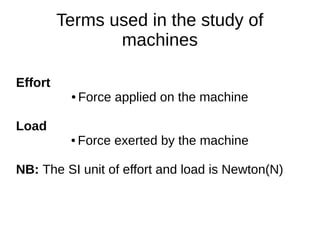
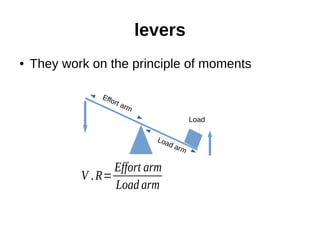
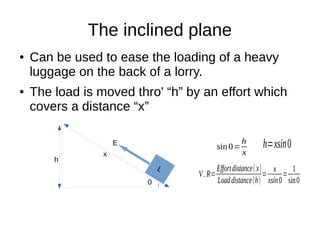
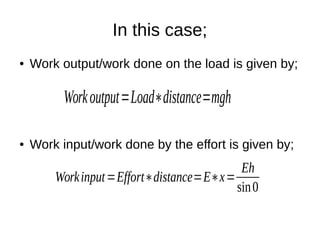
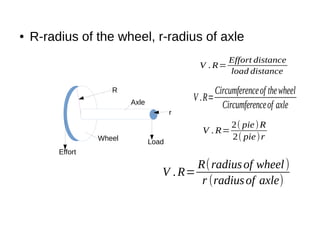
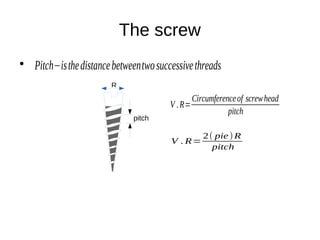
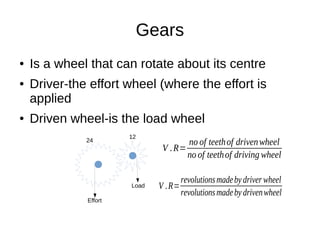
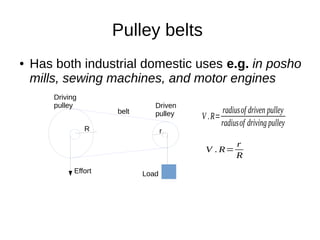
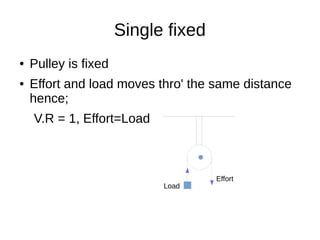
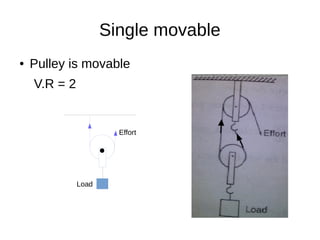
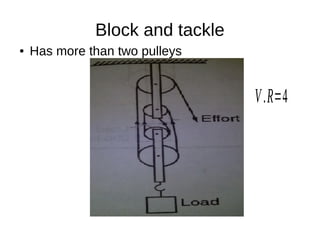
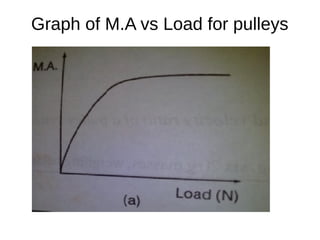
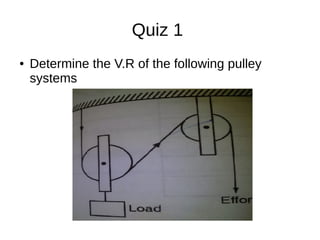
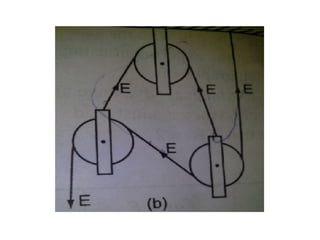
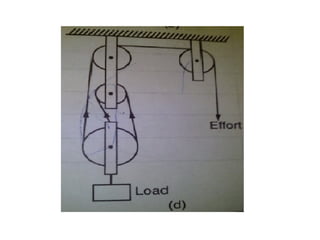
This document discusses simple machines and their characteristics. It defines simple machines as devices that make work easier by transmitting force through a mechanical advantage. Examples of simple machines discussed include levers, pulleys, gears, inclined planes, screws, and the wheel and axle. Key terms like effort, load, mechanical advantage, velocity ratio, and efficiency are defined and the relationships between them are explained mathematically. Several examples and quiz questions are provided to illustrate concepts.