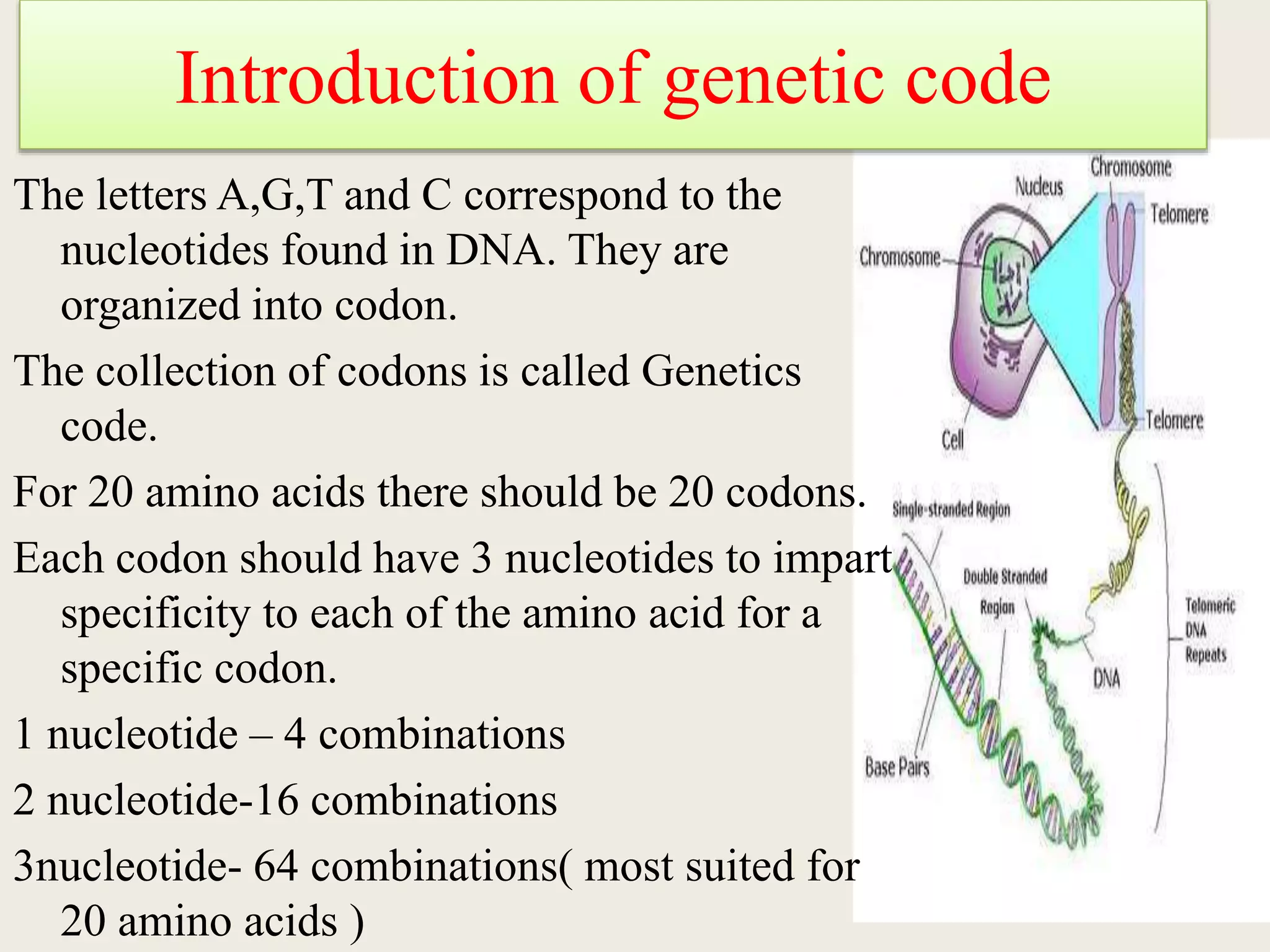
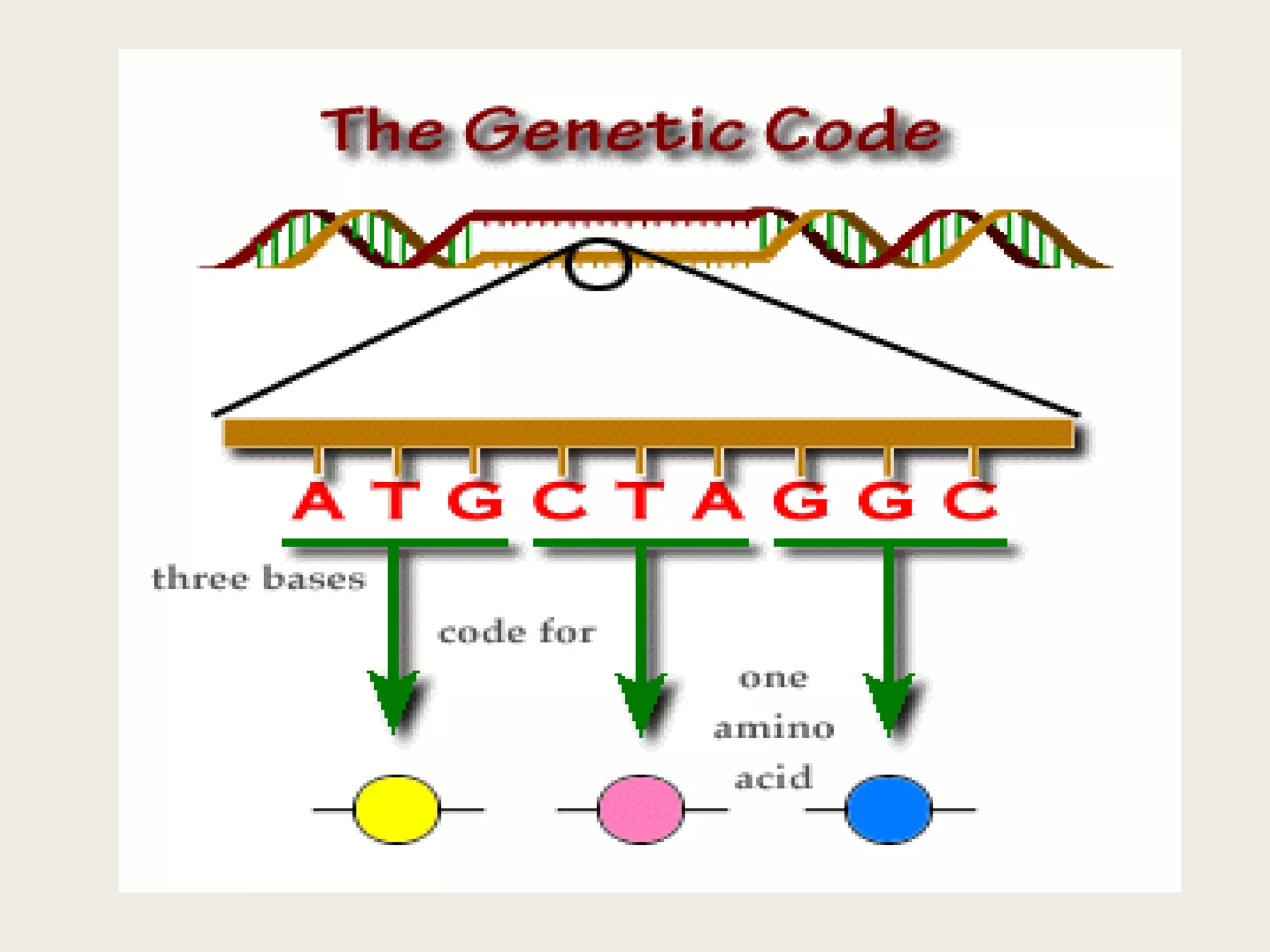
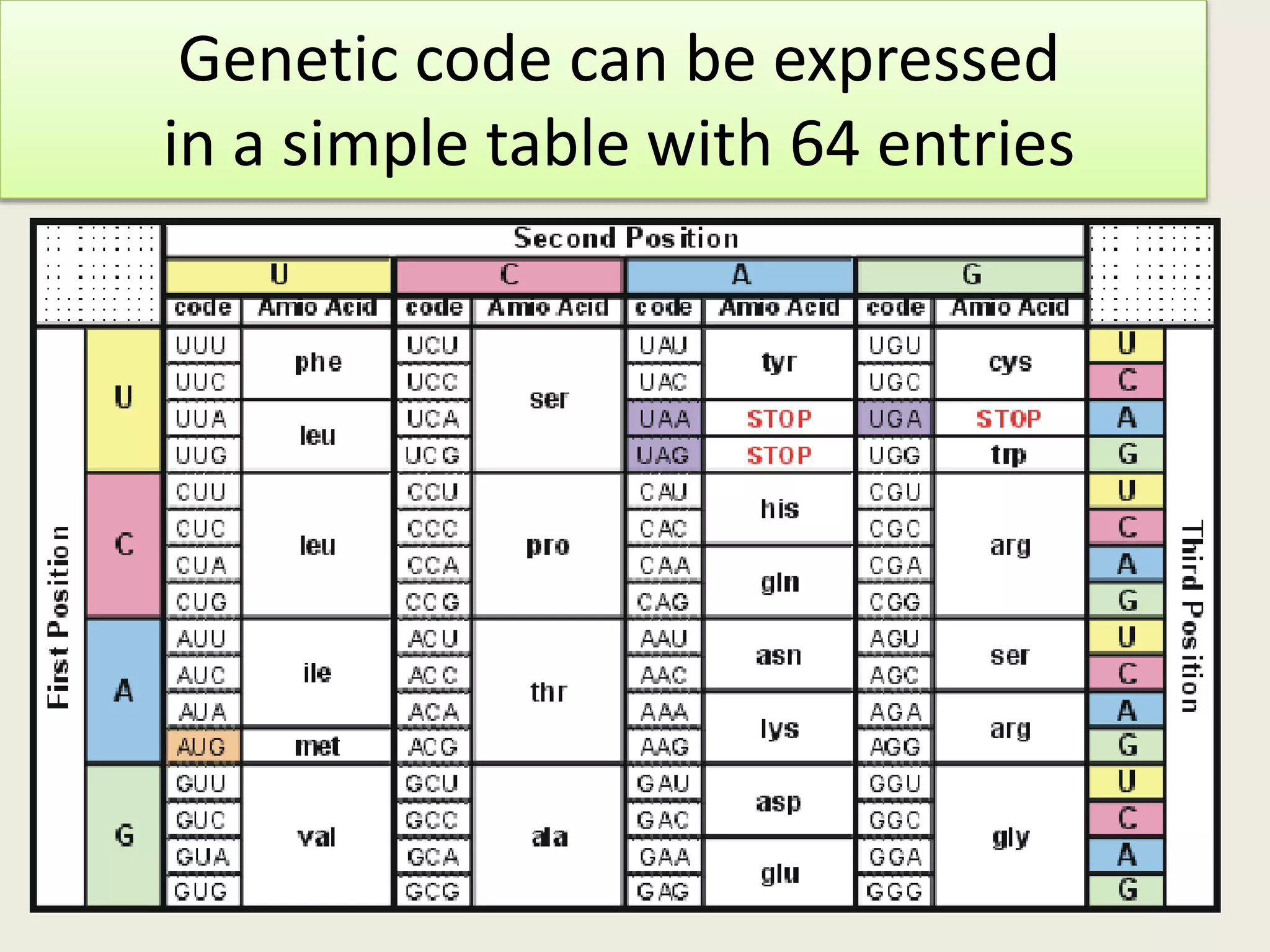
