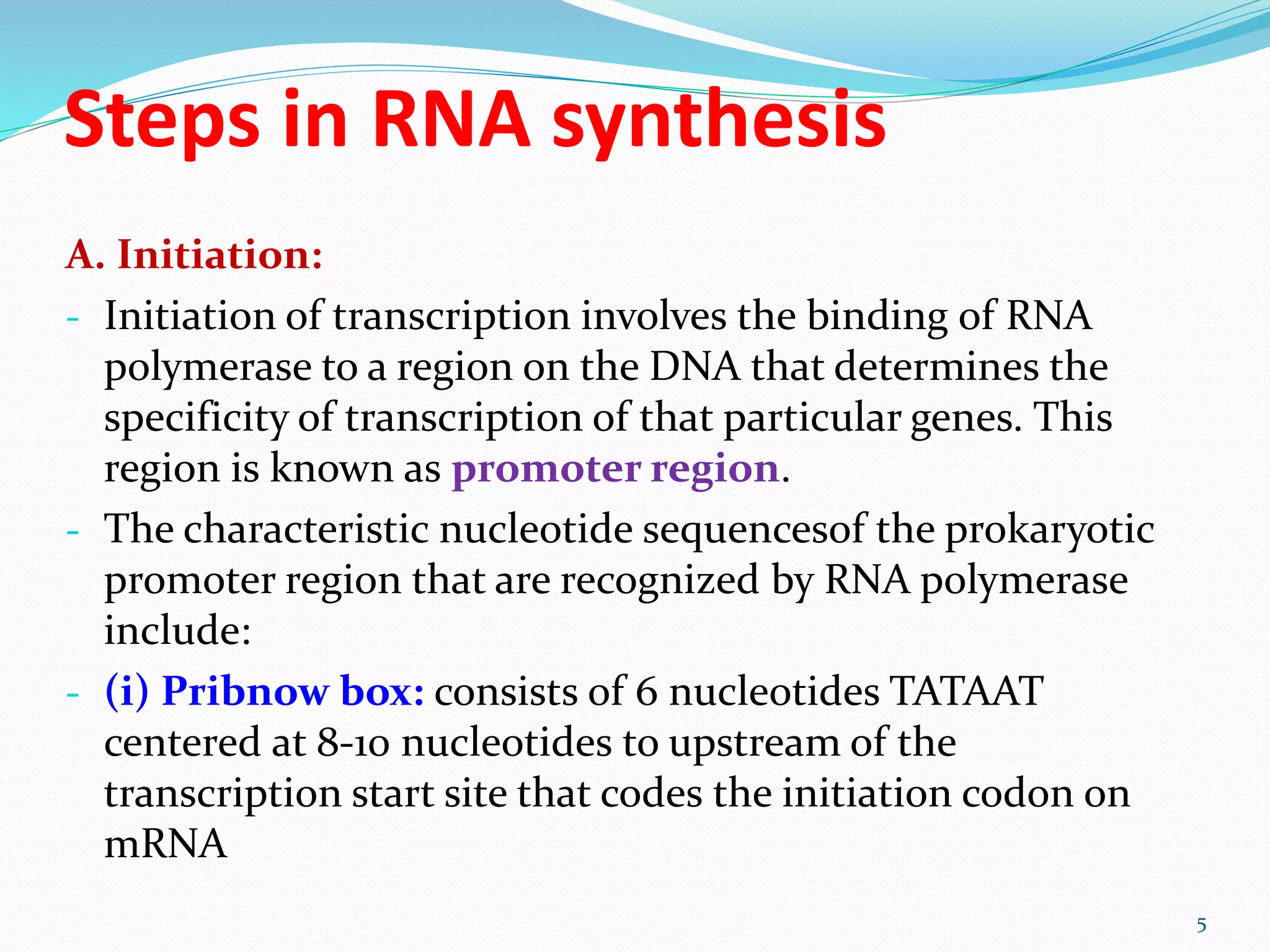
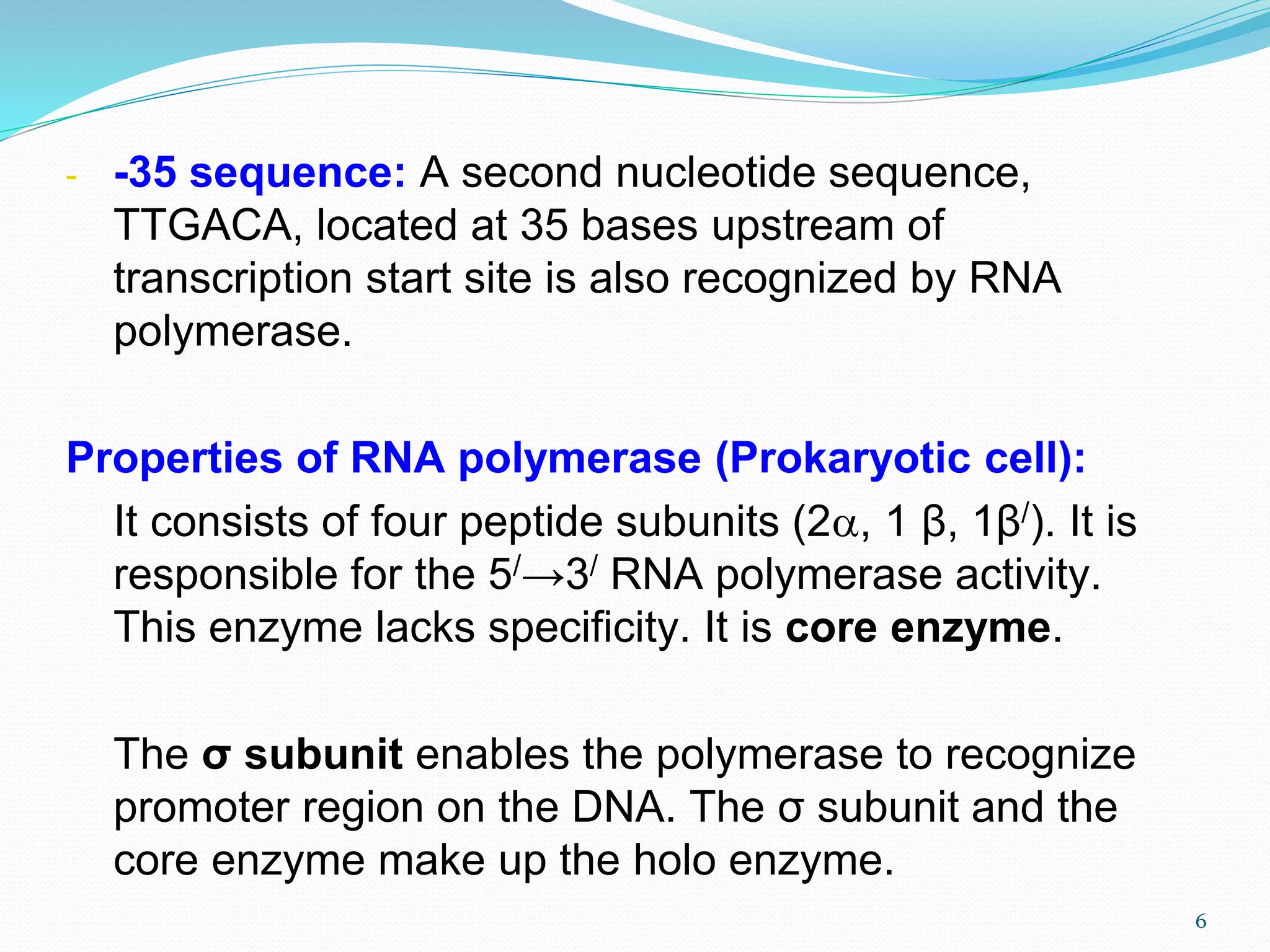
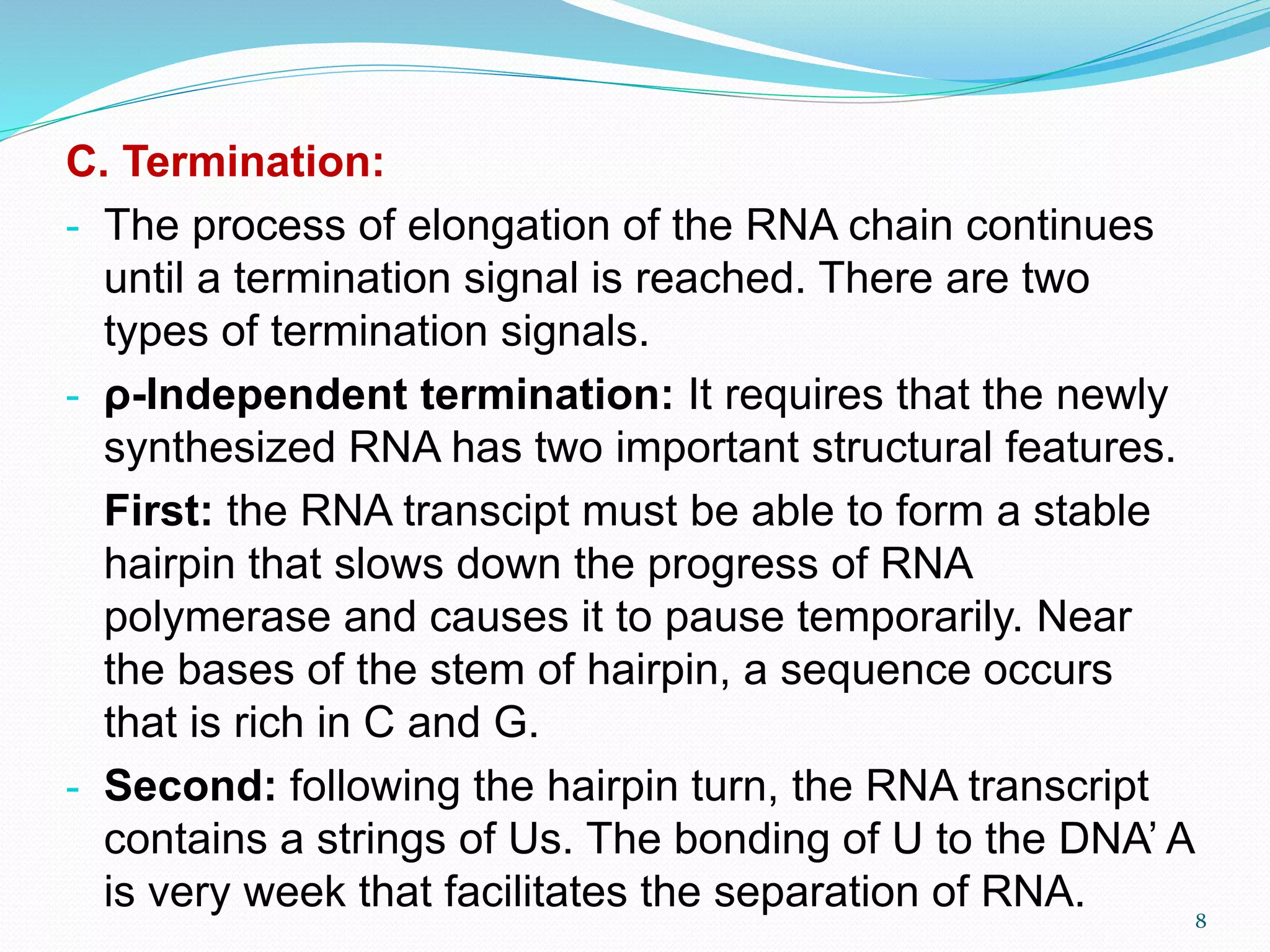
1) Transcription is the process where RNA is synthesized from DNA in the nucleus. The DNA unwinds and one strand is used as a template to produce mRNA using complementary base pairing.
2) There are three main types of RNA - mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. mRNA carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes. tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis. rRNA makes up the ribosomes.
