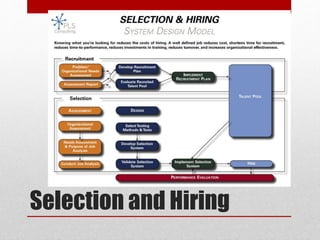
This document discusses talent management strategies for organizations. It begins with defining talent and examining employee satisfaction levels and factors. It then covers building blocks of talent management like competencies, performance management, and evaluating potential. It discusses developing a competency framework with clusters and attributes. The talent management process involves stages like entry, retention, development, and performance. Challenges in talent management include plateaued careers and succession planning. The document emphasizes identifying strategic roles and developing a players to fill them.