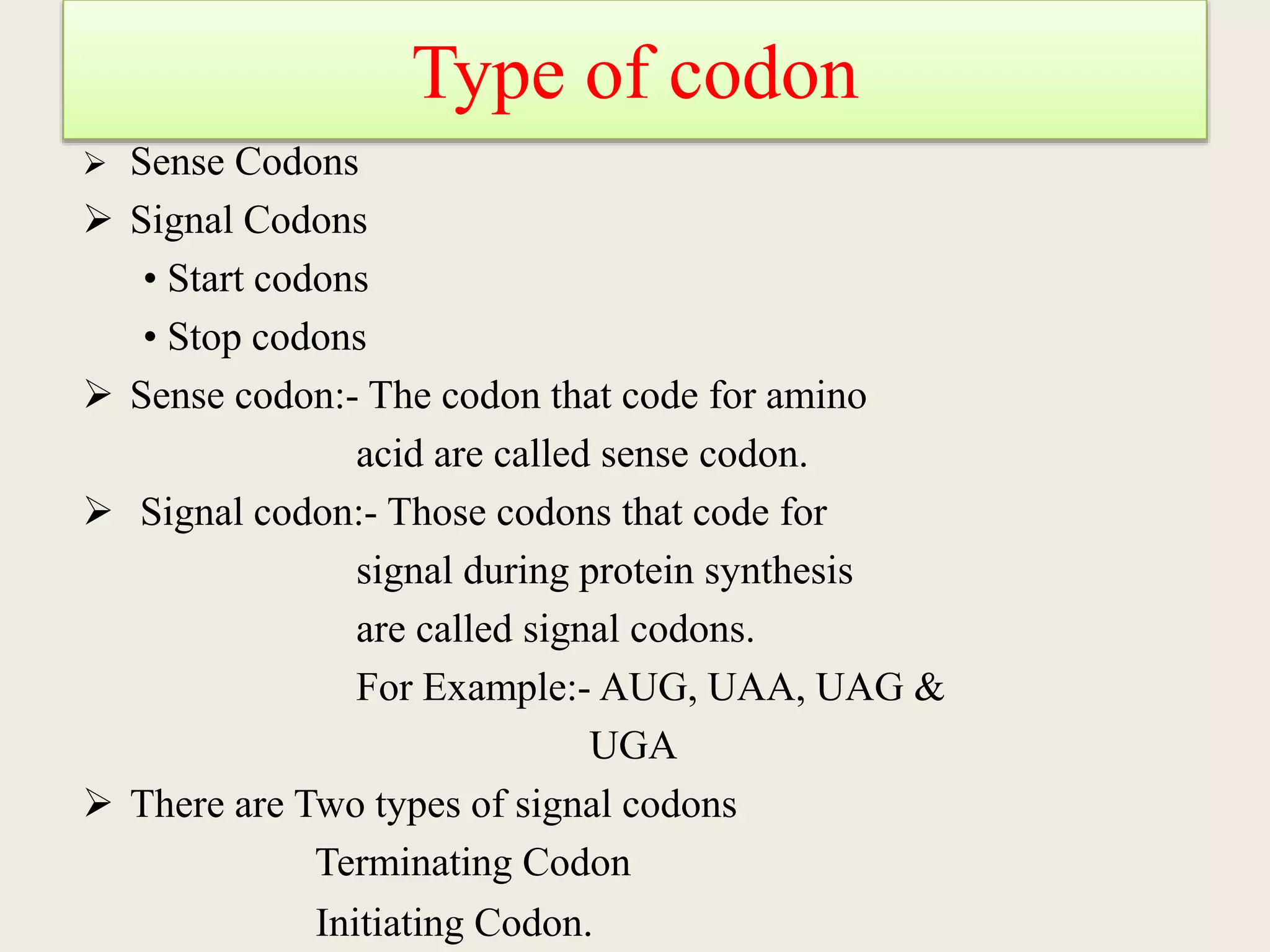
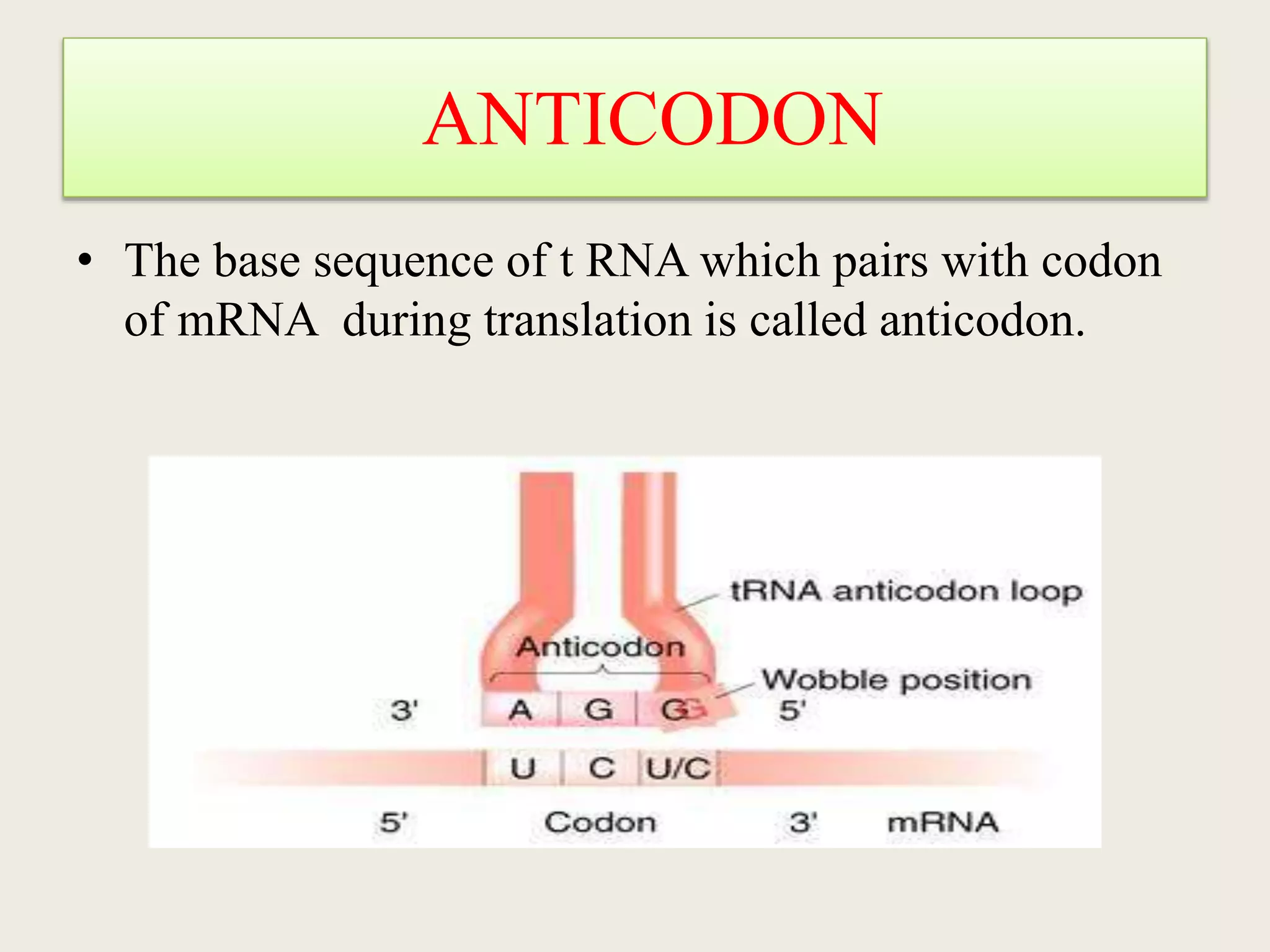
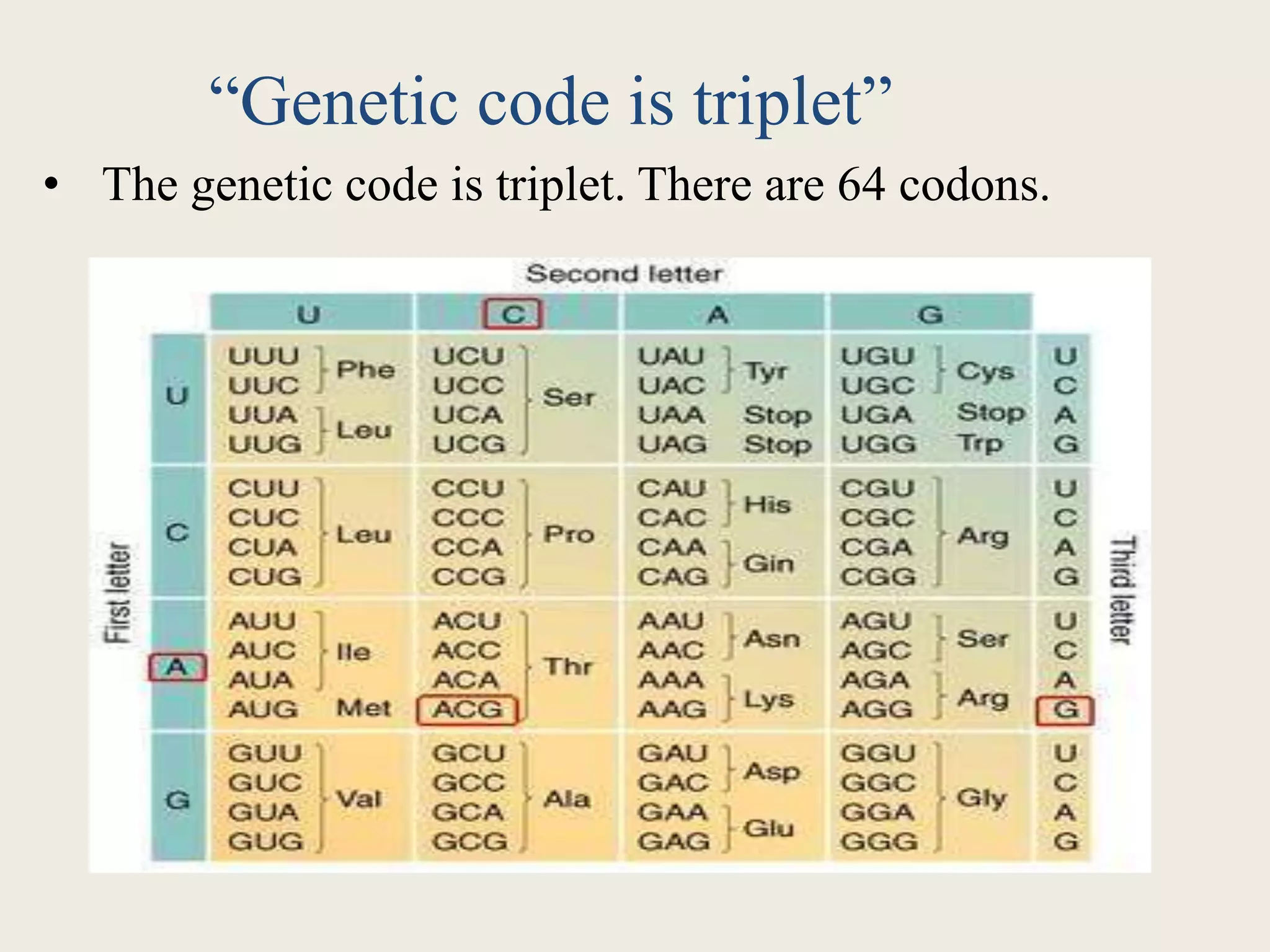
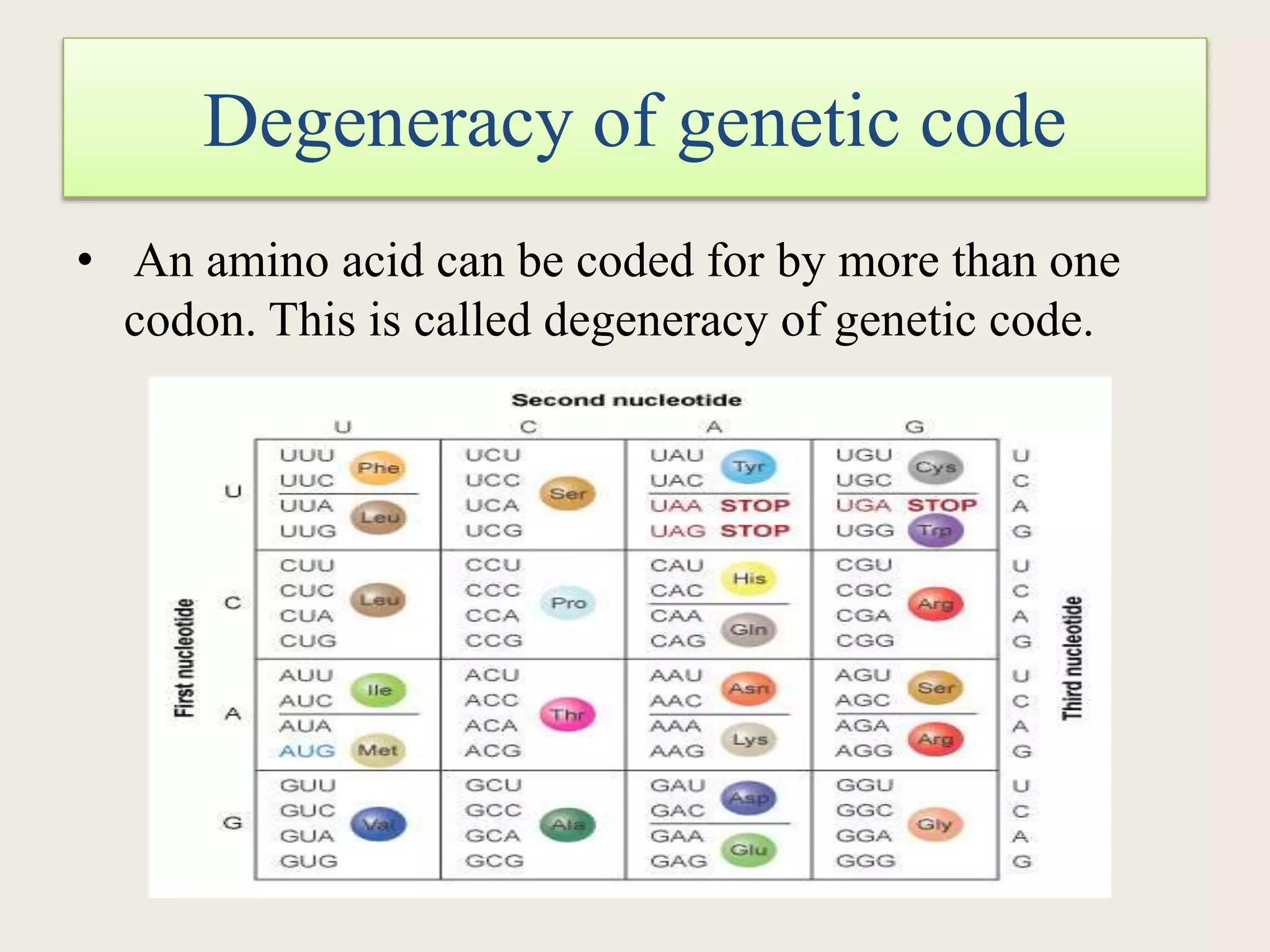
