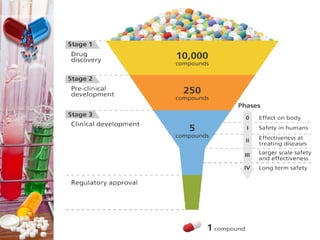
Preformulation studies investigate the physical, chemical, and mechanical properties of a new drug substance. This is done to develop a safe, effective, and stable dosage form and is an integral part of drug development. The main goals of preformulation studies are to establish the drug's physicochemical properties, determine its kinetic profile and stability, determine compatibility with excipients, and know appropriate processing and storage methods. To achieve these goals, preformulation studies examine parameters like the drug's organoleptic properties, bulk characters, solubility, and stability. This provides essential information to formulate the drug into a dosage form that can be safely administered.