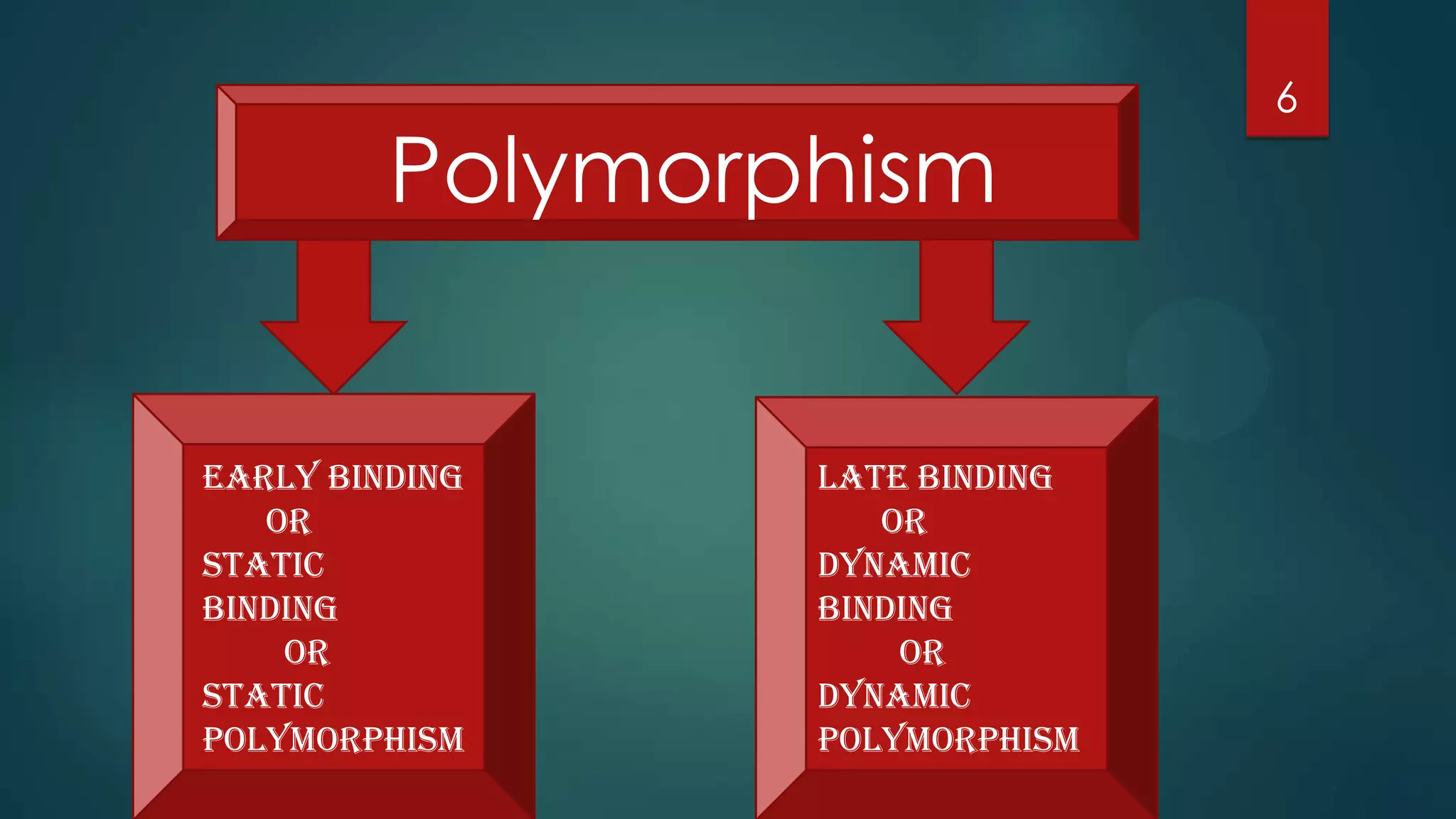
The document discusses polymorphism in object-oriented programming. It defines polymorphism as the ability for objects of different classes related by inheritance to respond differently to the same function call. Polymorphism can be achieved through virtual functions and allows late/dynamic binding at runtime based on the actual object type. The document also discusses early/static binding at compile time, pure virtual functions that define abstract base classes, and concrete derived classes that implement pure virtual functions from the base class.




![Simple program to access member
of class;
void show()
{
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
cout<<"Your name is "<<name;
class data
cout<<"Your age is "<<age;
}
{
private:
};
main()
char name[12];
{
int age;
public:
void input(){
cout<<"Entr your name“;
cin>>name;
cout<<"Enter your age"; cin>>age;}
data obj,*j;
j=&obj;
j->input();
j->show();
getch();
}
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymorpisum-140106223024-phpapp01/75/polymorphism-5-2048.jpg)