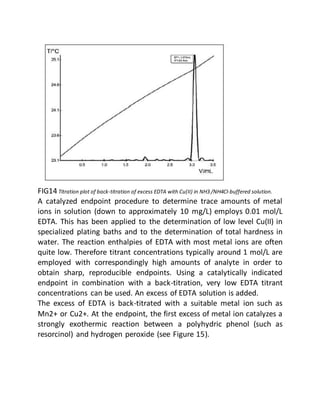
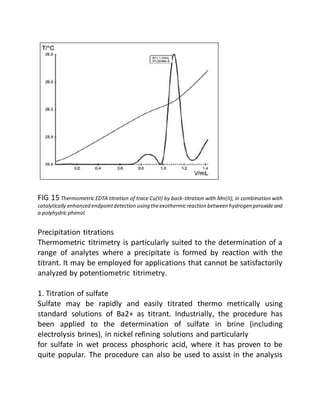
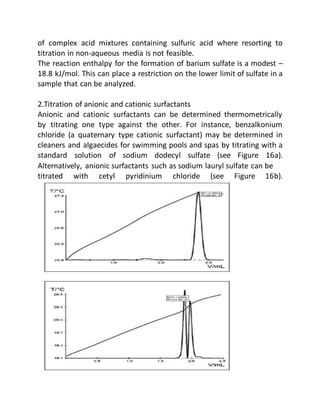
This document provides an overview of thermometric titration. Some key points:
- Thermometric titration measures temperature changes that occur during chemical reactions to locate endpoints precisely. It has advantages over subjective visual methods.
- The temperature change observed is directly proportional to the heat of reaction and moles of analyte. Second derivatives of temperature curves can precisely locate inflection points.
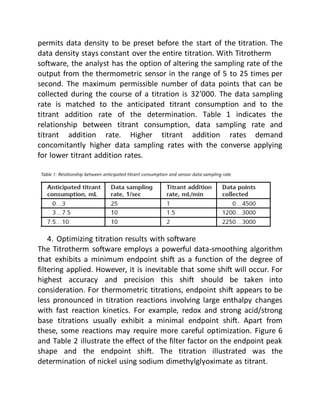
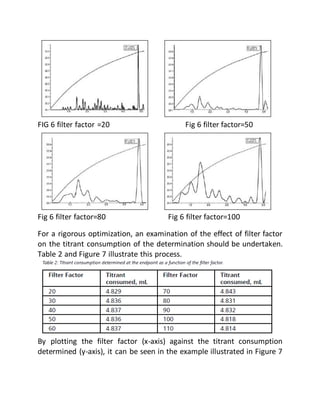
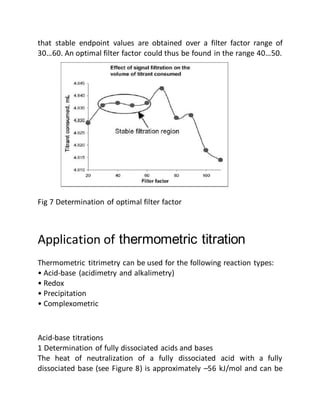
- Parameters like mixing, probe placement, data density, and software filtering must be optimized for accurate results.
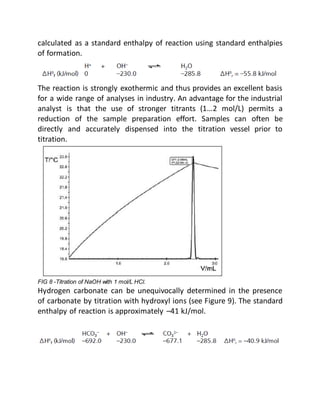
- Applications include acid-base, redox, precipitation, and complexometric titrations. Common determinations include acids, bases, and metal ions.