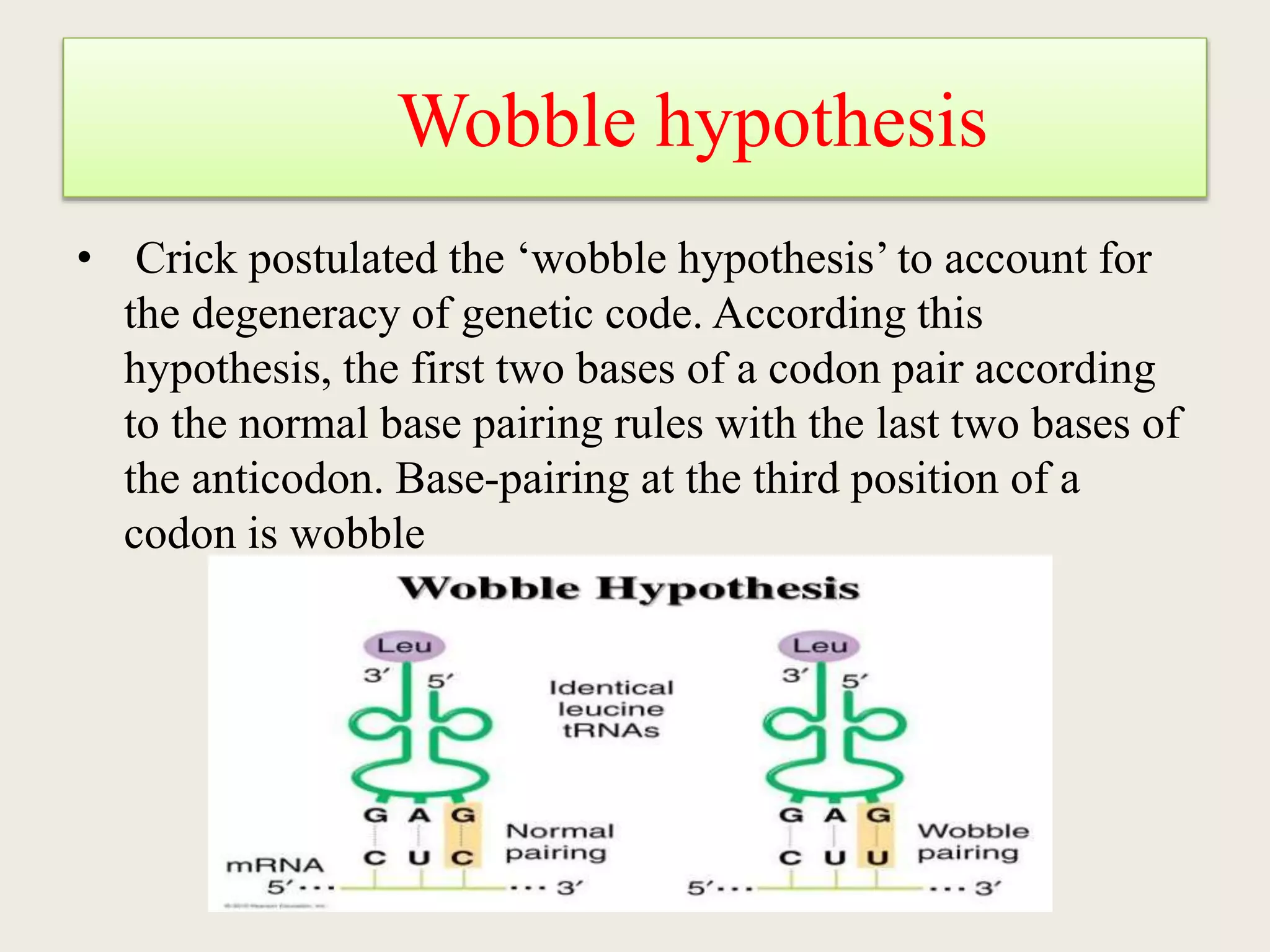
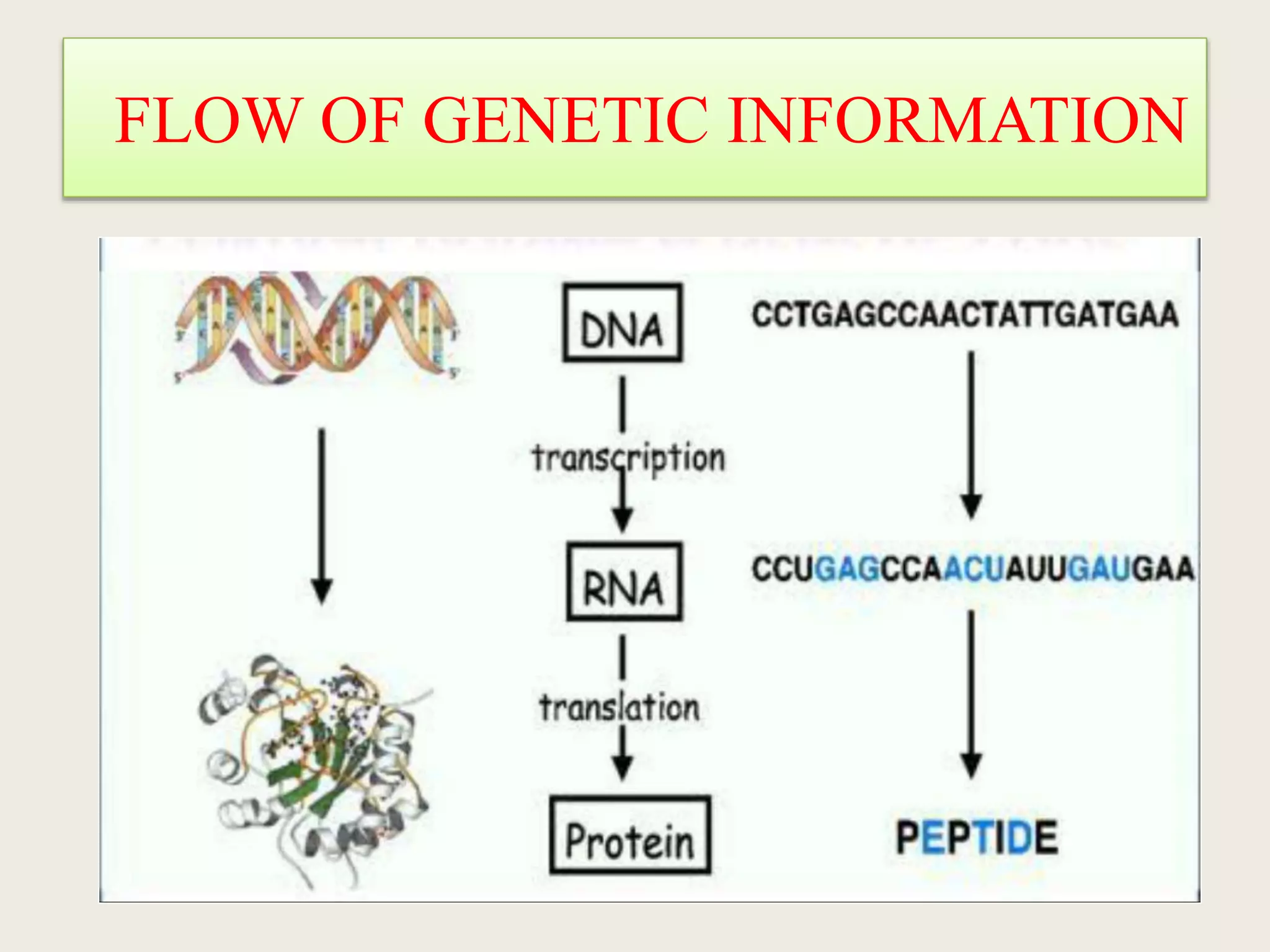
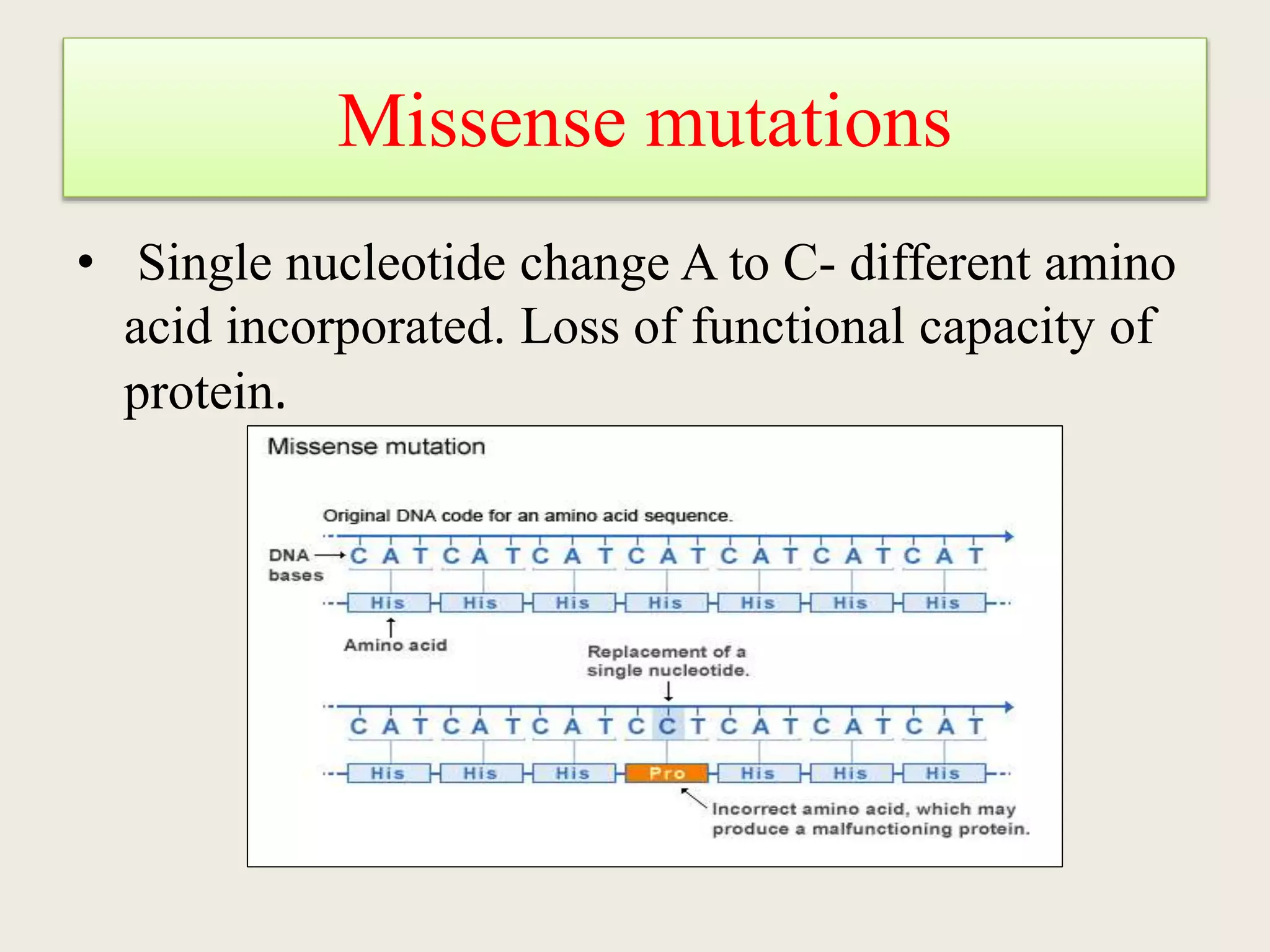
