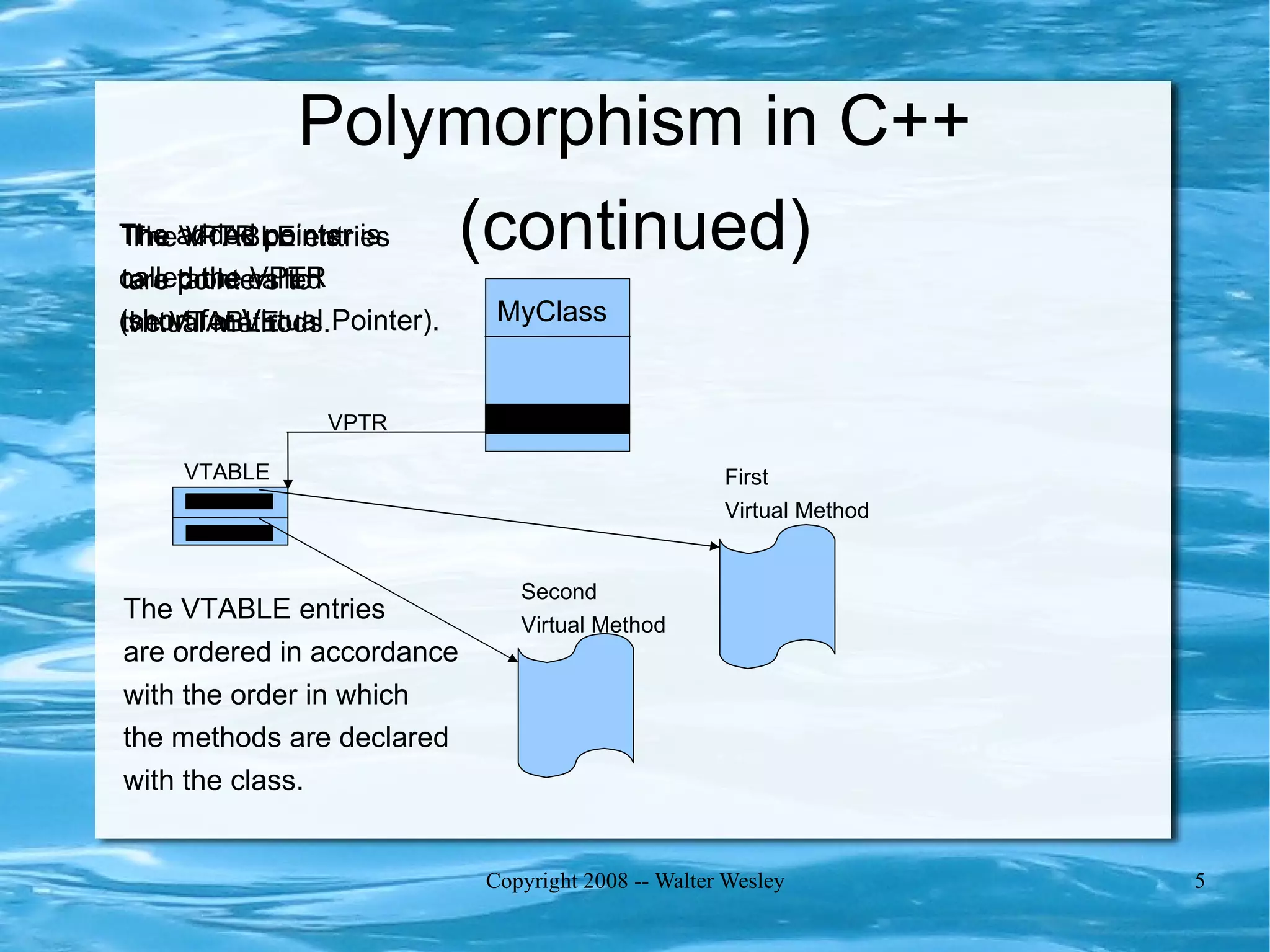
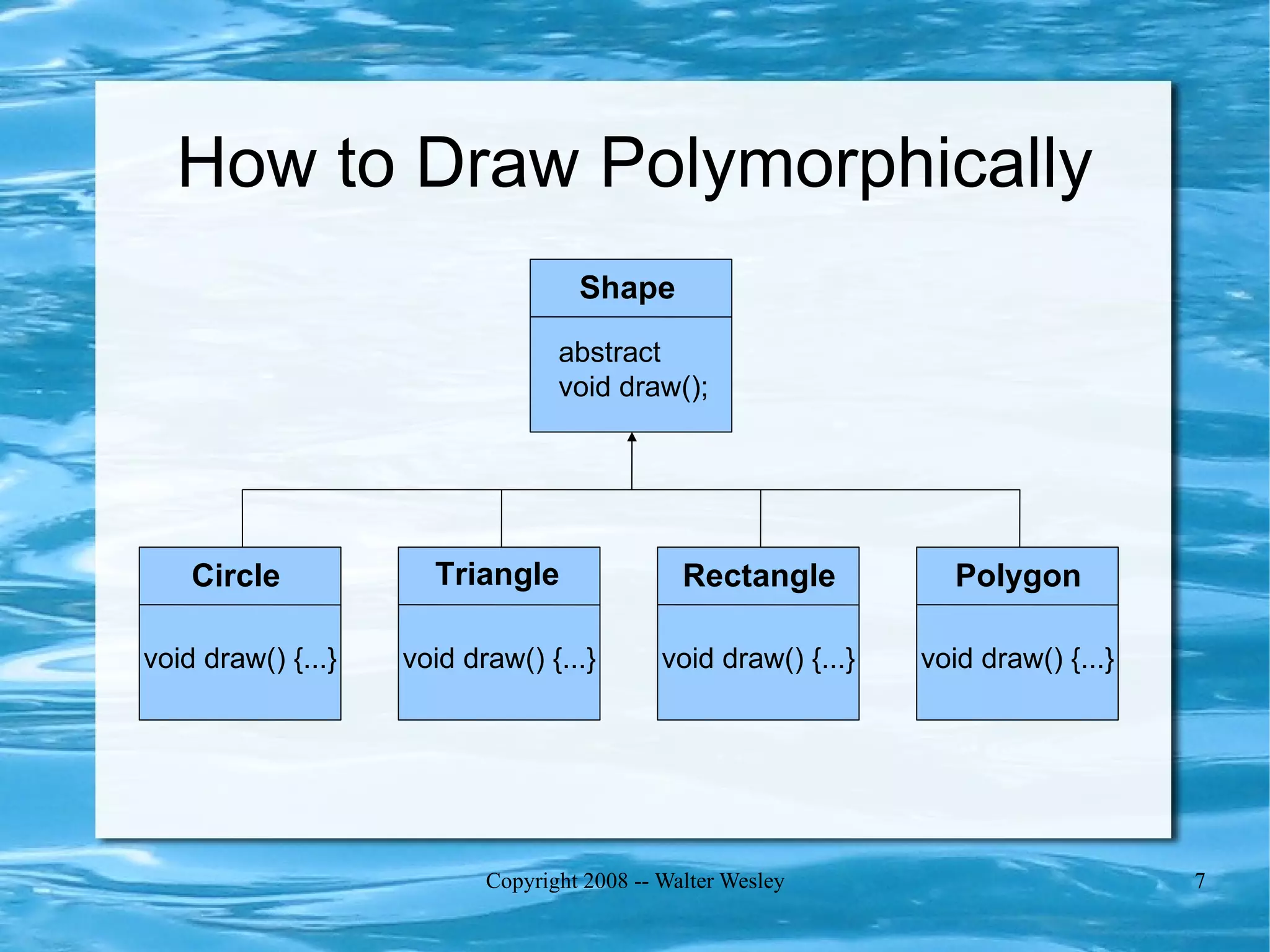
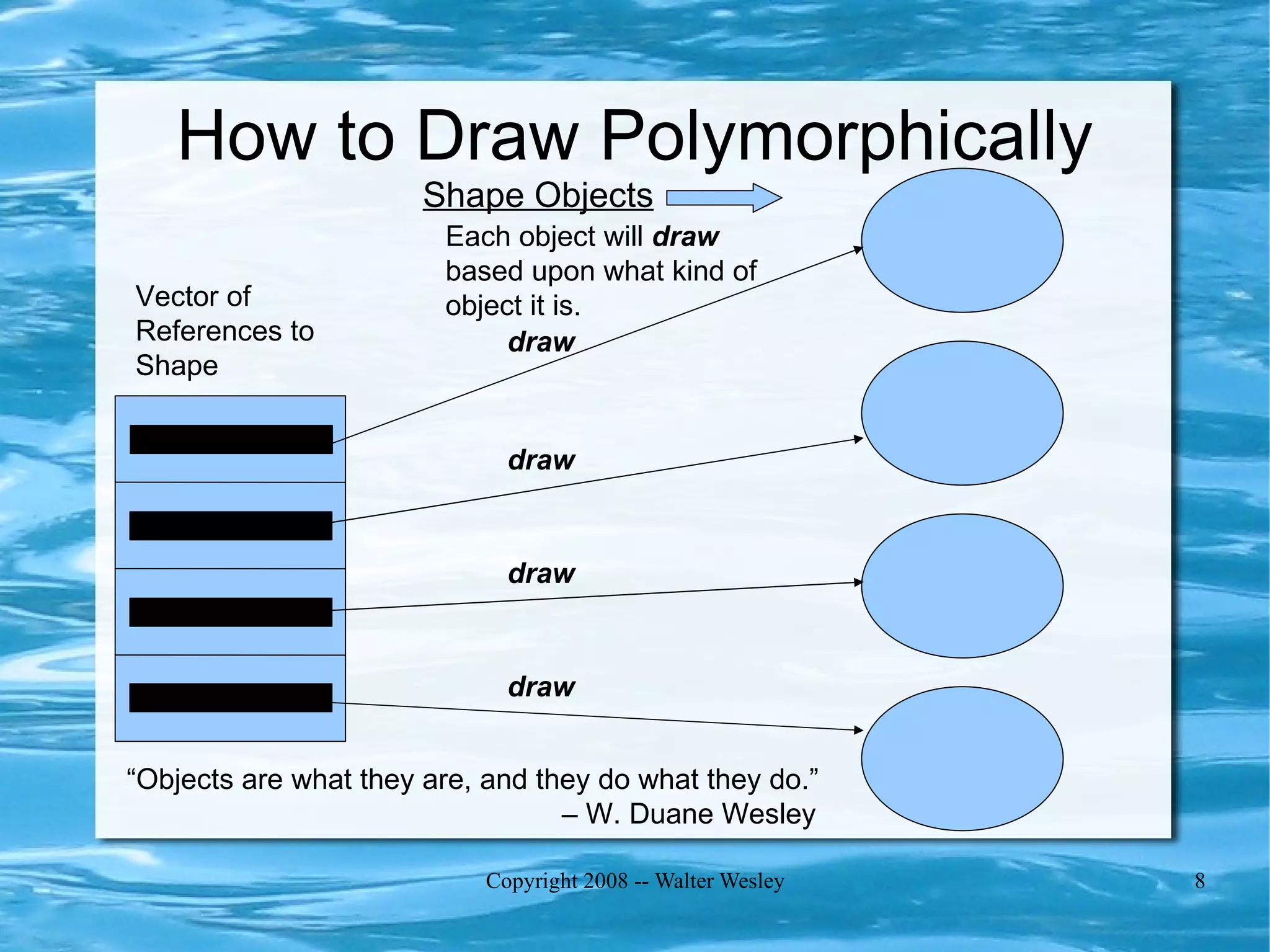
Polymorphism allows objects of different types to be treated as a common type. It is implemented by adding a virtual pointer (VPTR) to objects that points to a virtual function table (VTABLE) containing pointers to each object's virtual methods. This allows calling the same method on different types of objects in a polymorphic way while executing the correct implementation based on the object's actual type at runtime.