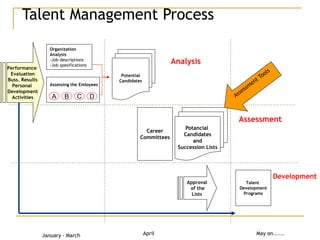
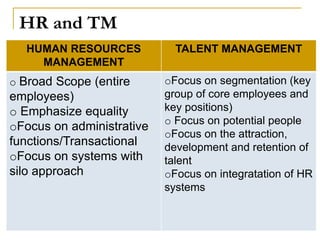
Talent management involves identifying, developing and retaining talented individuals through integrated systems of recruitment, performance management and development. It focuses on differentiating employees into A, B and C players and identifying key positions critical to company success. An effective talent management model links an organization's talent creed, strategy and systems by defining the competencies and behaviors tied to excellent performance through competency models. The goal is to develop leaders from within through assessment, training and succession planning processes that are embedded in and drive the organization's overall human resources strategy.