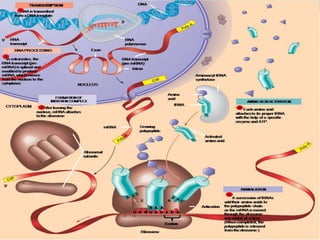
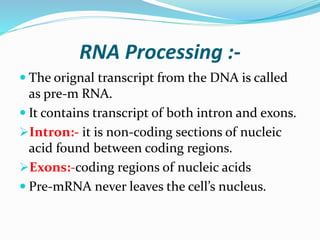
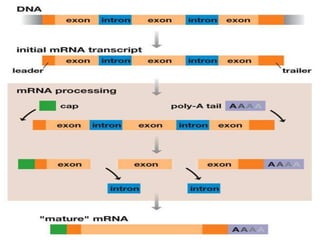
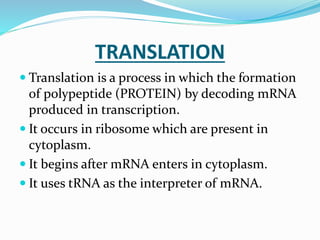
1. Transcription and translation are the two main processes of gene expression. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and produces mRNA from DNA. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm and produces proteins from mRNA.
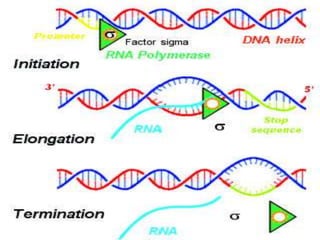
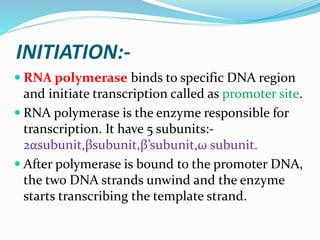
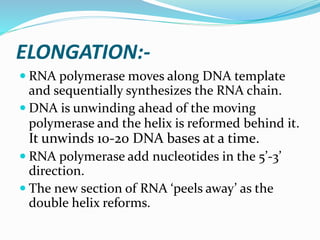
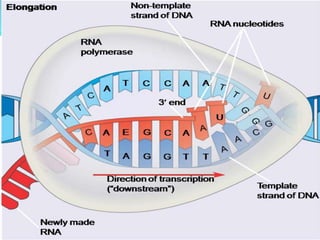
2. Transcription involves three main stages - initiation, elongation, and termination. RNA polymerase binds to DNA and synthesizes mRNA along the template strand.
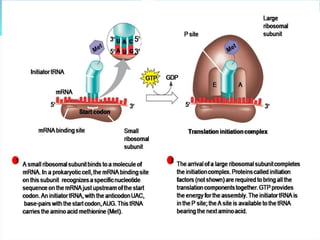
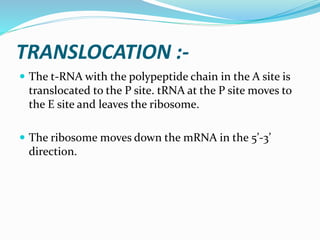
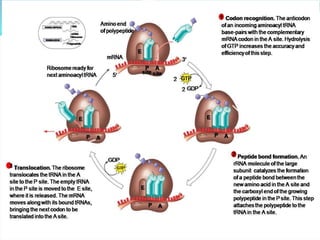
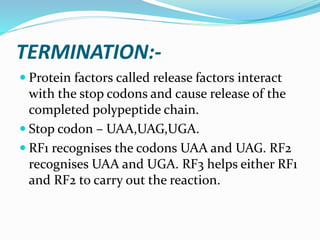
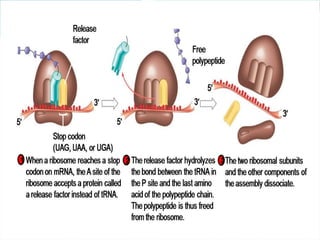
3. Translation also occurs in three stages - initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, the ribosome and initiator tRNA bind to mRNA. Then amino acids are added during elongation according to the mRNA codons. Termination occurs when a stop codon is reached.