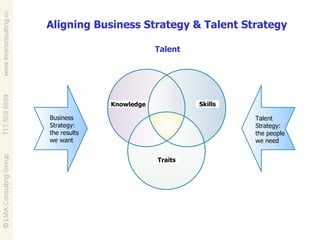
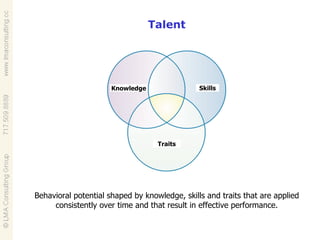
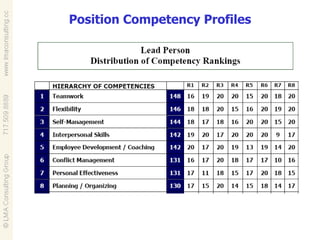
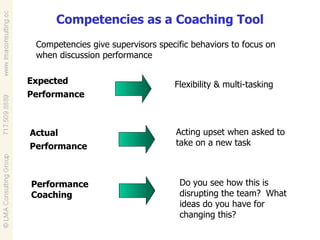
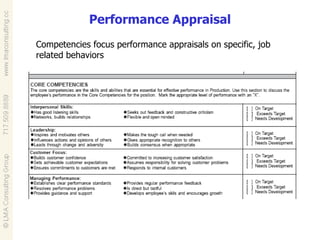
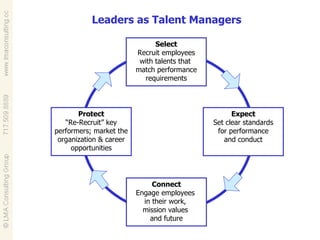
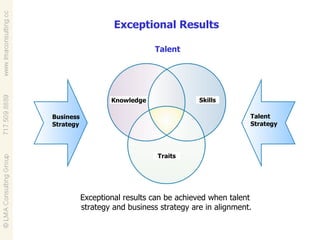
Talent management involves developing and implementing strategies to ensure an organization has employees with the necessary skills, knowledge and traits to achieve business objectives. This includes activities like competency modeling, assessments, performance management, coaching and development planning. When business and talent strategies are aligned, it can result in exceptional performance through having the right people in place.