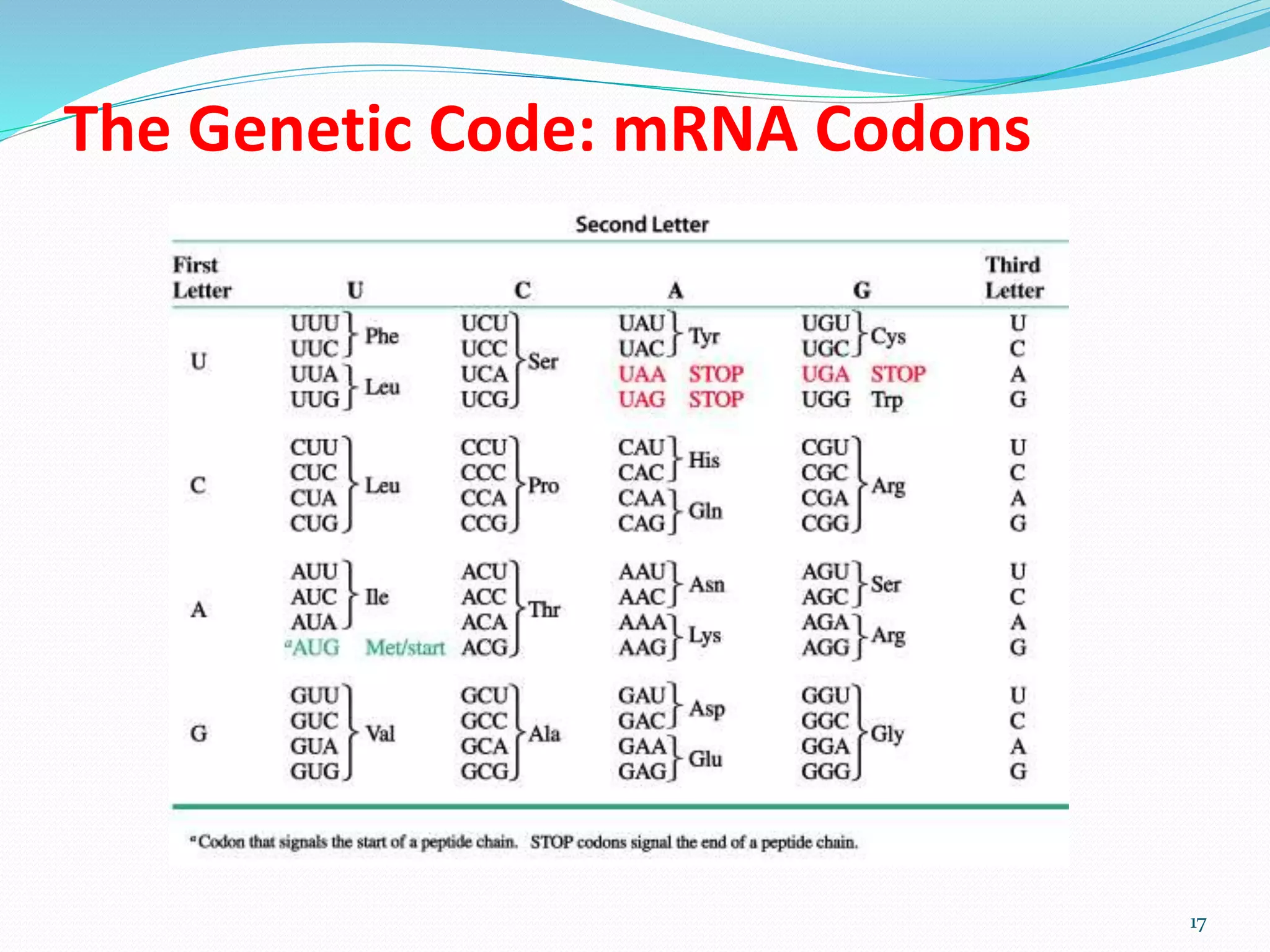
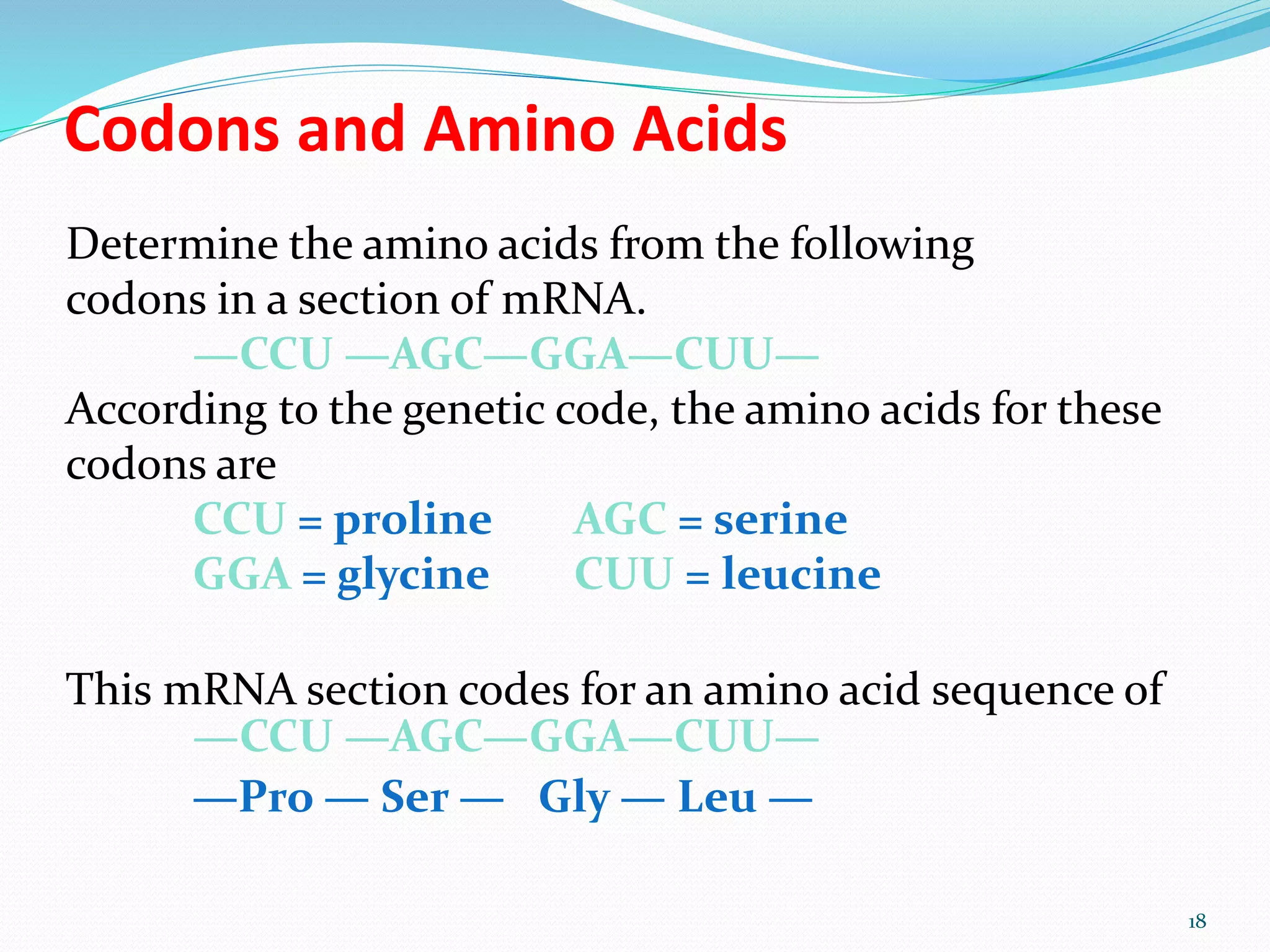
3) The genetic code consists of triplets of bases along mRNA that specify the 20 amino acids used to build proteins. Certain codons signal the start and end of a polypeptide chain.