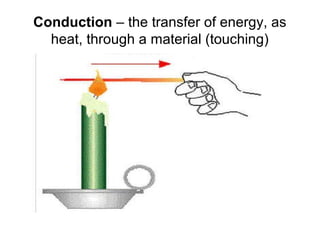
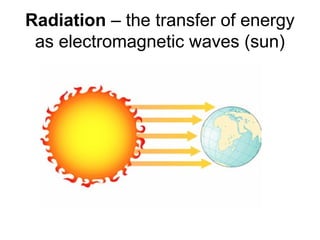
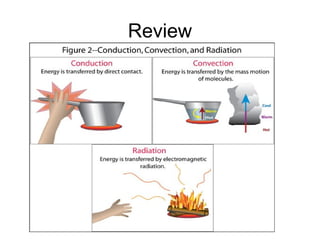
This document discusses key concepts relating to temperature and heat transfer. It defines temperature as a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in an object. As temperature increases, particles move faster, spreading out through thermal expansion. Different temperature scales are presented, with Fahrenheit and Celsius defined by their freezing and boiling points of water, and Kelvin having the lowest possible temperature of absolute zero. Heat is defined as the transfer of thermal energy between objects with different temperatures, while thermal energy is the kinetic energy within an object. Materials are classified as conductors or insulators based on their ability to transfer heat. The three main methods of heat transfer are conduction (direct contact), convection (movement of molecules in gases and liquids), and radiation (