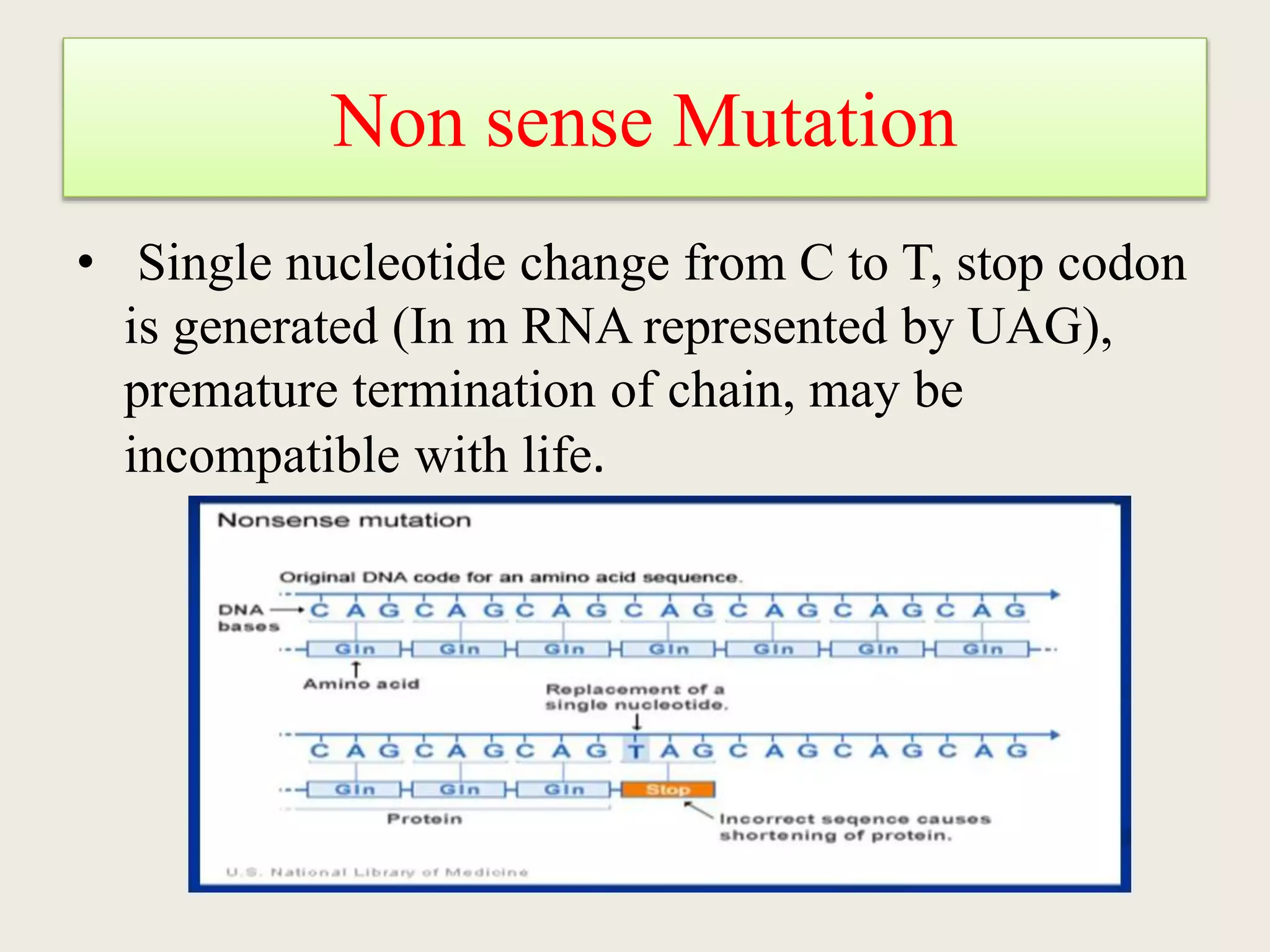
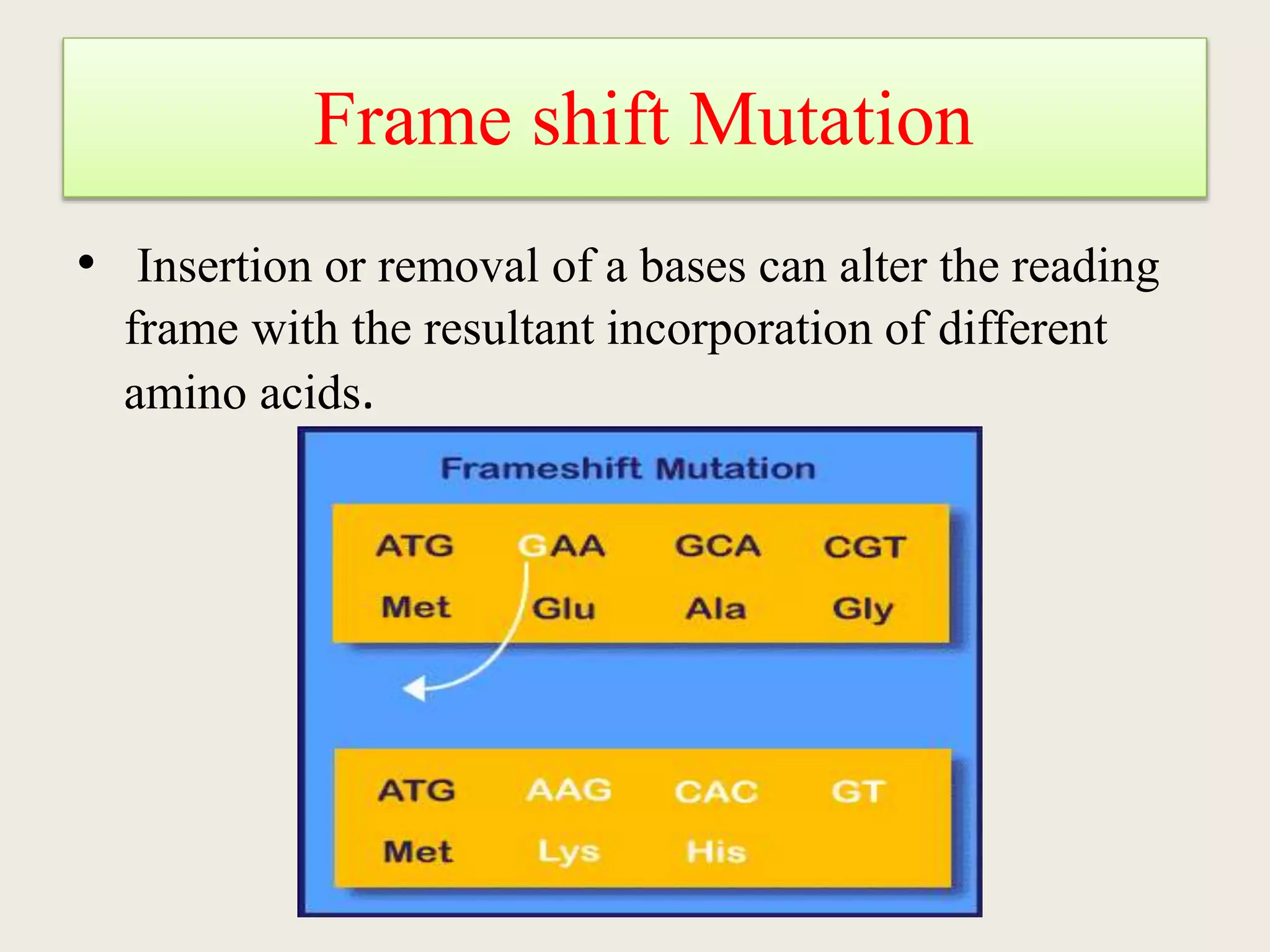
The genetic code is a set of rules that specifies how sequences of nucleotides in DNA and RNA correspond to sequences of amino acids in proteins. It defines codons, which are triplets of nucleotides that encode for specific amino acids or start and stop signals. The genetic code is nearly universal across all living organisms and is non-overlapping and triplet-based. It exhibits some level of degeneracy, where more than one codon can encode for the same amino acid. Mutations in the genetic code can lead to changes in the amino acid sequence of proteins and cause disease.