Embed presentation
Download to read offline



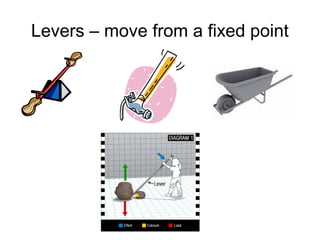
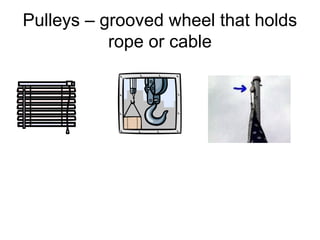
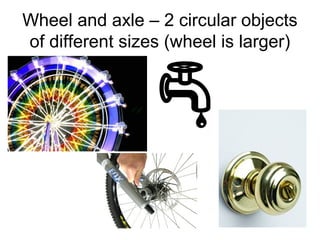
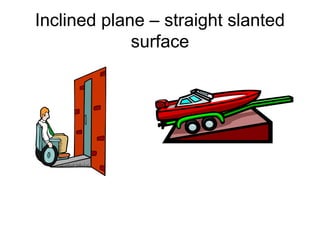





Work is defined as energy transferred by a force causing an object to move. The formula for work is W=Fxd. Power is the rate at which work is done and is calculated as P=W/t. Machines make work easier by changing the amount or direction of force applied. Simple machines include levers, pulleys, wheels and axles, inclined planes, wedges, screws, and compound machines which combine simple machines. Mechanical advantage is the number of times a machine multiplies force while efficiency is the ratio of work output to work input.











