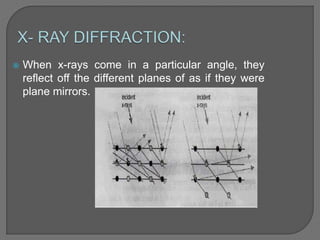
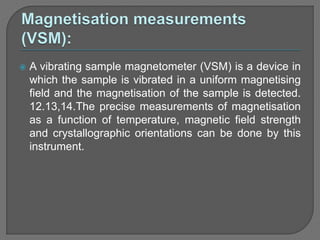
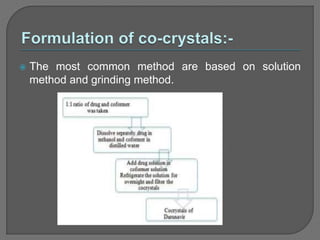
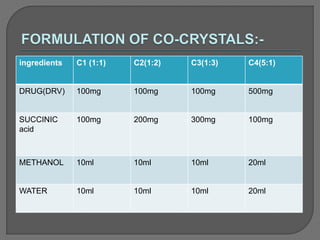
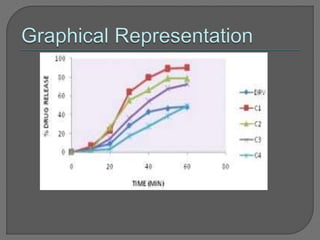
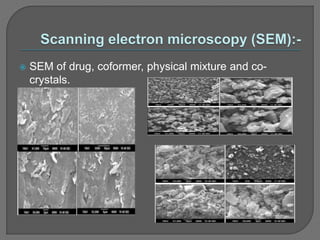
The document discusses various techniques used to characterize crystals and study their properties, including optical microscopy, etching, X-ray diffraction, FT-IR spectroscopy, thermal analysis, UV-visible spectroscopy, emission spectrometry, microhardness measurements, and vibrating sample magnetometry. It also summarizes a research paper on the formulation and evaluation of co-crystals of the poorly water soluble drug darunavir with succinic acid using different analytical techniques. The prepared co-crystals showed improved solubility, dissolution rate, flowability and stability compared to the pure drug.