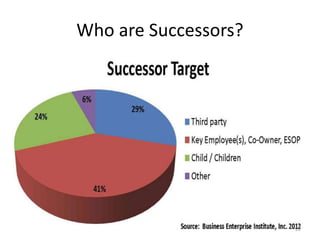
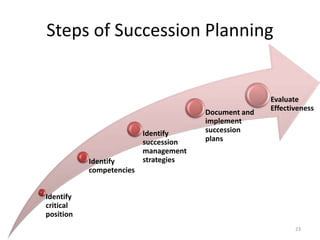
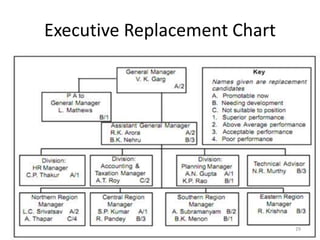
This document discusses career planning and succession planning. It provides details on the employee career planning process, which involves self-assessment, managerial assessment, information evaluation, and creating a plan. It also discusses what employees and managers can do to support career planning. For succession planning, it identifies the need to ensure critical skills and knowledge are maintained when employees leave key roles. The steps of succession planning include identifying critical positions and their competencies, identifying management strategies, documenting and implementing plans, and evaluating effectiveness.