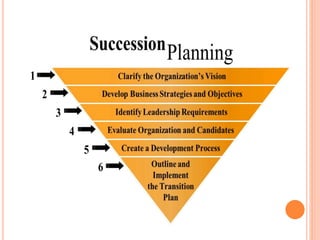
Succession planning is a systematic approach to ensure leadership continuity by building a talent pool, developing potential successors based on their strengths, and identifying the best candidates for positions. It recognizes that some jobs are too critical to leave vacant and aims to create an effective process for growing and retaining top leaders through identifying long-term strategic needs, analyzing talent gaps, developing a succession strategy, and continually monitoring and evaluating the process. When done effectively, it is linked to strategic planning and critical for organizational success.